Patterns of Life
advertisement

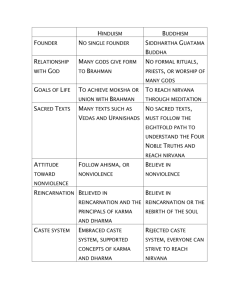
Patterns of Life 8.3 Caste system A. a rigid social system set up to maintain order 1. born into – can’t leave 2. influences all aspects of life 3. based on Hinduism B. Varnas 1. different categories ppl are born into 2. based on belief in (c)reincarnation, (b)karma, and (a)dharma 3. the higher the varna, the closer one is to (d)moksha 4. created by Aryans (ancient invaders) many subdivisions (2,000-3,000 jati) 5. made illegal in 1950 definitions a. dharma: duties; responsibilities b. karma: life and death cycle based on past deeds (dharma) c. reincarnation: rebirth of the soul in various forms until moksha is achieved d. moksha: freeing of the soul from the body to unite with Brahman (supreme god) 6. Brahmans: a. Priests, teachers, and intellectuals b. head of the caste system c. expected to live very frugally. 7. Kshatriays: a. warriors, police, and administrators b. they are the nobility, the protectors of society c. permitted a number of privileges - expected to display considerable strength of body and character. 8. Vaisyas: farmers, merchants, and business people (productive class) 9. Sudras: a. artisans and workers b. born to be servants to the other three varnas c. only section of society allowed to accept another's employment C. untouchables: a. outside of the caste system b. harsh life c. do menial and unappealing tasks http://magma.nationalgeographic.com/ngm/0306/feature1/ D. Rules 1. intended to keep people ritually pure 2. more strict for upper castes 3. contact with lower castes or untouchables may cause pollution