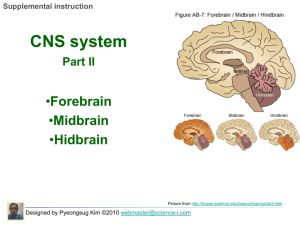
SI PPT: Eukaryotic cells
advertisement

Updated: Tuesday, July 6, 2010 Eukaryotic Microbes Supplemental instruction Fall 2010 For Dr. Wright’s Bio 7/27 Class Picture from http://berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2006/12/21_microbes.shtml http://sustainabledesignupdate.com/?p=409 http://www.mycology.adelaide.edu.au/gallery/hyaline_moulds/?template=print Designed by Pyeongsug Kim ©2010 sibio@att.net Eukaryotic microbes: Eukaryotic microbes: we considered unique features of each, their niche in the environment, and whether they might cause disease. Algae: as photosynthetic organisms, why are they so important in the environment? What features of algae are considered when classifying them? What are some potentially harmful effects of algae? Fungi: what features of fungi make them so unique that they are grouped in their own kingdom? How do fungi reproduce? Fungi are placed into groups according to what feature? What is the major contribution of fungi to ecosystems? What are some differences between yeasts and molds? What is a dimorphic organism? What are some potentially harmful effects of fungi? How can fungi cause disease? Protozoa: In what kingdom are protozoans found? What is the distinguishing feature of Mastigophora, Sarcodina, Ciliophora, Apicomplexa? How do they reproduce? Why is their complex life cycle a challenge in treating (or preventing) disease caused by protozoans? What is a parasite? What is a saprophyte? Which type of the above organisms can be parasitic? Which types can be saprophytes? Helminths: what are the three major types of worms that we discussed in class? Be able to give examples of each, the disease they cause, and explain how they are transmitted to the host? What do we mean by primary and secondary host? Which is which? Vector: what is the difference between a mechanical vector and a biological vector? Give examples of each. What do we mean by “vector control” and how is it achieved? Why might this help reduce the spread of certain diseases? -From Study guide Dr. Wright Bio27 Fall 2009 Symbiosis - living together; love each other http://plantbio.berkeley.edu/~bruns/tour/fungi2.html ; can be single love.; one side hates the other. 1) Mutalism (both beneficial) love each other. mycorrhizae = fungi +plant roots • ___________ fungi~ nitrogen fixation plant~ provide sugars •Lichen = ____________ Algae or cyanobacteria+fungi algae or cyanobacteria – provide sugars fungi – provide by retaining water *Cellulose –undigestible carbohydrate. •Cellulose-digesting symbiosis Herbivores + bacteria _________________ or protozoans Help to digest cellulose • Bacteria in the large intestine Help to digest Vitamin K and B. Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com www.naturfoto.cz 1) Commensalism (one beneficial; no harmful) Single love Bacteria living on the skin to get food and others. the host (human) – to get nothing; no harmful one side hates the 2) Parasitism (one beneficial; the other harmful) other. Parasites bacteria, protozoa, algae, fungi, and helminths that cause disease http://www.polconsultant.com/conteduc/immunolog y/invaders.htm http://www.ctahr.hawaii.edu/nelsons/kava/algae2.jpg Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Saprophytes -any organism living upon dead or decaying organic matter. -obtain nutrients from dead organic matter. -Most fungi in eukaryotes some bacteria in prokaryiotes Mycobateria What is the difference saprophytes from decomposers? ___________ Saprophytes are organisms that live and feed on dead organic matter. -Most fungi and some bacteria. ___________ Decomposers are organisms that breakdown complex organic (dead or decaying organisms) into simpler mineral components. -Fungi, bacteria, and protozoa. Picture from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saprotroph Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Protozoa (Kingdom protista) -Only unicellular -Not photosynthetic but, Euglena? -Sexual ~fusion of gametes, conjugation.. Asexual ~ binary fission or multiple fissions -Motile(flagellates, cilia) -Lack cell wall -some are decomposers Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Protozoa (cont’d) •Classified by… - mean of movement: cilia, flagella, peudopodia or nonmotile Mastigophora, Sarcodina, Ciliophora, Apicomplexa -Sarcomastigophora (Mastigophora) by flagella; pathogen -Ciliophora by cilia; free-living -Apicomplexa by pseudopodia; parasitize other hosts Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Protozoa (Kingdom protista) •Reproduction - polymorphic trophozoite ___________ ~ Vegetative or feeding form Favorable environment cyst ___________ ~ Resting form, also can reproduce Adverse conditions Protective cyst wall within the cytoplasm. Lack of nutrient, moisture or oxygen, toxic.. For dispersal and survival. - Sexual syngamy- gametes from different individuals. autogamy- gametes are formed and then fuse. Conjugation - Asexual ~ Binary fission; Budding; Schizogony (multiple fission) Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2009 Algae (Kingdom protista) -uni- or multicellular -Photosynthetic (chlorophylls and other photosynthetic pigments) -sexual ~ conjugation, fusion of Gametes,… asexual ~ binary fission. -No vascular system -Some motile -Rigid Cell wall ;cellulose a/w pectin; silica(diatoms) •Environmental -Photosynthetic; produce O2 -Primary producer: food source -Most live in fresh or salt water but, live nearly everywhere. -Lichen (symbiosis: Mutualism) Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Algae (Con’td) •Potential harm -”Bloom”; red tide by dinoflagellates - Toxin shellfish poisoning *Caution in the Lab - AIDS. •Classified by… - photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll a, b, carotenes…) Brown algae, green algae, red algae - storage molecules (starch, fats, oils) - habitat: fresh or salt water Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Euglena? -Kingdom protista -Photosynthetic -eye spot -motile: flagella -Alage? Protozoa? Controversial! Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Fungi(Kingdom fungi) -uni-(yeast) or multicellular -NOT photosynthetic: “saprophytes -Sexual ~ zygospore, asci, basidiospores Asexual ~ budding, binary fission -Dimorphic -Non-motile -Cell wall: Chitin -some decomposers, some saprophytes some parasites -Food production: bread, cheese Infectious athletes foot! Picture from http://knol.google.com/k/will-johnson/athlete-s-foot-tinea-pedis/4hmquk6fx4gu/227 Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Helminths(Kingdom animalia) -multicellular -Sexual -nematodes (roundworms) trematodes (flukes) cestodes (tapeworms) -parasites Arthropods (Kingdom animalia) -multicellular -Sexual -insects, ticks, fleas, lice, mites -some parasites Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com cyst trophozoite Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Fungi(Kingdom fungi) -uni- or multicellular -NOT photosynthetic: “saprophytes -Sexual ~ zygospore, asci, basidiospores Asexual ~ budding, binary fission -Dimorphic (mold or yeast form) -Non-motile -Cell wall: Chitin -Antibiotics, Vaccines •Classified by… -means of sexual reproduction. Zygomycetes ~ Zygospores Basidomycetes ~ Basidiospores Ascomycota ~ Ascus Deuteromycetes ~ budding, absent or unknown. Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ___________Dimorphic can exist as mold/hyphal/filamentous form or as yeast. Fungi grow … as mycelia(mold) in soil or spores in the air. as yeast-like cells in the body. •Yeast - single-celled - Asexual •Mold - Multicellular - Hypae (collectively mycellium) binary fission or budding *Yeast infection *Food spoilage Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ___________ Dimorphic - can exist as mold/hyphal/filamentous form or as yeast. in fungi Spores in the air are inhaled develop into yeast-form in the lungs disease Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Helminths(Kingdom animalia) -multicellular -nematodes (roundworms) trematodes (flukes) cestodes (tapeworms) -Sexual -Parasites •Cause disease through… -Primary/secondary host -Ingesting infected food (beef, pork..) -Swimming infected water (penetrating skin). Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Arthropods (Kingdom animalia) -multicellular -sexual -insects, ticks, fleas, lice, mites -allergens -carry cysts of protozoa Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com ______ Vector - transmit microorganisms or viruses to human. •_________ Mechanical vector -transfer contaminated food from one location to other. - Flies Biological vector •_________ - act as a host for a pathogen before it is transmited to another organism. - Mosquitoes Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com _________ Host :an organism that harbors a virus or parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. _______________ Primary host -a host in which the parasite reaches maturity -reproduces sexually. trophozoite -usually human, big animals but not always. ________________ Secondary host -host is a host that harbors the parasite only for a short transition period. -Mosquito, fly harbors cysts. Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com •Vector control Medication Vaccination Genetic engineering? Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com