Shopping - Curriculum Support
advertisement

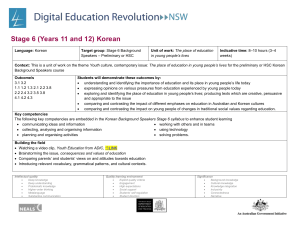
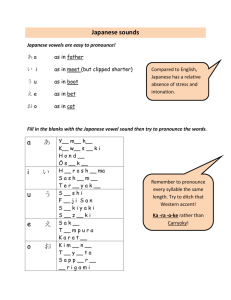
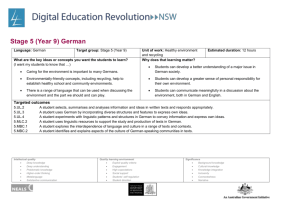
Language: Japanese Target group: Stage 5 (Year 9) Unit of work: Shopping Duration: 4 weeks What are the key ideas or concepts you want the students to learn? The key concepts I want students to learn are that: there is a range of language in Japanese to talk about shopping there are differences and similarities between shopping in Japan and shopping in Australia. Why does that learning matter? The learning matters because: it is important that students learn to communicate with Japanese people in an everyday context it is important that students understand and appreciate the differences and similarities between Japanese and Australian cultures. Targeted outcomes 5.UL.1, 5.UL.2, 5.UL.3, 5.UL.4, 5.MLC.1, 5.MBC.2 Socio-cultural content Japanese department stores 100 yen shop different products available in Japan different approaches to advertising. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Students learn about: ways in which texts are constructed for specific purposes the manipulation of structure, format and choice of vocabulary to achieve specific purposes ways in which texts are constructed for specific purposes cultural attitudes that add meaning to text. Building the field (e.g. the connections to background knowledge and cultural knowledge) Look at sample advertisements for various products in Australia and Japan View Japanese explorers and the In the neighbourhood segment on Japanese shops <www1.curriculum.edu.au/nalsas/explorers/japanese/explorers.html> Compare shopping in Japan and Australia Gift giving in Japan (Hai 5/6 page 40) View video Arigato learning object, Stage 5 Japanese <lrr.dlr.det.nsw.edu.au/Web/arigato/> Brainstorm the language they might use for shopping. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Students learn to: identify purpose and distinguish between main points and specific detail in texts, e.g. in an advertisement select and incorporate particular structures to achieve specific purposes, e.g. in a product description, in a conversation in a store make linguistic choices to enhance their intended meaning identify and discuss cultural influences in specific texts, e.g. advertisements, videos. Cross-curriculum content and policies Literacy – advertisements, choosing appropriate language register, constructing a meaningful text Numeracy - prices and numbers, counters. Abbreviations LR Listening and responding RR Reading and responding W Writing S Speaking. Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Suggested resources Teaching and learning activities Introductory activities Hai 5/6 chapter 4 1. Introduce vocabulary using shopping bags of items. 2. Ask for and receive items – pair work. 3. View Segment 11 of Video: Japanese for junior secondary students. Complete worksheet p. 159 4. Complete vocabulary quizzes*. 5. Use Japanese magazine advertisements and menus to practise 〜はいくらですか。 Kimono 2 chapter 7 Mirai 2, U8 Skills S,LR S,LR LR,RR,W LR,S,W S,RR Moshi Moshi p. 54 Obentoo 2 U7 and 8 TaLe <www.tale.edu.au/> Assisted construction activities 1. Create and present simple dialogues at a variety of shops. 2. Complete Information gap activities (IGA) as pair work. 3. Match pictures to text: classifiers, vocabulary. 4. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Complete online activities Sugoi! 1,2,3: Prices; Sugoi! My clothes, buying clothes <www.tale.edu.au/> Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction S,LR,RR, W S,LR,RR, W S,RR,LR Evidence of learning: Evidence of learning would be gathered by the demonstration of outcomes in all class activities including the following: Teacher observation Vocabulary Katakana quizzes Role plays Continuous informal class assessment Writing a report Formal assessment. RR,LR Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Grammar/ Structures 〜をください。 はい、どうぞ。 いくらですか。 〜はいくらです か。 いらっしゃいませ (まいど)ありがとう ございます。 5. Translate the prices at the school canteen into Japanese. 6. Create an advertisement. 7. View Japanese space voyage games learning object on TaLe and complete SOS to purchase the required articles <www1.curriculum.edu.au/nalsas/explorers/jap anese/games.html> 8. Read shopping scenarios, Moshi Moshi, Saburo and Yukari shopping trips S,LR S,RR,W RR,S,LR LR,R,W RR Feedback: Informal teacher observations in class – all skills Verbal feedback in class – all skills Written annotations on written work Peer assessment of roleplay via checklist Parent teacher night – all skills Student interviews – all skills. Simple independent construction activities S,LR,RR 1. Play shopping games using the Japan Foundation コンビニ mat Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative なんぼんですか。 いっぽんです。 いくつですか。 むっつです。 なんまいですか。 にまいです。 Script Kanji for numbers 円 Bringing it all together independent construction activities 1. Write a report:今日デパートへいきました。* 2. Create a Japanese department store scene in the classroom. In groups, students set up うりば and go shopping (video presentations). 3. Japanese virtual shopping activity on Japanese Stage 5 <lrr.dlr.det.nsw.edu.au/Web/arigato/> Assessment strategies: Activities above marked * could be used for assessment. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction W 本 katakana S,LR,RR, W Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Evaluation and variation Considerations: Time allocated for unit; variety of teaching strategies used; opportunities for teacher feedback and student reflection; suitability of resources; suitability of ICT/laptop activities; literacy/numeracy links. Teacher’s name and signature: ______________________________ Date: Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication ______________________________ Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative