Flashcards - knomi.net

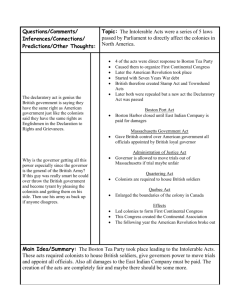
Taxation without Representation
Boston Massacre
Boston Tea Party
Unalienable Rights
Battles of Lexington and Concord,
Saratoga, and Yorktown
Declaration of Independence
Articles of Confederation
Taxation without Representation
Boston Massacre
Boston Tea Party
Unalienable Rights
Battles of Lexington and Concord,
Saratoga, and Yorktown
Declaration of Independence
Articles of Confederation
Proclamation of 1763
Stamp Act
Intolerable Acts
Mercantilism
Lack of representation in Congress
British economic policies following the
French and Indian War
British Parliament law; colonists were forbidden to settle west of the
Appalachian Mountains,
*Britain wanted a buffer zone between the colonists and the Native Americans, but the colonists wanted to settle the fertile Ohio River Valley
Required all legal documents and papers have an official stamp showing that a tax had been paid.
British used this to generate revenue to help cover the cost of the French and Indian
War; colonists reacted by rioting through groups such as the Sons of Liberty;
Stamp Act Congress meets in October,
1765, to take action and ask Parliament to repeal the act
British reaction to the Boston Tea Party
Closed the port of Boston until tea was paid for
Restructured Massachusetts government by taking away local control
Troops were quartered in Boston and British officials accused of crimes were sent to
England or Canada for trial
Colonists reacted by boycotting British goods
First Continental Congress is formed,
September, 1774
A system by which a nation increases its wealth and power by obtaining from its colonies gold, silver, and other raw materials.
It includes a favorable balance of trade.
The colonies became a source of raw materials for the mother country (England.)
The colonies are expected to be the purchasers of manufactured goods from the mother country.
Belief that a colony exists for the economic benefit of the mother country.
Since the formation of the colonies, the colonists had set up their own legislative assemblies.
Colonists were unhappy about Britain’s insistence on the supremacy of Parliament
(taxation).
The debate turned into one regarding representation in Britain’s law-making body
(Parliament).
Britain argued that the colonies had “virtual representation.”
Lawyer and politician
Defended the British soldiers after the
Boston Massacre
A member of the Continental Congress
(representing Massachusetts)
Strong supporter of independence
Member of the committee that wrote the Declaration of Independence
Wife of John Adams
Served as John Adams’ confidant and support while he served in the Continental
Congress, when John and others were considering a declaration of independence.
Abigail reminded him to “remember the ladies”; take care of the women who could not hold themselves bound by laws in which they had no voice.
Advocate for women’s rights.
African American Patriot
Like Paul Revere, he made an all-night ride back from Boston to warn his community to the impending British invasion
Served in the Continental Army
Fought at the Battle of Saratoga
American Patriot
Played a role in many of the events which contributed to the Revolution
Including: Sons of Liberty, organized opposition to the Stamp Act and the
Boston Massacre
Member of the Continental Congress
(representing Massachusetts)
Cousin to John Adams
Wife of a Massachusetts Patriot
Anonymously wrote several propaganda pieces supporting the Patriot cause
*Slave in Virginia
*Marquis de Lafayette recruited him as a spy for the Continental Army.
*Posed as a double agent, forger and servant at British headquarters.
*He moved freely between the lines with vital information on British troop movements for Lafayette
*Contributed to the American victory at
Yorktown.
A member of the committee that wrote the
Declaration of Independence.
*Spent most of the time during the
American Revolution in France.
*He represented the colonies as the
American envoy starting in 1776 and returned in 1785.
*He negotiated the alliance with France for support after the victory at Saratoga.
*Member of the committee that negotiated the terms for the Treaty of Paris in 1783 that ended the war.
