Blood and Blood Typing
advertisement

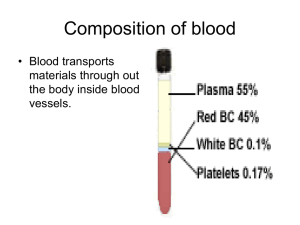
Fact or Fiction The average human body contains 10 liters of blood False, it contains 5 liters of blood (equal to 1.3 gallons) The amount of exercise someone gets accounts for varying levels of RBC’s in individuals True, the body needs more oxygen as it works Men have more RBC’s per microliter of blood than females True, in general men have a bigger body mass when compared to women Blood is purple until it is exposed to oxygen and then it turns red False, blood is always red regardless of oxygen exposure Oxygenated blood vs Deoxygenated blood The blood on the left is oxygenated, the right is deoxygenated blood (from a vein) Functions of Blood Transportation 1. E.x. 2. Regulation E.x. 3. Protection E.x. Components of Blood 1. Cells Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets 2. Blood Plasma Plasma (mostly water) Which type of tissue is blood classified as? Components of Blood Hematocrit The volume of blood cells in a sample What should it be? Plasma (45%) Cells (55%) RBC’s 99% WCB’s and platelets 1% Formation of Blood Cells (AKA hemopoiesis) Where does it occur? Red bone marrow Trabeculae (spongy bone) Did RBC formation begin here? No Pluripotent Stem cells Red Blood Cells (AKA Erythrocyte) Biconcave shape More surface area Carry oxygen O2 binds to hemoglobin Can vary in number between individuals Why? Hemoglobin Gives whole blood it’s red color O2 binding site Binds with O2= Bright red Releases O2= Dark red Hypoxia Prolonged oxygen deficiency What does this result in? Red Blood Cell Life Cycle Average lifespan 120 days Rupture (die) when passing through capillaries Destroyed by macrophages Red Blood Cell Life Cycle Hemoglobin breaks down Iron (heme) Amino acids (globin) Non-heme part of iron broken down Biliverdin Which is further broken down Why is your poo brown? Eventually biliverdin is converted into Urobilin (yellow) Urine 2. Stercobilin (pigment) Feces (poo) 1. Why are certain vitamins so important? They are need to synthesize hemoglobin B12 Folic acid Help absorb iron Vitamin C Anemia Too few RBC’s or hemoglobin Erythropoiesis Formation of RBC’s Usually occurs as RBC’s are destroyed Disruption in balance causes hypoxia Causes more RBC’s to be made More EPO is released Erythropoietin (EPO) Hormone made by kidneys It Stimulates RBC production More RBC’s = more O2 sent to tissues Blood Doping https://www.youtube.com /watch?v=G7KZxIR1t-o Blood Concept Map Terms Protect/transport/regula te RBC’s Hemoglobin Erythropoiesis Oxygen Homeostasis Leukocytes Bone Marrow Nucleus Spleen Biconcave disk Water Plasma White Blood Cells AKA Leukocytes Function to protect the body Five different types A. Granulocytes (Granules in cytoplasm) Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils B. Agranulocytes (no granules) Monocytes Lymphocytes Neutrophil First to respond to infection Active phagocytes Destroy invaders by releasing enzymes Present in pus of wounds 60% of WBC Monocyte Migrate into infected tissues Become macrophages Destroy invaders and clean up cellular debris Eosinophils Have enzymes that combat against allergic reactions Mainly attack parasites Ex. Worms What does a high count mean? Allergic reaction Or Parasitic infection Basophils Involved in inflammatory Liberate histamine and heparin Lymphocytes B cells Develop into plasma cells Produce antibodies Destroy bacteria and their toxins Lymphocytes T Cells Attack Viruses Fungi Transplanted cells Cancer cells Some bacteria Lymphocytes Natural Killer cells (NK) Attack Variety of microbes Tumor cells Blood Concept Map Terms Albumins Inflammatory Reaction Antibodies Monocyte Eosinophils Platelets Defend against disease Phagocyte Globulins Hemostasis WBC Life Span Only phagocytize a certain amounts Live for days or hours Die off faster during infection Why? Platelets AKA Thrombocytes Help blood clot by sticking to the lining of blood vessels Hemostasis Sequence of events that occur to stop bleeding Involves Coagulation (thickening of blood) Clotting of blood Three Events in Hemostasis Blood vessel Spasm 2. Plate plug forms 3. Blood coagulation 1. Blood Clot Story Board Brainpop 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What are the two components to your blood type? What is hemolysis? What is the Rh factor? What is the most common blood type in Americans? What is the least common blood type in Americans? ABO Blood Groups What are the four blood types? A B AB O Whole Blood Antegens Type of antigen on RBC will determine blood type E.x Antibodes Non-matching antibody found in plasma E.x. Rh Factor Makes blood type either + or – Rh+ Rh antigen present Rh No Rh antigen Blood Typing Antibodies Type of WBC Defends the body Found in plasma React with antigens Agglutination Occurs when matching antibodies and antigens bind What happens if that occurs in a RBC? ABO Blood Types Chart Blood Type A B AB O Antigen on RBC Antibody in Plasma Compatibility of blood types Can a person with A positive blood donate to a person with A negative blood? Why or why not? Why can’t a person with B blood donate blood to a person with type A blood? When does the Rh factor effect blood compatibility? When a ________ type mixes with a _________ Most common in _________ Why is this dangerous? Organ and Tissue Rejection