File - Ruawai College Science
advertisement

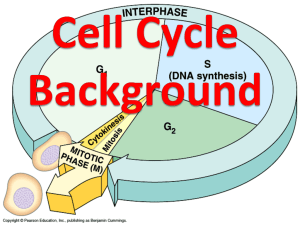
Name: ANSWERS Mitosis Workbook Year 12 Science Ruawai College 2014 Mitosis is the process of cell division for growth and repair of cells. Mitosis produces 2 ‘daughter’ cells that are exact replicas of the ‘parent’ cell. The ‘daughter’ cells are genetically identical to the ‘parent’ cell. All organisms start life as a single cell and growth occurs by cells dividing into two repeatedly. 1. What is mitosis? Cell division 2. When does mitosis occur? For growth or to repair cells 3. How many ‘daughter’ cells are produced from one ‘parent’ cell? 2 4. How many cells are produced after 3 divisions? 8 5. Are daughter cells genetically identical to parent cells? yes 6. Why are all the cells in the diagram above genetically identical? All originated from same cell Before cell division can occur the DNA of each chromosome must be copied. 7. What shape is a chromosome? X shaped 8. How many chromatids are there in a chromosome? 2 9. What is the joining point of the chromatids called? centromere Cells go through a series of stages in a cycle and mitosis is one part of the cell cycle. Although mitosis is a continuous process, certain stages have been recognised and given names. 10. How many stages are in the cell cycle? 8 11. How many stages are in the mitosis? 4 12. What are the names of the stages in mitosis? Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase 13. How many stages in interphase? 3 14. What are the names of the stages in interphase? G1, S, G2 15. What is the name of the stage between mitosis and interphase? Cytokinesis DNA replication occurs prior to cell division during interphase (the time between cell divisions). A cell spends about 90% of its time in interphase – the cell grows, carries out processes such as protein synthesis and production of ATP, and gains nutrients needed for DNA replication and mitosis. 16. Put the stages of the cell cycle in order starting with interphase: Prophase Anaphase Telophase Interphase – prophase – metaphase – anaphase – telophase Interphase Metaphase 17. How much time does a cell spend in interphase? 90% 18. When does DNA replication occur in the cell cycle? Interphase 19. What processes occur during interphase? Protein synthesis, ATP production 20. When does the cell grow? During interphase 21. When does the cell gain nutrients for DNA replication and mitosis? During interphase 22. Put arrows into the diagrams to show the order of the stages of mitosis. Interphase stages G1 S First gap – cell is active with all its jobs (synthesising proteins and enzymes) and the organelles such as ribosomes begin to be duplicated DNA replication occurs G2 Second gap – cell prepares for mitosis 23. What is G1 the abbreviation for? First gap 24. What happens during G1? Proteins and enzymes are made, organelles duplicated 25. What happens during S? DNA replication occurs 26. What is G2 the abbreviation for? Second gap 27. What happens during G2? Cell prepares for mitosis 28. What happens during prophase? Chromosomes become visible Nuclear membrane disappears 29. What happens during metaphase? Chromosomes line up in centre of the cell 30. What happens during anaphase? Chromosomes separate – chromatids go to ends of the cell 31. What happens during telophase? Nuclear membrane reforms During cytokinesis The cytoplasm divides between the two nuclei so two new ‘daughter’ cells are formed. 28. Complete the paragraph using the keywords below: growth biochemical Cytokinesis replication chromosomes microtubule membrane mitosis mitosis interphase chromatids centromere interphase chromatids interphase The cell cycle The cell cycles between interphase and division / mitosis, spending approximately 90% of the time in the interphase and approximately 10% of the time in mitosis . Interphase is the time of growth and biochemical activities eg. synthesis of proteins, DNA and ATP. DNA replication occurs during interphase. At the end of interphase, the chromosomes shorten and thicken and become visible as two chromatids joined by a centromere. They line up at the centre of the cell and then the chromatids are separated to each end of the cell by microtubule contraction. Nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes. Cytokinesis occurs and the two new identical cells that have formed enter interphase. The rate of mitosis is rapid: in periods of growth following tissue damage Some areas are more active in replacing wornout or damaged cells than others: dermis of the skin in humans bone marrow active in forming new red blood cells in plants – root tips, stems, side branches in plants – springtime, seedlings The rate of mitosis can be influenced by temperature, availability of nutrients, presence of cancer-causing agents 29. Outline the main events in the cell cycle. Cells cycle between interphase and dividing . 90% of the time, cells are in interphase – utilising nutrients, carrying out essential processes such as synthesis of proteins and enzymes. DNA replication occurs late in interphase – allowing for chromosome replication. Mitosis ensures each new cell gets a full set of chromosomes, so it can grow and carry out processes during interphase that follows. 30. Draw a series of labelled diagrams to describe mitosis. 31. The rate of mitosis is not always the same. Evaluate the statement above. In your answer, you should include: factors that affect the rate of mitosis stages in the life of an organism when the rate of mitosis is likely to be higher locations in an organism where the rate of mitosis is likely to be higher Identifies and describes factors affecting the rate of mitosis. Eg, temperature, pH, presence of mutagens such as alcohol or radiation, availability of raw materials in the cell. Mitosis is usually higher during periods of growth and repair during infancy /childhood /early development in animals following the breaking of dormancy, and during seasonal growth in plants following damage to the organism when repair of tissue is necessary. Mitosis occurs at a higher rate in areas where most growth or replacement of cells is occurring, such as: root /shoot tips hair follicles bone marrow skin cells mucous membranes etc. Mitosis rates increase in areas of cellular repair, the site of damage. Mitosis rates increase in Cancer cells.