Blood and the Lymphatic System - TangHua2012-2013
advertisement

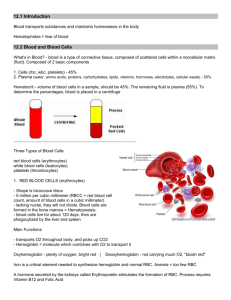
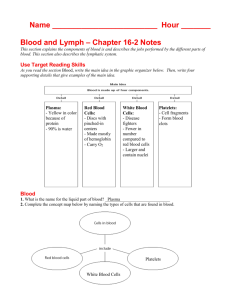
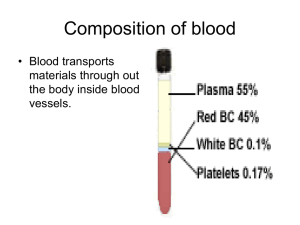
1/6 Blood and the Lymphatic System Inquiry into Life – pg. 226-230, 240-251 Today’s Objectives: Describe the components of blood, including: Describe the shape, function, and origin of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets List the major components of plasma Explain the roles of antigens and antibodies Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the lymphatic system, including: Describe the functions of the lymphatic system Identify and give functions of lymph capillaries, veins, and nodes Components of Blood A) __________: 55% of blood B_________________: 45% of blood _____________ (Red Blood Cells) _____________ (White Blood Cells) _____________ (Platelets) FEATURE RED BLOOD CELLS WHITE BLOOD CELLS SHAPE Variable, Amoeboid FUNCTION ORIGIN PLATELETS Blood clotting Bone marrow Lymphoid Tissue ALSO CALLED Thrombocytes CONSTITUENTS OF PLASMA NAME A. Water (90%) FUNCTION __________________________________________ __________________________________________ B. Plasma Proteins a) Albumen b) Fibrinogen c) Globulins __________________________________________. -___________________________ -___________________________ -___________________________ C. Gases a) Oxygen b) Carbon Dioxide -___________________________ -___________________________ D. Nutrients a) A.A. Glucose, Fatty acids, Glycerol Energy source - _____________________________ 2/6 E. Salts ____________________________ ____________________________ F. Wastes _________________________________________. Shape, Function, and Origin of RBC Red Blood Cells (_______________) Live about 120 days Produced in ______ _______ _____________ (in skull, ribs, vertebrae, and long bones) Myeloid _______ ________ form RBC These stem cells are called Erythroblasts, which will differentiate into Erythrocytes Produce about 5 million/second RBC contain a protein called hemoglobin Old RBC destroyed in the ________ and _________ Hemoglobin Hemoglobin contains _______ (gives its red color) Picks up _________ in the lungs then releases is it in the tissues Approximately ________________ hemoglobin molecules in one RBC If hemoglobin was not packaged in RBC, oxygen would leak out of the circulatory system Shape, Function, and Origin of WBC White Blood Cells (_______________) Larger than RBC Have a __________ (RBC do not) Less numerous than RBC (________) Do not have a definite _________ Function: Fights against ____________ in two ways: ______________ Produce ______________ Types of White Blood Cells Granular Leukocytes (_________________) Have _________, or granules in their ____________ which are filled with enzymes and proteins to fight against microbes Formed in the _________ ____________ 60-70% of Leukocytes Example: ______________ – phagocytize and digest bacteria Agranular Leukocytes (_________________) _____ granules in cytoplasm Produced by ______________ __________ 25-30% of Leukocytes Example: _____________ (phagocytize pathogens and cellular debris) and _______________ (responsible for specific immunity) 3/6 Agranulocytes Monocytes: Largest WBC Take up residence in tissues Differentiate into larger ``_______________`` which phagocytize microbes and stimulate other WBC Lymphocytes: ______________ – produced in bone and lymphoid tissue ______________ – produced in the thymus and give rise to plasma cells Platelets (________________) 2 billion produced/day Broken fragments of larger cells Very important in ________ ____________ Blood Clotting: Need three things in blood: - ______________ - ______________ - ______________ 1) Platelets __________ at the site of the “leak” and partially close it 2) Platelets and the injured tissue together release an enzyme called Thromboplastin 3) Thromboplastin converts a blood protein (Prothrombin) into a new substance called Thrombin 4) Thrombin acts as an enzyme that breaks the ends off another blood protein called Fibrinogen 5) Fibrinogen is then converted into Fibrin 6) Fibrin has sticky ends and forms a lattice or network over the leak where blood cells get trapped, forming a clot 7) Fibrin clot is only temporary – as soon as the blood vessel repair is initiated, and enzyme called Plasmin destroys the network 4/6 Lymphatic System Functions: 1) Takes excess ________ ________ and sends it to the ________________ ___________ (lymphatic system joins the circulatory system at the ______________ _______) 2) Products of fat digestion are absorbed into __________ which lead to the _________ ____________ and __________ 3) Lymph nodes produce _______________ (a type of WBC) and help the body defend against __________ 4) Lymph nodes act as __________ and trap _________ and other _________ (helps to purify the body fluids) Lymphatic Structures ___________: Largest Lymphatic Tissue Produces lymphocytes and stores excess _________ If your blood pressure is _________, stores blood so blood pressure lowers If your blood pressure is ______, it contracts and squeezes out blood, sending it back to the system so that blood pressure rises __________________: Bi-lobed structure which is important In the maturing of _______________ Gets smaller as you age _____________ _____ ____________: Contain lymphoid tissue Thought to help remove invading organisms and viruses _____________ ___________: Produce lymphocytes and stores excess blood __________ ____________: Similar to veins, but fluid only travels in one direction (lymph veins and capillaries, but no lymph arteries) __________ _________: Small oval or round tissues which filter fluids and produce lymphocytes ___________: Sacs in villi of digestive system which absorb products of fat digestion Infection Fighting – Inflammatory Response Foreign Substances (bacteria or viruses) attack Monocytes and Neutrophils engulf the bacteria or viruses in amoeboid fashion (___________) These WBC are able to travel to the site of the infection through ___________ network Dead tissue, cells, bacteria, dead and living neutrophils all together make up ______ Lymphocytes Produce ______________ One antibody fights a specific _____________ (foreign protein) 5/6 Antigen + Antibody ____________ ____________ _______________: A protein found in the outer membrane of _______ Stimulate an _____________ ____________ (production of antibodies) The type of protein determines the _________ _________ Can also be a foreign protein introduced to the body _______________: A protein found in the __________ Attack unwanted proteins (__________ ___ __________) End result is ________________ ABO BLOOD SYSTEM Blood Group A B AB O Proteins on Red Blood Cells (Antigen) Clumping Chemicals in Plasma (Antibody) Can Accept Transfusions from Group(s) 6/6 Rhesus Factor Red blood cells may have another antigen called _________ ____, known as the _________ __________ This distinguishes blood as being ______ or ______. Therefore there are ____ possible blood types.