16. CV I - Heart Anatomy.doc
advertisement

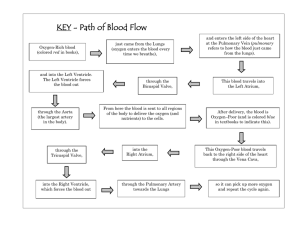
D’YOUVILLE COLLEGE BIOLOGY 108/508 - HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LECTURE # 16 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM GENERAL ORGANIZATION - HEART ANATOMY 1. Introduction: • cardiovascular system = heart + blood vessels Heart: filled by blood from veins; pumps blood into arteries Arteries: convey blood away from heart Veins: convey blood toward heart Microcirculation: microscopic capillaries; site of exchange between blood and tissues; fed by arterioles (smallest arteries); drained by venules (smallest veins) (fig. 19 - 1) Two Circuits (fig. 18 - 5): a. Pulmonary Circuit: conveys oxygen-poor blood from right heart to lung; returns oxygen-rich blood to left heart (fig. 19 - 19) b. Systemic Circuit: conveys oxygen-rich blood from left heart to rest of body; returns oxygen-poor blood to right heart (fig. 19 - 20) 2. Heart Anatomy: heart is a double pump consisting of four chambers (located in the mediastinum of the thorax) (figs. 18 - 1 & 18 - 4): a. Right Atrium: receives from systemic circuit via: superior vena cava (drains head, neck, thorax and upper limbs), inferior vena cava (drains abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs), coronary sinus (drains wall of heart) • feeds right ventricle via atrioventricular (AV) orifice - right AV (tricuspid) valve b. Right Ventricle: pumps to pulmonary trunk; thinner walled due to lower pressures required to irrigate pulmonary circuit; opening to pulmonary trunk controlled by pulmonary semilunar (SL) valve c. Left Atrium: receives from pulmonary circuit via four pulmonary veins (left and right, superior and inferior) • feeds left ventricle via AV orifice - left AV (bicuspid or mitral) valve d. Left Ventricle: pumps to systemic circuit via aorta (largest artery in the body); thicker walled due to high pressures required to irrigate systemic circuit; aortic opening controlled by aortic semilunar valve Coverings and Wall Layers (fig. 18 - 2): • heart enclosed in double sac consisting of parietal and visceral pericardia • wall has 3 layers: epicardium, myocardium, & endocardium (heart valves) Internal Features (fig. 18 - 4e): • ventricular myocardia are laced with trabeculae carneae and finger-like intrusions (papillary muscles) that attach to free margins of AV valves via tiny tendons (chordae tendineae) • interatrial and interventricular septa separate right and left sides of heart Coronary Circulation (fig. 18 - 7): Bio 108 lec. 21 - p. 2 • left coronary artery supplies anterior interventricular and circumflex) • right coronary artery supplies posterior interventricular & marginal) - coronary circulation drained by cardiac veins that feed coronary sinus