Blood Vessels and the Heart
advertisement

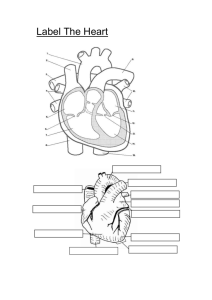
Blood Vessels and the Heart Blood Vessels • Three Types – Arteries: carry blood away from the heart • Thick walled, smaller vessels are called arterioles – Veins: carry blood towards the heart • Thin walled, smaller vessels are called venules • Contains valves – Capillaries: connect the arteries to the veins • Smallest of the blood vessels • RBC’s travel single file through capillaries • Branch like system to increase surface area for diffusion • Site of gas exchange Arterial System • Transports blood under pressure. • Blood moves in a pulse-like wave. • Contraction & relaxation of arterioles is the major determinant of the overall blood pressure. Venous System • Thinner walls, larger diameters & less muscle than arteries. • Contains 70% of total blood volume. • Most veins work against gravity. – Valves allow one-way flow. – Contraction of skeletal muscles pushes blood toward heart. Pathways of Blood • Pulmonary Circuit – Right side of heart. – Low-pressure system. – Takes deoxygenated blood to the lungs and back to the heart • Systemic Circuit – Left side of heart. – High-pressure system. – Takes oxygenated blood to the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart Pulmonary Circuit • Right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from: – Superior vena cava. – Inferior vena cava. • Blood flows through the tricuspid valve or the right atrioventricular (AV) valve to the right ventricle. Blood from body Blood from body Pulmonary Circuit • Blood flows through the pulmonary semi-lunar valve & enters the pulmonary trunk, which divides into the left & right pulmonary arteries. – Divides into capillaries where external gas exchange (respiration system) occurs. • Oxygenated blood enters the left & right pulmonary veins, returning blood to the left atrium. Systemic Circuit • Blood flows through the left AV-valve or bicuspid (mitral) valve to the left ventricle. – Left ventricular walls are two times thicker than in the right ventricle. • Blood travels through the aortic semi-lunar valve to the aorta. Systemic Circuit • Aorta branches into smaller systemic arteries, which branch into arterioles & then capillaries. – Internal gas exchange occurs. • Capillaries rejoin as venules & then veins. • Deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium via the superior & inferior vena cava. Coronary Circulation • Delivers oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. • Consists of the left & right coronary artery.