Earth’s Structure
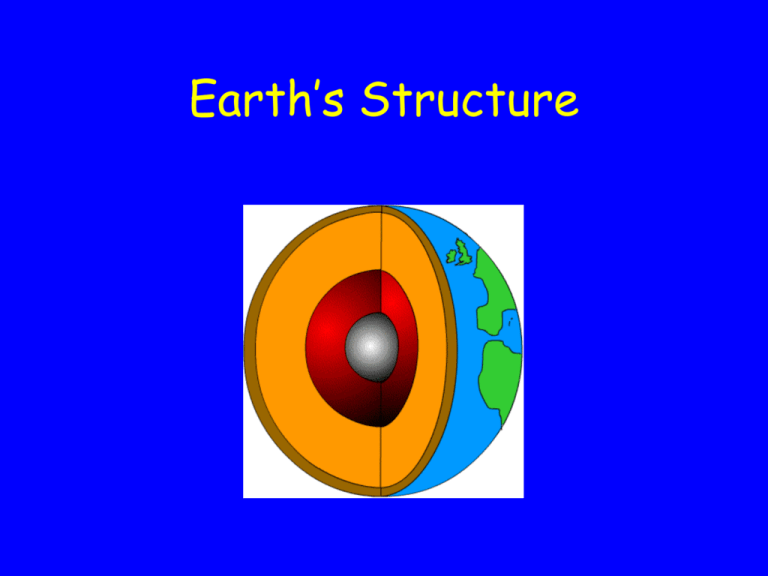
Layers of the Earth
• CRUST
• MANTLE
• CORE
LAYER 1
•CRUST
•outer most layer
•thinnest layer
•consists of loose rocks
and soil
•2 types of crust
•continental-dry land
•oceanic- ocean floor
LAYER 2
•MANTLE
•thickest layer
•carries the most mass
•hot solid rock
LAYER 3 and 4
•CORE
•inner or center layer
•2 parts
•outer coreliquid layer that
contains melted iron
and nickel
•inner coresolid layer that
contains solid iron
and nickel
RESTLESS CONTINENTS
ALFRED WEGENER
THEORY OF
CONTINENTAL DRIFT
•The idea that the
continents were once
part of a giant land
mass.
•The one giant land
mass is called
“PANGAEA.”
WEGENER’S EVIDENCE
•Fossil Evidence
•fossils are remains
of living things that
lived long ago.
•similar fossils have
been discovered in
matching coastlines
on different
continents.
•Mountain Evidence
•some mountain
ranges on different
continents seem to
match.
•mountain range in
eastern Canada
seems to match one
found in Norway and
Sweden.
•Rock Evidence
•The age and kind of
rocks and minerals
along the edge of one
continent match
rocks and minerals
along the edge of
another continent.
THEORY OF PLATE
TECTONICS
•Earth’s lithosphere is
divided into tectonic
plates that are in
constant, slow motion,
driven by convection
currents in the mantle.
CONVECTION CURRENTS
•The movement of a gas
or a liquid caused by
differences in
temperature.
•Hot material from
deep within the Earth
rises while cooler
material near the
surface sinks
Sea-Floor Spreading
• The proof of
sea-floor
spreading
supported
Wegener’s
original idea.
•Sea-floor spreading is the process by
which new oceanic lithosphere is created as
older materials are pulled away.
•Takes place at Mid-ocean ridges.
•Mid-ocean ridges are underwater
mountain chains that run through Earth’s
ocean basins.
Mid-Atlantic
Ridge.
TECTONIC PLATES
•Pieces of the
lithosphere that
move around on top
of the
asthenosphere.
•Carry the
continents, parts of
the ocean floor, or
both.
MAJOR TECTONIC PLATES
•NORTH AMERICAN
•SOUTH AMERICAN
•PACIFIC
•INDIAN
•AUSTRAILIAN
•ANTARCTIC
•EURASIAN
plate movement
•As the plates move,
they produce changes
in Earth’s surface,
including volcanoes,
mountain ranges, and
deep-ocean trenches.
•The edges of different pieces of the
lithosphere meet at lines called plate
boundaries
•FAULTS
•edges of
different
pieces of the
lithosphere
•form at
these
boundaries
DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES
•When two tectonic
plates move away from
one another.
Sea-floor Spreading
•When the plates pull
apart, magma rises
and fills in the gap.
•At mid-ocean ridge,
the rising magma
cools to FORM NEW
OCEANIC
LITHOSPHERE.
Continental Rift
•When two continental
plates pull away.
•The continents form a
RIFT.
Divergent Boundaries
© All Rights Reserved.
Diverging
Africa
Diverging Iceland
CONVERGENT
BOUNDARIES
•When two tectonic
plates push into one
another.
Continental vs. Continental
•When two continental
crustal plates collide,
the continents buckle
upward and form
mountains.
Himalayas- Asia
Oceanic vs. Continental
•The oceanic plate
slides under the
continental plate.
•The continental crust
crumbles and forms
new mountains.
Oceanic vs. Continental
• Ex: Andes mtn in S.
America
Cascade
Mtns. in N.
America- Mt.
Oceanin vs. Oceanic
•Two oceanic plates
collide, one of the
oceanic plates slides
under the other.
•also called a
subduction zone
Oceanic vs.
Oceanic Hawaiian
Islands
TRANSFORM
BOUNDARIES
•When two tectonic
plates slide past each
other horizontally.
•Produce
EARTHQUAKES.
San
Andreas
Fault
New Madrid Fault
WHICH TYPE OF
BOUNDARY?
Rift forming
in Iceland
San Andreas Fault in
California
WHICH TYPE OF
BOUNDARY?








