CMOS Gates
advertisement

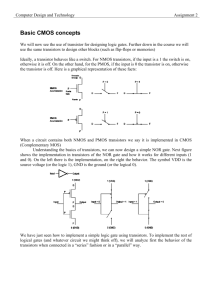
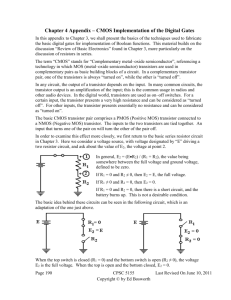
EE 5900 Advanced Algorithms for Robust VLSI CAD, Spring 2009 CMOS Combinational Gate CMOS Combinational Circuits Implementation of logic gates and other structures using CMOS technology. Basic element: transistor 2 types of transistors: n-channel (nMOS) and p-channel (pMOS) Type depends on the semiconductor materials used to implement the transistor. We want to model transistor behavior at the logic level in order to study the behavior of CMOS circuits view pMOS and nMOS transistors as swithes. 18-Mar-16 Combinational Logic PJF - 2 CMOS transistors as Switches 3 terminals in CMOS transistors: G: Gate D: Drain S: Source nMOS transistor/switch X=1 switch closes (ON) X=0 switch opens (OFF) 18-Mar-16 pMOS transistor/switch X=1 switch opens (OFF) X=0 switch closes (ON) Combinational Logic PJF - 3 Networks of Switches Use switches to create networks that represent CMOS logic circuits. To implement a function F, create a network s.t. there is a path through the network whenever F=1 and no path when F=0. Two basic structures: 18-Mar-16 Transistors in Series Transistors in Parallel Combinational Logic PJF - 4 Transistors in Series/Parallel nMOS in Series X a Y a X:X Y:Y b nMOS in Parallel Path between points a and b exists if both X and Y are 1 X•Y a X X Y X:X’ Y:Y’ b 18-Mar-16 a X:X b b Y:Y b Path between points a and b exists if either X or Y are 1 X+Y pMOS in Parallel pMOS in Series a Y a Path between points a and b exists if both X and Y are 0 X’•Y’ a X b Combinational Logic Y a X:X b Y:Y Path between points a and b exists if either X or Y are 0 X’+Y’ b PJF - 5 Networks of Switches (cont.) In general: 1. 2. 3. 4. nMOS in series is used to implement AND logic pMOS in series is used to implement NOR logic nMOS in parallel is used to implement OR logic pMOS in parallel is used to implement NAND logic Observe that: 18-Mar-16 1 is the complement of 3, and vice-versa 2 is the complement of 4, and vice-versa Combinational Logic PJF - 6 CMOS Inverter +V X F = X’ X F = X’ Logic symbol GRD Transistor-level schematic Operation: X=1 nMOS switch conducts (pMOS is open) and draws from GRD F=0 X=0 pMOS switch conducts (nMOST is open) and draws from +V F=1 18-Mar-16 Combinational Logic PJF - 7 Fully Complementary CMOS Networks Basic Gates 18-Mar-16 Combinational Logic PJF - 8 Fully Complementary CMOS Complex Gates Given a function F: 1. First take the complement of F to form F’ 2. Implement F’ as an nMOS net and connect it to GRD (pull-down net) and F. 3. Find dual of F’, implement it as a pMOS net and connect it to +V (pull-up net) and F. 4. Connect switch inputs. 18-Mar-16 Combinational Logic PJF - 9 Fully Complementary CMOS Networks Complex Gates - Example F = (A+B)(A+C’) F’ = A’B’+A’C=A’(B’+C) 18-Mar-16 Combinational Logic PJF - 10