LEAVES - Questions
advertisement

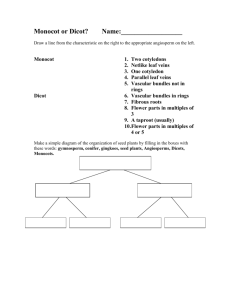
Name - ________________________ Class Period - _____ LEAVES - Questions: 1. What is the stalk that joins the leaf to the stem called? ____________ 2. How does water vapor escape from a leaf? What is the process called? __________________________________________________________ 3. Where would the greatest number of chloroplasts be found in a leaf? __________________________________________________________ 4. What protects the surface of a plant from water loss? _______________ 5. Why are the air spaces between the spongy mesophyll cells are important? _________________________________________________________ 6. When water is lost from a plant, why does the plant looked wilted? _________________________________________________________ 7. What is the edge of a leaf called? ____________________________ 8. If the edge of the leaf appears toothed, what type of leaf edge is this? ________________________________________________________ 9. The smaller veins in the leaf connect to the _____________ of the leaf. 10. Leaves attach to a stem at a site called the ____________. 11. A(n) _________________ or scar appears at the base of the petiole where the petiole attaches to the stem. 12. Give 2 examples of modified leaves. ____________________________________________________________ Flower & Their Life Cycle Questions: 1. Name the four whorls found on simple flowers. 2. What part of a flower produces pollen? 3. What is the difference between pollination and fertilization? 4. Name the 3 parts of the pistil of a flower. 5. What supports the anther of a flower? 6. Where are the eggs or ovules located in a flower? 7. Explain how sperm are able to reach an egg to fertilize it. 8. Explain the difference in ray and disc flowers in composites. 9. What are the leaf like parts in simple flowers called? in composite flowers? 10. What helps attract pollinators? 11. What is the difference between self and cross pollination? 12. Name the 2 types of flowers in composites and describe each. 13. What are bracts? Monocot & Dicot Comparison Questions: 1. Give two examples of plants that are monocots. _____________________________________________ 2. Give two examples of plants that are dicots. _________________________________________________ 3. What is a cotyledon? _______________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the radicle? ________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the coleoptile? ______________________________________________________________ 6. What is the function of the endosperm? _____________________________________________________ 7. Fill out the table below. Number of Seed Leaves Type of Leaf Venation Number of Flower Parts Type of Roots Example Monocot Dicot 8. An unknown plant is brought to you and your job is to determine whether it is a monocot or a dicot. You observe that the plant has 6 petals and its leaves have parallel veins. Is it a monocot or a dicot? Flower Structure & Reproduction Questions: 1. What is an angiosperm? 2. The flower attaches to what part of the plant? 3. Why are flowers brightly colored? 4. Name two mammals that might pollinate a plant. 5. If the petals of a flower are reduced or absent, how is the plant pollinated? 6. The female reproductive structures are called the: 7. Name the three parts of the pistil: 8. Where are the ovules stored? 9. Name the two parts of the stamen: 10. Describe sexual reproduction in plants. 11. The ovary develops into what structure? 12. Define fruit. 13. Some flowers are not brightly colored at all, but have a very pungent odor that smells like rotting meat. How do you think these flowers are pollinated? 14. In many flowers, the pistils and stamens reach maturity at different times. Considering what you know about pollination, why would this be an advantage to the plant? LEAVES COLORING Figure 1 - Parts of a Leaf Figure 2 – Leaf Margins Figure 3 – Cross Section of a Leaf Figure 4 – Twigs Figure 5 – Leaf Modifications Flowers & Their Life Cycle Coloring Label and color the parts of the pistil! Color and Label the Parts of a Composite Flower! Monocot & Dicot Comparison Coloring V V V Flower Structure & Reproduction Coloring