Name: Date: Block: ______ Unit 1 Notes – Plate Tectonics I. The
advertisement

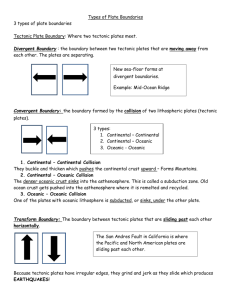
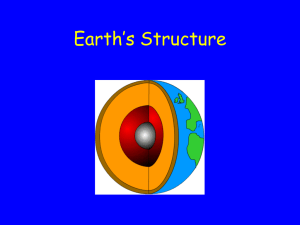
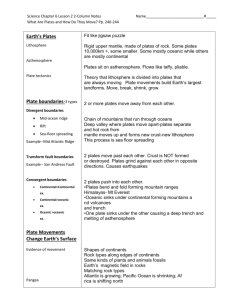
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _______ Unit 1 Notes – Plate Tectonics I. The Changing Marine Environment A. Did the oceans (white area) always look like this? 1. Since their formation, oceans have experienced considerable _________________________. B. Alfred Wegener 1. Studied the close fit between the coastlines of ___________________ and _____________ _______________________________. 2. In ___________ , Alfred Wegener proposed The ____________________________ _____________________ Theory to explain the “jigsaw-puzzle” fit of some continents. 3. This theory proposes that landmasses at one point were part of a super-continent called _______________________________. 4. The main piece of evidence used was how the continents appeared to _____________________________________________________________________________. C. _______________________________ 1. Was a _____________________________ of Alfred Wegener’s theory. 2. Added to the theory that the supercontinent broke into ___________ mega-continents. a. _____________________________ in the North b. _____________________________ in the South D. Current _____________________________________ in support of Alfred Wegener’s theory 1. ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Fossil Records - _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Glacial Till - __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Paleomagnetism - _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ a. Magnetic fields were __________________________on opposite sides of oceanic ridge. 5. Satellite imagery - _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ E. Cross Section of Earth 1. Understanding plate tectonics starts with knowing Earth’s basic _______________________. 2. If you could slice through our planet, you’d find it is made up of ___________ major layers. a. ______________ – made of iron and nickel; inner core is solid and outer core is liquid. b. _________________________ – made of rock; moves like toothpaste c. _________________________– oceanic crust forms the ocean floor; continental crust forms the continents 3. Lithosphere - _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Asthenosphere - ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Lithosphere is broken up into huge rocky slabs called ____________________________ ____________________. 6. These plates are _______________________. They ride along the top of the asthenosphere. F. Tectonic Plates 1. Continental plates are mostly comprised of ________________________________________. 2. Oceanic plates are mostly comprised of ___________________________________________. G. Tectonic Plate Diagram - Use Page 7 in the textbook to label the tectonic plates below. H. Convection – How do these huge slabs of Earth’s crust (a.k.a. tectonic plates) __________________? 1. Diagram 2. Convection - _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Example - Soup that is heated from below rises. When it reaches the top of the pot it moves outward, cools slightly, then sinks downward along the sides of the pot. When it reaches the bottom, it’s heated up again and process repeats. I. Plate Boundaries 1. _________________ ______________________ are places where two or more plates meet. 2. Scientists give the plate boundaries different names based on the _____________________ of the plates. 3. Divergent Boundaries – occurs where plates are moving _________________ and new crust is being formed. a. Oceanic – Oceanic - _____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example: _______________________________________________________________ b. Continental – Continental - _______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example: _______________________________________________________________ 4. Convergent Boundaries – occurs where two or more plates are coming together or _________________________________. a. Oceanic – Continental - __________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example: _______________________________________________________________ b. Oceanic – Oceanic - _____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example: _______________________________________________________________ c. Continental – Continental - _______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example: _______________________________________________________________ d. Transform Boundary - ___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example: _______________________________________________________________ II. The World Ocean A. Oceans cover _________________________ of the Earth. B. Ocean Floor