HND – 2. Individual Behavior
advertisement

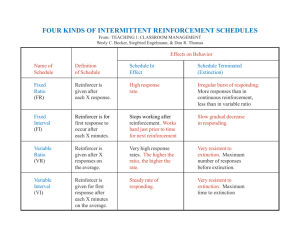
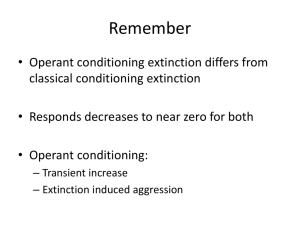
Lim Sei Kee @ cK How biographical characteristics (such as age and gender) and ability (which includes intelligence) affect employee performance and satisfaction. Personal characteristics – such as age, gender, and length of tenure- that are objective and easily obtained from personnel records. Age Gender Tenure An individual’s capacity to perform the various tasks in a job. Intellectual Abilities Physical Abilities The Ability- Job Fit Those needed to perform mental activities- for thinking, reasoning, and problem solving. Examples: IQ (Intelligence quotient) tests, GCE ‘O’ level. Dimensions of Intellectual Ability: Number aptitude, Verbal comprehension, Perceptual speed, Inductive reasoning, Deductive reasoning, Spatial visualization, Memory. The capacity to do tasks demanding stamina, dexterity, strength, and similar characteristics. Nine basic Physical Abilities: Dynamic strength, Trunk strength, Static strength, Explosive strength, Extent flexibility, Dynamic flexibility, Body coordination, Balance, Stamina. Jobs make differing demands on people and that people differ in their abilities. Employee performance is enhanced when there is a high ability-job fit. Employees are likely to fail. Organizational efficiencies and possible declines in employee satisfaction. Learning: Any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs as a result of experience Theories of learning: Classical conditioning – Individual responds to some stimulus that would not ordinarily produce such a response. Operant Conditioning – Desired voluntary behavior leads to a reward or prevents a punishment. Social Learning – Individual learn through observation and direct experience. Experiments to teach dogs to salivate in response to the ringing of bell, conducted in the early-1900s by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov. Meat: Unconditioned stimulus Reaction that took place: Unconditioned response Bell: Conditioned stimulus Behavior of the dog: Conditioned response # Your romantic partner always uses the same shampoo. Soon, the smell of that shampoo makes you feel happy. # You have a meal at a fast food restaurant that causes food poisoning. The next time you see a sign for that restaurant, you feel nauseous. # The nurse says “Now this won’t hurt a bit” just before stabbing you with a needle. The next time you hear “This won’t hurt” you cringe in fear. Behavior is a function of its consequences. People learn to behave to get something they want or to avoid something they don’t want. A child learns to clean his/her room after being rewarded with TV time, every time he cleans it. A person stops teasing his fiance about an issue after she gives him the silent treatment. Individuals can also learn by observing what happens to other people and just by being told about something, as well as by direct experiences. Advertisements are prime examples of Social Learning Theory. We watch them, then copy them. If your a new person to IGS and it's lunch time, and you finish with your lunch but you don't know where to put the tray you would follow someone who knows what their doing. So you learn off of other peoples examples. Systematically reinforcing each successive step that moves an individual closer to the desired response Four - ways Positive reinforcement Negative reinforcement Punishment Extinction Positive Reinforcement Following a response with something pleasant. Negative Reinforcement Following a response by the termination or withdrawal of something unpleasant. Punishment attempts to decrease the probability of specific behaviours being exhibited (eliminate undesirable behavior.) Extinction Eliminating any reinforcement that is maintaining a behavior. its purpose is to reduce unwanted behavior. Schedules Of Reinforcement : The timing of the behavioural consequences that follow a given behavior. Reinforcement Schedule Nature Of Reinforcement Effects On Behavior Example Continuous Reward given after each desired behavior Fast learning of new behavior but rapid extinction Compliments Fixed Interval Reward given at fixed time intervals Average and irregular performances with rapid extinction Weekly Paychecks Variable Interval Reward given at variable time intervals Moderately high and stable performance with slow extinction Pop Quizzes Fixed Ratio Reward given at fixed amounts of output High and stable performance attained quickly but also with rapid extinction. Piece-rate Pay Variable Ratio Reward given at variable amounts of output Very high performance with slow extinction Commissioned Sales Well pay Vs Sick pay Employee Discipline Developing Training programs Self-management