A Mineral is ?
advertisement

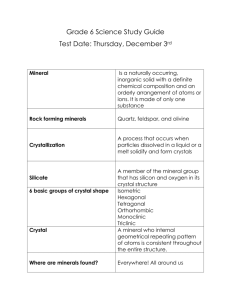
Minerals! What is a mineral? • In order for a substance to be classified as a mineral it must maintain FIVE characteristics. • 1. Naturally occurring • 2. Inorganic • 3. Solid • 4. Definite chemical composition • 5. Definite crystal pattern (shape) Describe each characteristic! Naturally Occurring Inorganic Solid Not man made, must occur in nature Not living and not made of any living materials A substance with a definite shape and volume Definite Chemical Composition Definite Crystal Pattern A specific shape A specific from which the formula (either a mineral single element or crystallizes or a compound) grows atomically What does the abundance of each mineral depend on? • Where they form. Location within the earth! • The abundance of the elements from which they form. • The rate at which they form. Speed! There are 2500 known minerals, but only 20 are common , they are referred to as ROCK FORMING MINERALS QUARTZ CALCITE AUGITE HEMATITE MICA FELDSPAR AMPHIBOLE DOLOMITE GYPSUM OLIVINE All minerals are broken into mineral groups based on their CHEMICAL COMPOSITION! • • • • • • • • • 1. Silicates **** 2. Sulfides 3. Sulfates 4. Carbonates 5. Oxides 6. Native Elements 7. Halides *ate = Oxygen *ide = Metal Quartz SiO2 Silicon Oxygen 2 proton s electrons neutrons atoms elements minerals silicates Silicon + Oxygen sulfides Sulfur + Metal sulfates oxides Sulfur Oxygen + + Oxygen Metal halides Chlorine and /or Bromine and/or Fluorine and/or Iodine + metal carbonates Carbon + Oxygen Native Elements Any Single Eleme nt A Mineral is ? •1. •2. •3. •4. •5. Naturally occurring Inorganic Solid Definite chemical composition Definite crystal pattern (shape) There are 2500 known minerals, but only 20 are common, they are referred to as ROCK FORMING MINERALS Quartz Feldspar Regardless of the number of minerals in the world each has its own unique set of characteristics. These characteristics are referred to as: Physical properties Physical Properties Color Visual property easiest to identify, but least reliable! talc dolomite malachite copper Luster Non-metallic The way a mineral reflects the light. Metallic Looks or reflects the light like metal Does not reflect the light as metal Breakage Result of arrangement of atoms, bonding Cleavage: to break along a smooth plain or in a particular pattern. Fracture: Breakage To break with uneven, rough, or jagged edged. No pattern Streak The powdered residue left behind as a mineral is rubbed across a porcelain tile. Crystallization Growth A mineral grows by crystallizing: the arrangement of atoms in a repeating pattern. Minerals crystallize as magma coolsSlow cooling, large crystals Fast cooling, small crystals Atomic structure Outward appearance Crystal (Shapes) Structures tetragonal hexagonal orthorhombic triclinic monoclinic cubic Hardness The ability of a mineral to resist being scratched. Absolute hardness Relative hardness Comparison of mineral hardness. -Talc is the softest -Diamond is the hardest. Example: Apatite is harder than Fluorite, softer than Feldspar. estimate Physical test using a series of items and recording the numerical measurement. Example: exact Feldspar is not scratched by the penny, nail, or file. Its hardness is >6. Example Luster Color Hardness Unique Feature Streak Chemical Composition Crystal (Shapes) Structures Structure: hexagonal Formula: SiO2