Botany Part 1
advertisement

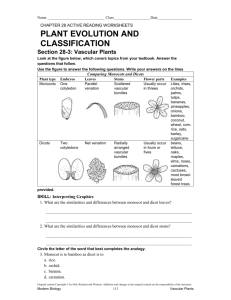
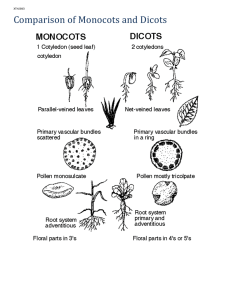
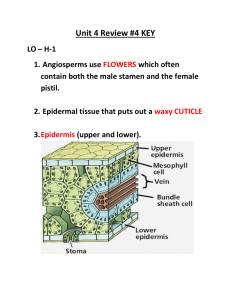
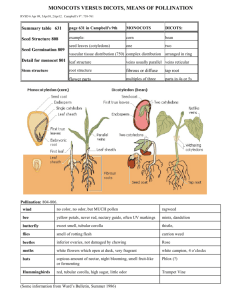
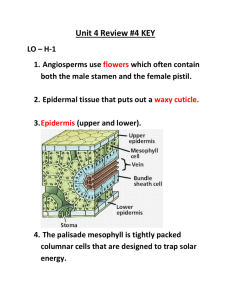
Botany Review Kingdom Plantae General Characteristics • • • • • Contain Chlorophyll a Multicellular Made up of Eukaryotic Cells Photosynthetic Autotrophs Cell Walls made of Cellulose (polysaccharide) • Produce sugars as glucose, transport sugars as sucrose and store sugars as starch (a polysaccharide). Review of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use the energy of sunlight to combine carbon dioxide and water to form glucose and oxygen. Light Energy + 6CO2 + 6H20 Reactants C6H12O6 + 6O2 Products Factors that Affect Photosynthesis • • • • Amount of available Sunlight Amount of available Water (rainfall) Amount of Carbon Dioxide Optimal Temperatures Adaptations plants made to survive on land • Developed Cuticles – waxy, protective outer coverings which prevent water loss. • Developed vascular tissues for transportation of water and sugars. • Developed spores/seeds for reproduction. • Developed tissues to strengthen stems to overcome gravity. The Classification of Plants Bryophytes – • are described as plants that lack xylem and phloem (vascular tissue) Tracheophytes – • are plants that have xylem and phloem (vascular tissue) Xylem is a type of vascular tissue that transports water upward from the roots to the leaves. Phloem is a type of vascular tissue that transports sugars (nutrients) from the leaves downward The Tracheophytes are divide into five groups…. The largest of the five groups are the: Non-Seed Bearing Plants And Seed Bearing Plants The Seed Bearing Plants are divided into two groups: Gymnosperms (naked-seed Plants) and Angiosperms (encased-seed plants) The Angiosperms are the Flowering Plants. Angiosperms are divided into two groups: Monocotyledons (Monocots) and Dicotyledons (Dicots) 4 Differences between Monocots and Dicots Monocots Leaves – parallel veins Petals - multiples of 3 Seeds - one cotyledon Dicots netted veins multiples of 4 or 5 two cotyledons Vascular tissues in a monocot stem are arranged randomly and look like “monkey faces”. Vascular tissues in a dicot stem are arranged in a ring surrounding the pith. Venation of Leaves Monocots venation is parallel Dicots venation is netted Number of Petals Monocots multiples of 3 Dicots multiples of 4 or 5 New Information! Seasonal Adaptations Evergreens – • plants that remain green year round…. • Pine trees Deciduous – • plants that lose all their leaves all at one time…. • Apple trees, grapes Short and Long Day Plants • Short-day Plants – Flower when the days are shorter than 12 hours… like onions, garlic, chrysanthemums • Long-day Plants Flower when the days are longer than 12 hours… like tomatoes and beans. Growth Cycles (from seed to seed) • Annuals – complete their entire life cycle in one growing season. Example: mums • Biennials – complete their entire life cycle in two growing seasons. Example: Broccoli • Perennials – continue to grow year after year…. Example: Apple trees Stem Types Herbaceous – Green, soft…. will wilt if water loss is extreme…. Sour grass, celery Woody – Brown, rigid…. Will remain erect even after they are dead…. Trees, roses Tropisms are the responses plants have to stimuli. A Negative (-) response is “away” from the stimuli A Positive (+) response is “toward” to stimuli Phototropism – a plant’s response to light Gravitropism – a plant’s response to gravity Hydrotropism – a plant’s response to water Chemotropism – a plant’s response to chemicals Thigmotropism – a plant’s response to touch Phototropism a plant’s response to light Gravitropism - (also called Geotropism) a plant’s response to gravity A Corn Root responds positively to gravity Thigmotropism a plant’s response to touch…the tendrils of a bean plant wraps around a garden post. Plant Hormones • Cytokinins – stimulate cell division, and promote the germination of dormant seeds • Auxins – are involved in plant-cell elongation, apical dominance, & rooting • Gibberillins – promotes shoot growth, “bolting”, and seed germination