CNS system PartII
advertisement
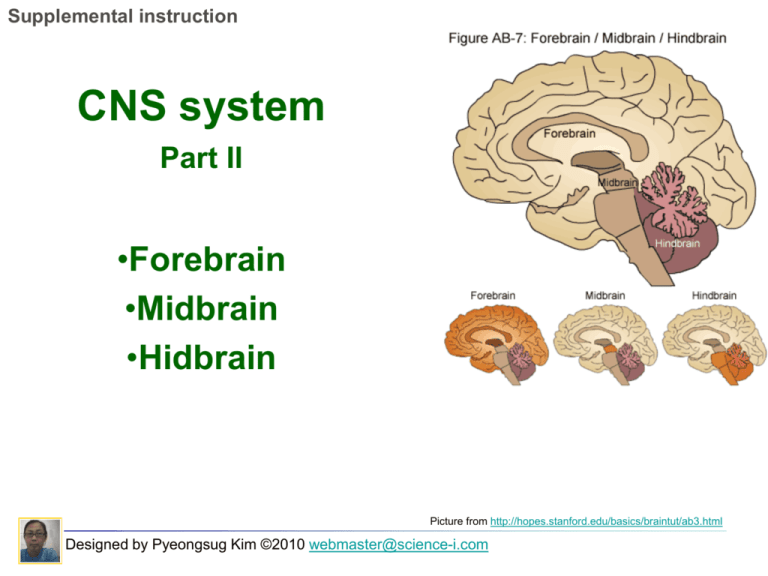
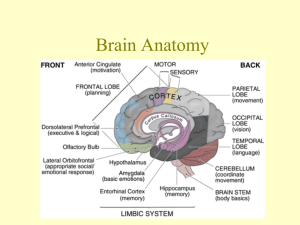
Supplemental instruction CNS system Part II •Forebrain •Midbrain •Hidbrain Picture from http://hopes.stanford.edu/basics/braintut/ab3.html Designed by Pyeongsug Kim ©2010 webmaster@science-i.com Developmental categorization of CNS system. -Forebrain ~ telencephalon ~ forming hemispheres of cerebrum. diencephalon ~ -Midbrain ~ does not subdivide. -Hindbrain ~ metencephalon ~ pons, cerebellum myelencephalon ~ Medulla oblongata, RAS Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Forebrain -comprised of cerebrum and diencephalon -Involved in emotion, learning and memory ____________ Cerebrum -Regulate sensory info and motor response. -Basal nuclei in deep region. ____________ Diencephalon -Thalamus/epithalamus -Hypothalamus -Pituitary gland Picture from http://www.stanford.edu/group/hopes/sttools/figureid.html Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Diencephalon (in forebrain) -Thalamus/epithalamus(pineal gland) -Hypothalamus -Pituitary gland Thalamus _________ - relay center to cerebrum all sensory information except smell epithalamus __________ - includes pineal gland which secrets melatonin. _____________ Hypothalamus - integrates nervous and endocrine systems - Regulates anterior and posterior pituitary glands. - Hunger and thirst, body temperature, emotions -coordinate autonomic and endocrine responses. Picture from http://www.stanford.edu/group/hopes/sttools/figureid.html Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Pineal gland SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) -regulate ______________ Circadian rhythms(biological clock) -Adjusted daily by light from eyes. -Controls pineal gland secretion of __________ melatonin to regulate circadian rhythms *Melatonin is involved in aligning physiology with sleep/wake cycle and seasons. -Secreted at night -Inhibited by light Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Choose Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus Thalamus ________ -relay center to cerebrum all sensory information except smell alertness. -Role in level of arousal. Hypothalalmus ____________ -integrates nervous and endocrine systems(hormone). -contains neural centers for hunger, thirst, body temperature. Epithalamus ___________ -contains choroid plexus and pineal gland. choroid plexus secretes CSF. ____________ pineal gland ____________ secretes melatonin *Melatonin: involved in sleepDesigned cycle and seasonal reproduction. by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Midbrain -visual and auditory reflexes -connects with cerebrum and cerebellum; motor reflexes - Superior colliculi, Inferior colliculi, Red nucleus , substantia nigra Superior colliculi - involved in visual reflexes ______________ ______________relay auditory information Inferior colliculi Red nucleus and substantia nigra involved in motor coordination _______________________- Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Dopaminergic pathways -Neural pathways in the brain which transmit the neurotransmitter __________. dopamine -Motor coordination •Mesolimbic dopamine pathway - involved in reward and drug addiction. - Abused drugs cause dopamine release from the nucleus accumbens. *heroin and morphine- production cocaine and amphetamines- inhibit reuptake Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com •Nigrostiatal dopamine pathway - Motor control pathway Dopamine neurons in ______________ Substantia nigra degenerate in Parkinson’s disease. Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Hindbrain A: pons C: Celebellum B: Medullar oblongata Contains______, _______ medulla pons _________,and cerebellum __________ cerebellum motor coordination; motor learning; trained voluntary activity __________ cerebellum ataxia caused by damage to this area. A B Ataxia: Loss of the ability to coordinate muscular movement. __________ Includes two important respiratory control centers pons ________________ Medullar oblongata several crucial centers for breathing and cardiovascular systems. Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com C Hindbrain Reticular Activating System (RAS) ___________________________ - an ascending arousal system. - composed of several neuronal circuits connecting the brainstem to the cortex. * Textbook says “…originates in groups of neurons in the pons, midbrain reticular formation, hypothalamus and basal forebrain.” - promotes wakefulness, but inhibits sleep. - Regulating Sleep-Wake Transitions -Stimulation in RAS causes wakefulness. -Damage to RAS causes coma. Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com Disorder in RAS -Loss of general sense of consciousness or wakefulness. -result in alterations of sleep-wake cycles and disturbances in arousal. -Narcolepsy:excessive daytime sleepiness -Coma * Be careful! RAS ~ Promotes wakefulness and inhibits sleep at the day time! Melatonin in pineal gland ~ Promotes sleep at the night! Designed by Pyeongsug Kim, ©2010 www.science-i.com