Hinduism and Buddhism
advertisement

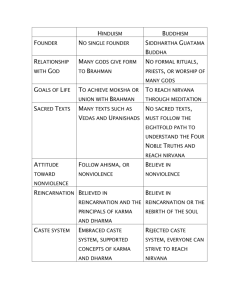
Ch 4 – Hinduism & Buddhism: A Comparison Identify whether the following are characteristics of Hinduism, Buddhism, or characteristics of both religions. Write out the characteristics in the appropriate space on the Venn diagram. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. Siddhartha Gautama spent his life searching for truth and an end to suffering. Belief in non-violence Cannot be traced back to any one person; grew from a collection of religious beliefs Began in India before spreading to other regions Worships a variety of gods that gave form to Brahman (Brahma-Creator, Vishnu– Preserver, and Shiva–Destroyer) Rejected the caste system; since no one is superior, everyone can reach nirvana regardless of birth. The entire universe is part of the unchanging, all-powerful spiritual force called Brahman. The Eightfold Path will help you understand the Four Noble Truths and reach nirvana, the union with the universe and release from reincarnation. Belief in karma, or the idea that actions in life affect ones fate in the next life The Tripitaka, or “The Baskets of Wisdom”, a collection of Buddha’s teachings, is considered to be a sacred text. To escape the wheel of fate, one must have good religious and moral duties, or dharma. By obeying dharma, a person acquires merit for the next life. Achieving moksha or nirvana is the ultimate goal of existence and can’t be done in one lifetime so reincarnation is necessary. The Vedas (prayers and hymns), Bhagavad-Gita (ethical ideas), and Upanishads (dialogue between the teacher and student on moksha) are sacred texts. No formal rituals or priests; no worship of many gods All existence is ranked. Concepts of karma and dharma ensure the social order by supporting the caste system. Four Noble Truths & the Eightfold Path: 1. 2. 3. 4. All life is suffering. The cause of suffering is desire. To cure suffering, overcome desire. To overcome desire, follow the Eightfold Path.