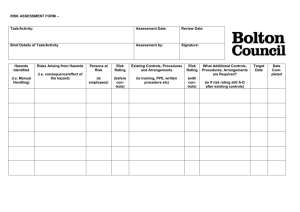
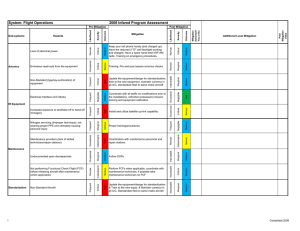
Risk Management
advertisement

Risk Management Risk is the product of – Probability that something will go wrong And – Severity of its consequences How to reduce risk? – Reduce probability that something will go wrong – Reduce severity of consequences Risk Management Failure mode and effects analysis – FMEA involves reviewing as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify failure modes, and their causes and effects. For each component, the failure modes and their resulting effects on the rest of the system are recorded in a specific FMEA worksheet. From Wiki Risks are Everywhere Think of some task you like to get done today – Does it have a clear, specific, and desired outcome? • • • • • Exercise for an hour Get a bearing for the mini project Get some lab report done Endure this class Endure this class without screaming (desired outcome) Think of an overseas travel Think of your capstone project – What are the desired outcomes? Technical Risk Management TRM TRM 4-step Methodology – – – – Risk Identification Risk Assessment Risk Mitigation Risk Monitoring Risk Identification Risk Identification is best done as a group – – – – – Identify the desired outcomes Use brainstorming methods to identify risks Only include meaningful risks Continue until no more risks are identified Keep track of risks as a part of the project plan Risk Assessment Risk Assessment – What are the odds of the risk event occurring • • • • • Rare Unlikely Possible Likely Frequent Risk Assessment Risk Assessment – What are the consequences of the risk event • • • • Catastrophic Severe Marginal (not severe but significant enough) Negligible – In design projects, the consequences are usually in terms of time, budget, and product meeting PDS targets. Risk Scoring Matrix Frequent Likely Possible Unlikely Rare Catastrophic E E H H M Severe E H H M L Marginal H M M L L Negligible M L L L L Risk Assessment Levels of Risk – – – – Extreme – Do not accept level of risk High – Do not accept level of risk Medium – Mitigate if resources allow Low - Accept Risk Mitigation Plan Reducing the probability of failure More knowledge Less Risk – More accurate assessment • • • • Research + Analysis Simulation Experimentation Published studies, statistical data – Design changes Risk Mitigation Plan Reducing consequences of events – More accurate assessment of consequences • • • • Research + Analysis Simulation Experimentation Published studies – Design Changes Example Assessment: • Bolt failure for a fuel tank is initially a probable event and its consequences are catastrophic. Mitigation • Detailed analysis shows it is extremely unlikely. • Further investigation shows consequences are not as severe as initially perceived. OR • Select higher strength or larger bolts • Add features to contain damage in case of failure Example Risk – Magnets stuck to the disk may fly off • Probability: High • Consequences: Severe injury or death – Risk Assessment: Extreme Example – Mitigation (Reducing odds of the event) • More accurate assessment of forces and probability of magnets flying off at maximum 1000 rpm – Conclusions: Very unlikely • Design Changes – Add screws or other retaining parts – Use epoxy – Add speed sensors and automatic cut off Example – Mitigation (Reducing consequences) • More accurate assessment of consequences – Remains catastrophic • Reducing consequences of the event – Add an enclosure – Operate remotely