bioii ch10 ppt ol
advertisement

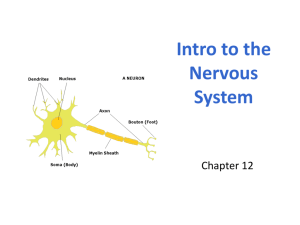
BIOII CH10 PPT OL NAME_____________________________ Please complete the following outline by filling in blanks and answering numbered questions CHAPTER 10 The Nervous System The PPT can be found on my CH10 website Cell Types of Neural Tissue Neurons Neuroglial Cells Divisions of the Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Peripheral Nerves Spinal Cord Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Divisions of Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Picks up sensory information and delivers it to the ___________________________ Motor Division Carries information to ___________________________and glands Divisions of the Motor Division Somatic – Carries information to __________________________ muscle Autonomic – Carries information to smooth muscle, _____________ muscle, and glands 1. Give an example of a stimulus that would raise heart rate. Functions of Nervous System Motor Function Decisions Are Acted Upon Impulses Are Carried To Effectors Sensory Function Sensory _________________ Gather Information Information Is Carried To The CNS Integrative Function Sensory Information Used To Create Sensations ___________________ 2. How is memory stored? thoughts decisions Neuron Structure Myelination of Axons 3. What does myelin do? White Matter contains myelinated axons 4. Why is Myelin white? Gray Matter contains unmyelinated structures cell bodies, dendrites Classification of Neurons Bipolar two ________________________ 5. Give an example of a bipolar neuron eyes, ears, nose Unipolar one process 6. Is this the most common type of neuron? ganglia Multipolar many processes 7. Is this the most common type of neuron? most ___________________ of CNS Classification of Neurons Sensory Neurons _______________________ carry impulse to CNS most are unipolar some are bipolar 8. Compare AFFERENT and EFFERENT pathways Classification of Neurons Interneurons link neurons multipolar in CNS Types of Neuroglial Cells Schwann Cells peripheral nervous system myelinating cell Oligodendrocytes 9. What does oligo mean? CNS myelinating cell Microglia CNS phagocytic cell Motor Neurons multipolar carry impulses _______________ from CNS carry impulses to effectors Astrocytes CNS scar tissue mop up excess ions, etc induce synapse formation connect neurons to blood vessels Ependyma CNS ciliated 10. What do the ependyma produce line central canal of spinal cord line _____________________________ of brain Resting Membrane Potential Inside Is _____________________ Relative To The Outside 11. Why Is It Negative? Polarized Membrane Due To Distribution Of Ions Na+/K+ Pump Potential Changes At Rest Membrane Is __________________________ 12. What Does Polarization Mean? Threshold Stimulus Reached Sodium Channels Open And Membrane Depolarizes Potassium Leaves Cytoplasm And Membrane Repolarizes Local Potential Changes Occur on membranes of dendrites and cell bodies Caused by various stimuli Chemicals Temperature Changes Mechanical Forces If membrane potential becomes more negative, it has hyperpolarized If membrane potential becomes more positive, it has depolarized Graded _____________________________ can lead to threshold stimulus that starts an action potential 13. What does summation mean? Action Potentials Nerve impulse Occur on axons All-or-none Refractory period absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential Action Potentials Impulse Conduction 14. Draw the Action Potential Saltatory Conduction The Synapse Nerve impulses pass from neuron to neuron at synapses Synaptic Transmission Neuro-transmitters are released when impulse reaches synaptic knob Synaptic Potentials EPSP 15. Name an excitatory neurotransmitter _____________________ postsynaptic potential graded depolarizes membrane of postsynaptic neuron action potential of postsynaptic neuron becomes more likely IPSP 16. Name an inhibitory neurotransmitter _______________________ postsynaptic potential graded hyperpolarizes membrane of postsynaptic neuron action potential of postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely Summation of EPSPs and IPSPs EPSPs and IPSPs are added together in a process called summation More EPSPs lead to greater probability of action potential Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system, where it activates the ____________________ and the central nervous system, where it acts as a neuromodulator upon plasticity, arousal and reward. It is one of many neurotransmitters in the autonomic nervous system and the only neurotransmitter used in the motor division of the somatic nervous system. Dopamine 17. What disease is associated with dopamine? Dopamine is produced in quite a few areas of the brain, including the substantia nigra and the ventral tegmental area. Dopamine is also a neurohormone released by the hypothalamus. Its principle hormonal role is to inhibit the release of prolactin from the anterior lobe of the pituitary. Dopamine has important roles in behavior and cognition, voluntary movement, motivation, punishment and reward, sleep, mood, attention, working memory and learning. Serotonin 18. What condition is associated with serotonin Serotonin is a monoamine neurotransmitter, usually found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets and the central nervous system. This chemical is also known as the “happiness hormone”, because it arouses feelings of pleasure and well-being. Low levels of serotonin are associated with increased carbohydrate cravings, depression, sleep deprivations and hypersensitivity to pain. Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Gamma Aminobutyric Acid is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene. GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre and postsynaptic neuronal processes. The primary role of this neurotransmitter is to ____________________ down the neuron activity. Glutamate This is the most abundant ________________________ neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It is also the major excitatory transmitter in the brain, and major mediator of excitatory signals in the mammalian central nervous system, involved in most aspects of normal brain functions including cognition, memory and learning. Epinephrine and Norepinephrine 19. NE is also known as These are separate but related hormones secreted by the medulla of the adrenal glands. These chemicals are also produced at the ends of sympathetic nerve fibers, where they serve as chemical mediators for conveying the nerve impulses to effector organs. They are responsible for concentration, attention, mood and both physical and mental arousal. Endorphins 20. This class is also known as ENDOGENOUS _________________________ Endorphins are produced by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus in vertebrates during exercise, excitement, pain, consumption of spicy food, love and orgasm. Endorphins contribute to the feeling of well-being and act similarly to opiates. They are also known to reduce pain and anxiety. Neurotransmitters 21. The most common excitatory neurotransmitter is ___________________________ and it tastes like _____________________________ soup 22. The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS is ______________ and its part of a great song by the Ramones Impulse Processing Neuronal Pools groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other interneurons work together to perform a common function each pool receives input from other neurons each pool generates output to other neurons Convergence neuron receives input from several neurons incoming impulses represent information from different types of sensory receptors allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources Divergence one neuron sends impulses to several neurons can amplify an impulse impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle contraction Clinical Application Multiple Sclerosis Symptoms blurred vision numb legs or arms can lead to paralysis Treatments no cure bone marrow transplant interferon (anti-viral drug) hormones Causes myelin destroyed in various parts of CNS hard scars (scleroses) form nerve impulses blocked muscles do not receive innervation may be related to a virus check out the cool case study on MS in time for your next TEST ESSAY