Leisure - Curriculum Support
advertisement

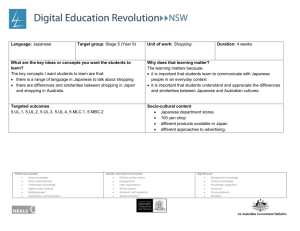
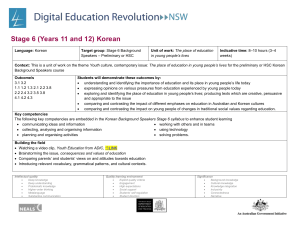
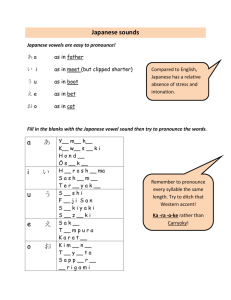
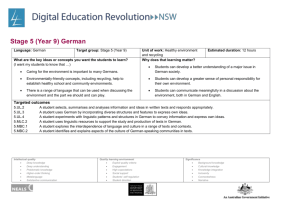
Language: Japanese Target group: Year 11 Japanese Continuers What are the key ideas or concepts you want the students to learn? The key concepts I want students to learn are that: there is a range of language in Japanese to talk about hobbies, spare time and sporting activities we are part of a global community with diverse cultures and languages. Topic: Leisure Indicative time: 4 weeks Why does that learning matter? The learning matters because: it is important that students learn to communicate with students from other language backgrounds it is important for students to understand the diversity of cultures, and how this is reflected in lifestyles. Unit description: Students learn about the leisure interests and lifestyles of young Japanese people. At the end of this unit, students will be able to: express their interests and preferences in Japanese express that they like doing various activities explain or clarify their preferences ask for and offer explanations talk about club activities in Japanese schools. Key competencies: The following key competencies are embedded in the Stage 6 syllabus to enhance student learning: communicating ideas and information working with others and in teams collecting, analysing and organising information using technology planning and organising activities solving problems. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Objective 1 The student will exchange information, opinions and experiences in Japanese Outcomes: The student: 1.1 uses a range of strategies to maintain communication 1.2 conveys information appropriate to context, purpose and audience 1.3 exchanges and justifies opinions and ideas Objective 2 The student will express ideas through the production of original texts in Japanese 2.1 applies knowledge of language structures to create original text 2.2 composes informative, descriptive, reflective, persuasive or evaluative texts appropriate to context, purpose and/or audience 2.3 structures and sequences ideas and information Objective 3 The student will analyse, process and respond to texts that are in Japanese 3.1 conveys the gist of texts and identifies specific information 3.2 summarises the main ideas 3.4 draws conclusions from or justifies an opinion 4.3 reflects upon significant aspects of language and culture. Objective 4 The student will understand aspects of the language and culture of Japanese-speaking communities. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Suggested teaching, learning and assessment activities: Note: teaching and learning activities marked with an asterisk (*) could be used as formal assessment tasks Sub-topic: Interests, sports Building the field: Brainstorm and discuss interests and popular sport/leisure activities in Australia and Japan. Show video/DVD to introduce sub-topic (sport), for example: o 高校生の日本語1 (Sumo, Interesting facets of Japan in Sydney) o 高校生の日本語2 (Japanese dance, Kendo) o Sumo do, Sumo don’t (しこふんじゃった) Extract and identify useful cultural information, vocabulary and language structures from the video/DVD. 1. 2. 3. 4. Activities It is suggested teachers and students use eHSC Unit 7, Hobbies, to introduce and practise the language structures, vocabulary and cultural background for this topic. Note: To log on to the eHSC, government school teachers should email sally.shimada@det.nsw.edu.au Practise saying what you like/dislike doing using flashcards and eHSC Unit 7 section 1 step 6. Complete class survey: どんなスポーツをするのがすきですか。 ~にきょうみがありますか。 Participate in whole class activity: Find someone who likes…” Pairwork: ~たり~たり exercise from ALC 50 Games and drills p. 57 Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Evidence of learning and ongoing feedback for students throughout unit of work Class discussion and teacher feedback on student contributions Student use of appropriate vocabulary and structures Student ability to sequence ideas Student use of culturally appropriate behaviour Teacher observation of level of participation in class discussion and oral feedback. Ongoing feedback through: teacher observation oral/written feedback student self-evaluation peer evaluation. Listening activities: teacher observation and oral feedback on audience, purpose and content Speaking activities: teacher provides oral feedback on correct pronunciation and vocabulary and ability to maintain an interaction. Peer evaluation. Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Registration/Date 5. eHSC Unit 7 section 1 step 8. 6. Read Hobbies Mirai 5 pp. 88 and 89 to find out about Japanese students’ leisure activities. Complete activity book p. 74. 7. eHSC Unit 7 section 3 step 2. Read about school clubs in Japan and complete activities 15, 16 and 17 to reinforce vocabulary for club activities. Record conversations based on Mirai 5 workbook p. 75 using Audacity. Conduct a class survey to find out about popular sports and interests. Read the advertisements on Mirai 5 page 94 seeking pen friends, and respond.* Write a composition about popular Australian sports.* eHSC Unit 7 section 3 step 4 – Read the role play scenarios and complete the speaking task recording your response using Audacity. Grammatical items するのが好き/好きじゃないです ~にきょうみがあります ~たり~たりします ~た+ことがあります ~と~とどちらのほうが ~は~より ~のほうが 一番 の/んです Suggested kanji: 好 耳 手 元 気 足 8. 9. 10. 11. Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication 楽 持 外 買 読 聞 乗 体 心 目 口 Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Discussion activities: teacher observation and oral feedback on how well students participate, recognise and use the vocabulary and structures. Reading activities: teacher gives oral/written feedback on identifying general or specific information, audience, purpose and content. Written activities: teacher observation and written feedback on audience, purpose and content; and use of language structures and script. Laptops with Learning/ICT activities: use of online learning site to consolidate and reinforce new structures and to provide additional listening, speaking, reading and writing activities that allow for independent student progression Resources eHSC course Games and drills pp. 57, 62 Japanese for everyone p. 225 Japanese for senior secondary students pp. 129–130 Japanese in modules 1 (p. 72) and 2 (pp. 16, 20) 50) Mirai 5 Course book and activity book Wakatta! pp. 254–255. Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative Registration/Date Evaluation and variation Considerations: Time allocated for unit; variety of teaching strategies used; opportunities for teacher feedback and student reflection; suitability of resources; suitability of ICT/laptop activities; literacy/numeracy links. Date commenced: Date completed: Class teacher signature: Head Teacher signature: Intellectual quality Deep knowledge Deep understanding Problematic knowledge Higher-order thinking Metalanguage Substantive communication Quality learning environment Explicit quality criteria Engagement High expectations Social support Students’ self-regulation Student direction Significance Background knowledge Cultural knowledge Knowledge integration Inclusivity Connectedness Narrative