Chapter 7
advertisement

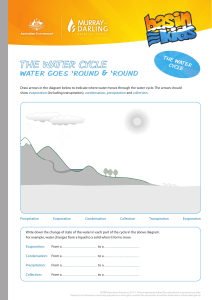
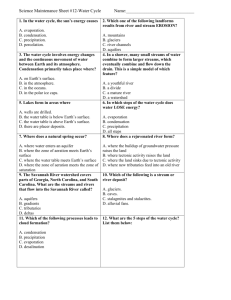
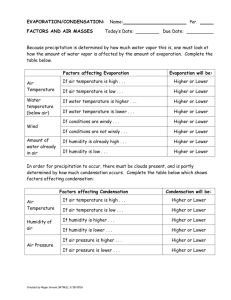
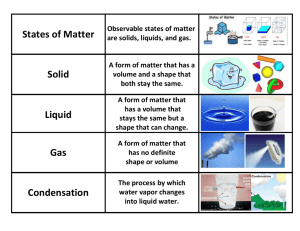
Chapter 7 Multiple Choice 1. The circulation of water from one part of the general Earth system to another is known as the: a. Condensation cycle b. Hydrologic cycle c. Environmental cycle d. Evaporation cycle 2. As the temperature of a parcel of air increases, its ability to hold water vapor __________. a. Increases b. Decreases c. Remains constant d. Increases, then decreases 3. If an unsaturated parcel of air is cooled it will eventually reach a temperature where the air will become saturated; this temperature is known as the: a. Environmental b. Dew point c. Lifting condensation level d. Adiabatic 4. The amount of water vapor in the air at any one time and place is called: a. Capacity b. Saturation deficit c. Humidity d. Precipitation potential 5. The process by which plants give up moisture to the air is: a. Evaporation b. Transpiration c. Evapotranspiration d. None of these 6. The rate of evaporation is affected by: a. Temperature b. Relative humidity c. Wind speed d. All of these 7. A precipitation type caused by mountains or highlands is: a. Convectional b. Frontal c. Orographic d. Rain 8. A cloud type formed by strong convection currents is: a. Cirrus b. Lenticular c. Stratus d. Cumulonimbus 9. The term nimbus, when used in describing clouds, means: a. Precipitation b. Ice crystals c. Highest d. Lightning and thunder 10. Many of the great deserts of the world coincide with the: a. Equatorial low b. Subtropical highs c. Subpolar lows d. Polar highs True/False 11. The higher the relative humidity the more comfortable people tend to feel. 12. In general, the polar regions have low precipitation. Matching (Condensation nuclei; Potential; Cumulus; Rain) 13. __________ are minute particles in the atmosphere that provide a surface upon which condensation can take place. 14. __________ evapotranspiration is a theoretical term used to estimate the maximum loss of moisture through evaporation and transpiration. 15. __________ is by far the most common form of precipitation. 16. There are three basic forms of clouds: cirrus, stratus, and __________. Answers: 1. b 2. a 3. b 4. c 5. b 6. d 7. c 8. d 9. a 10. b 11. F 12. T 13. Condensation nuclei 14. Rain Cumulus