States of Matter & Physical Properties Worksheet
advertisement

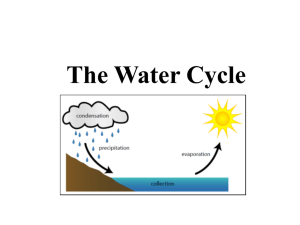
States of Matter Observable states of matter are solids, liquids, and gas. Solid A form of matter that has a volume and a shape that both stay the same. Liquid A form of matter that has a volume that stays the same but a shape that can change. Gas A form of matter that has no definite shape or volume Condensation The process by which water vapor changes into liquid water. Evaporation The process by which liquid water changes into water vapor. Precipitation Water that falls from the sky. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail are kinds of precipitation. Water Cycle The movement of water from Earth to the air and back again. (Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation) Mass Weight Mass is the space an object takes. (This would be the same on the Earth or the Moon.) Weight is how much mass an object has on EARTH. (This would NOT be the same on the Earth or the Moon because of gravity.) Matter Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. temperature The degree of hotness or coldness on a body or environment. C = Celsius thermometer F = Fahrenheit (USA) An instrument for measuring temperature. C = Celsius F = Fahrenheit (USA) volume The amount of space inside a three-dimensional object. Physical Attributes of Matter Ways to compare physical attributes of matter are by: color, volume, mass, texture, temperature, transparent, flexibility, size, and shape. Measurement Determining the size of something using weights and measures is measurement. (weight, mass, length or height, temperature, volume and capacity). Texture Texture is the appearance and feel of a surface (bumpy, smooth, shiny, rough, grainy, slimy, bumpy, sticky, velvety, spongy, hard, greasy, hairy, soft, fluffy, dry, wet, bouncy) Compare Examine two or more objects or ideas in order to note similarities (sameness). Physical Property Anything that you can observe about an object by using one or more of your senses. Physical Change A change in which the form or shape of a substance changes but the substance still has the same chemical makeup. Chemical Change A change in one or more substances, caused by a reaction, that forms new and different substances. fulcrum The balance point on a lever that supports the arm but does not move.