Chapter 12: Fresh Water - Stephanie Dietterle Webpage
advertisement

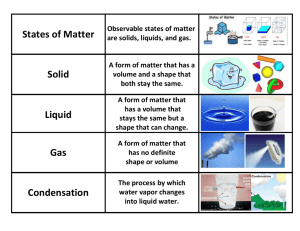
CHAPTER 12: FRESH WATER Multiple Choices 100 Fill-in-the- True/False Short Blank Answer 100 100 100 Illustration 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 600 600 600 600 600 700 700 700 700 700 The process of supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops is called: A. conservation B. condensation C. Irrigation D. Evaporation Irrigation What is the source of energy for the water cycle? A. Gravity B. Precipitation C. The oceans D. The sun Sun What is a habitat? A. a place where an organism lives B. one part of the water cycle C. where water is supplied to make crops grow D. a place where groundwater is found A place where an organism lives A high coliform count is an indicator that the water may contain A. high levels of minerals B. high pH levels C. acids D. large numbers of disease-causing organisms Large numbers of disease-causing organisms The water in an artesian well rises because of pressure in a(n) A. watershed B. reservoir C. aquifer D. point source Aquifer The layer of rocks and soil with pores that contain air as well as water is called the A. unsaturated zone B. water table C. saturated zone D. divide Unsaturated zone The process of passing water through screens to remove solid particles is called A. precipitation B. filtration C. coagulation D. concentration Filtration Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are forms of __________. Precipitation Most water in the atmosphere is invisible _________. Water vapor A small, shallow body of water in which sunlight can reach to the bottom is a(n) _________. Pond A wetland in a cool, northern area where mosses grow in acidic water is called a(n) __________. Bog Water cannot pass easily through materials that are __________. Impermeable When water is carried into fields in open irrigation ditches, much of it is lost to __________. Evaporation Any substance that causes water pollution is called a(n) ___________. Pollutant More than 97% of the water on Earth is fresh water. T or F (if F make it true) F; salt water The water cycle renews the supply of fresh water on Earth. T or F (if F make it true) True A tributary is a place where groundwater bubbles or flows to the surface. T or F (if F make it true) F; spring The amount of calcium and magnesium in water determines the water’s pH. T or F (if F make it true) F; hardness In water treatment, chlorination removes particles from water by getting them to stick to sticky globs called flocs. T or F (if F make it true) F; coagulation Water quality is a measure of the substances in water besides water molecules. T or F (if F make it true) True A lake that stores water for human use is called a watershed. T or F (if F make it true) F; reservoir What is added to drinking water to kill bacteria and other organisms? A. sand B. alum C. chlorine D. dissolved solids Chlorine Using a resource wisely so that it will not be used up is called A. filtration B. conservation C. distillation D. coagulation Conservation Describe the water cycle. The water cycle is the continuous process by which water moves through the living and nonliving parts of the environment. It includes the processes of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. What sources of water on Earth are available for human use? Explain. Household purposes, and agriculture Household purposes: washing, laundry Agriculture: irrigation What sources of water on Earth are available for human use? Explain. Industry, transportation, and recreation. Industry: product manufacturing Transportation: boating Recreation: swimming What is the purpose of drinking-water treatment? Drinking water treatment makes the water safe and appealing to drink. Describe a typical treatment process at a water treatment plant. The processes in such treatment include: filtration, coagulation, chlorination, aeration, and the possible addition of fluoride and other chemicals. What is this a picture of? Explain. Divide – a ridge of land that separates one watershed from another. Is this an example of a point source of pollution or a nonpoint source? Explain. It is an example of a point source because a specific source of pollution can be identified. What is occurring in the illustration that could affect a drinking-water supply? Chemicals from the factory are entering the river. What could a company do to stop the harm being done to the water in the river? The company could stop the flow of chemicals through the pipe and dispose of them in a safe way. What is this a picture of? Explain the 3 main components? The water cycle – evaporation, condensation, precipitation What is this a picture of? How can it help conserve water? Irrigation – maintains moisture in the soil, and helps with the germination of crops so they can grow How can water pollution harm our environment and our water supply? Opinion….Good Answer