Hinduism
advertisement

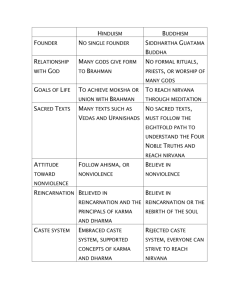
Today’s Vocab Polytheism: Belief in more than 1 God. Reincarnation: The belief that all souls/spirits can be born again. Moksha: The ultimate goal of Hinduism. A state of perfect understanding between Atman and Brahman. Samsara: The cycle of reincarnation. Atman is born again and again until Moksha is achieved. Caste System: Social class system within Hinduism. You are a part of the Caste you are born in your entire life. Dharma: The laws/customs of your Caste. Karma: How well you follow the Dharma of your Caste. Warm up? What purpose do religions serve for the people who follow them? ACTIVATING STRATEGY Theology, Enlightenment, Polytheism & Sacred Text WHAT YOU THINK THE DEFINITION IS ACTUAL DEFINITION EXAMPLES DRAW A PICTURE Commonalities of Major Religions All religions seek to answer big questions like where did the world come from; what is the purpose of life; what happens after we die, etc. 2. All religions set out guidelines for how to live, for what is right and wrong, for how to be a good person. 1. 3. Religious experiences occur for some people in all religions. These involve a feeling of peacefulness, joy, wholeness, and unity with the world. Different religions interpret these experiences differently. 4. Within each religion there is diversity of belief and practice. Some differences are about emphasis or style, while some are about primary religious questions, such as what is necessary for salvation. Within most religions there are some groups who feel that each word of the sacred text is literally true, while other groups do not. 5. All religions have deeply wise people, who are easily recognizable by anyone. 6. Most religions have people who wish to devote themselves wholly to their religions, such as monks and nuns. 7. Religion involves an element of faith, because it posits the existence of something that cannot be experienced by the five senses. Hinduism Possibly the world’s oldest religion, over 4000 yrs. old. Founder: unknown Belief that all things in the universe are cyclical Polytheistic Belief in numerous Gods & Goddesses. Brahman- The absolute universal power, spirit, force. Can not be understood by humans, so the many Gods worshipped represent aspects of this power. The 3 Main Gods are: Brahma The Creator Vishnu The Protector Shiva The Destroyer A part of Brahman is in all living things Atman Individual soul of living being Hindus believe in reincarnation An individual’s soul or spirit born again and again The Goal of Hinduism Moksha A state of perfect understanding of the relationship between atman and Brahman Become enlightened through good Karma and reincarnation. Samsara Cycle of reincarnation Atman or Soul is born again and again until Moksha is achieved Three paths to liberation from Samsara 1. Yoga 2. Devotion 3. Purification of the mind and body Honoring the Gods Dharma Obedience to the laws and customs of your Caste (Social System) BRAHMAN (Moksha) Priest Warrior Farmer/Merchant Laborer Reincarnation is based on how well you follow your Caste Dharma or duty. Karma is your record (report card) of your deeds, if it is good you go up, bad you go down. Untouchables or outcastes are not part of the caste system because of bad karma in a past life and are discriminated against. Gandhi renamed them Harijans (children of God) to help end the discrimination. COMPLETE GRAPHIC ORGANIZER Closing? What kind of effect do you feel the Caste System has on Hindu society?