Plate Movement Power Point
advertisement

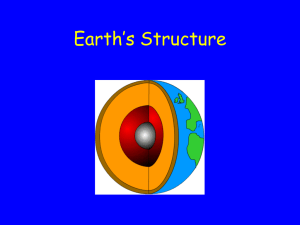
11/18/15 Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move on top of asthenosphere Theory of plate tectonics explains: • Continental drift • Sea-floor spreading Convection • Hot material from deep within Earth rises while cooler material near surface sinks • Motion of convecting mantle drags plates sideways Ridge Push • Occurs at mid-ocean ridges Higher elevation than surrounding lithosphere • Gravity causes the ridge to “push” oceanic plate down the lithosphereasthenosphere boundary Slab Pull • Oceanic lithosphere denser than asthenosphere • Oceanic plate sinks and pulls rest of tectonic plate with it Occurs because of process of subduction Occurs when two plates push into one another Three types (depends on plates involved) • Continental/continental • Continental/oceanic • Oceanic/oceanic Occurs when two tectonic plates move away from one another Results in new oceanic lithosphere (sea-floor spreading) Can also be found on continents East African Rift Occurs when two tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally Plates grind past one another often resulting in earthquakes • Tectonic plates are not San Andreas Fault smooth Movement affected by: • Type of plate Measure motion by use of GPS • Shape of plate • Interaction with surrounding plates Generally slow (few centimeters per year) • San Andreas fault is exception “Stationary” GPS satellites send signals to ground stations • Amount of time taken to receive signal in relation to distance determines rate