Spanish nobleman
*Became governor of the Spanish province of Louisiana (January 1777)
*protected American ships in the port of
New Orleans
*helped transport war supplies
*took up arms to fight the British and protect Louisiana
Polish-born Jewish immigrant to America
Played an important role in financing the
American Revolution
Arrested by the British as a spy
Used by the British as an interpreter with their
German troops
Helped British prisoners escape and encouraged German soldiers to desert the
British Army
Became a broker to the French consul and paymaster to French troops in the American
Revolution
African American male
Unemployed dockworker in Boston, MA
Became the first casualty (first to die) of the American Revolution
Shot and killed in what became known as the Boston Massacre, March 5, 1770
King of England during the Revolutionary
Era
*Feared the loss of one group of colonies would lead to the loss of others and the eventual decline of the empire.
*To prevent this, the Crown maintained an aggressive policy against colonial resistance.
George III struggled to enforce royal authority throughout his reign.
Member of the Virginia House of
Burgesses
Spoke against the Stamp Act
Famous quote, “Give me liberty, or give me death!”
During the American Revolution he served in the Continental Army
Virginian
Early leader in the American Revolution
Delegate to the Constinental Congress in
Philadelphia in 1776
Member of the committee that wrote the Declaration of Independence
Chief author of the Declaration of
Independence
*French aristocrat who joined Washington and his troops at Valley Forge, PA
*Played a leading role in both the
American and French Revolutions
*Respected the concepts of liberty and freedom and a constitutional government
*Commanded forces under George
Washington as a major-general in the
Continental Army
Propagandist
Journalist
In January, 1776, published a pamphlet,
“Common Sense”
Persuaded many Americans to join the
Patriot cause.
Virginian
*surveyor, planter
*a soldier in the French and Indian War
*a delegate to the First and Second
Continental Congresses
*commander-in-chief of the Continental
Army during the American Revolution
Declaring Independence
Writing the Articles of Confederation
Battles of Lexington and Concord
Battle of Saratoga
Battle of Yorktown
Enduring the winter at Valley Forge
Signing the Treaty of Paris 1783
Reaction to King George III’s refusal to acknowledge the colonial requests/demands, “dissolve the political bands” with Britain, provided philosophy for the establishment of the new nation
“…all men are created equal and endowed by their creator with unalienable rights, that among these are life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness”
Listed grievances against the King of England
Written by Thomas Jefferson
July 4, 1776
Second Continental Congress; Philadelphia
Occurred at the Second Continental
Congress
Created a new form of government for the independent colonies
Included one branch – a Congress
Each state had one vote
Created a very weak government with no executive
Lexington and Concord: Shot ‘heard round the world; first battles of the
American Revolution; April 19, 1775
Saratoga: turning point of the war;
France joined the colonists after this victory, tipping the scales in their favor
Yorktown: surrender of Cornwallis to the
British
Winter, 1777
After suffering several defeats, Washington took his army to Valley Forge for the winter of 1777
Outbreak of small pox
Martha Washington came to help care for the men
The men were trained by Frederick von Steuben to become a more professional army rather than militias
Thomas Paine wrote “American Crisis” to encourage the men to stay the course and follow
1783
Peace treaty that ended the American
Revolutionary War and recognized
American independence
Great Britain gave up almost all of its land claims in North America
Boundaries extended to Canada in the north, the Mississippi River in the west, and Florida in the South
Fundamental rights, or natural rights, guaranteed to people naturally instead of by the law.
In the Declaration of Independence,
Thomas Jefferson said these are the right to “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.”
Grievance in Declaration of Independence
Constitution
Taxation without representation
All states have representation in Congress, which sets taxes
King has absolute power
Congress has the power to override Presidential veto
Colonists not allowed to speak out against the King
1st Amendment – Freedom of Speech
Quartering Act forced colonists to house troops
3rd Amendment – No quartering of Troops allowed homes to be searched without warrants
4th Amendment – No unwarranted search & seizure
No trial by jury of peers
6th amendment—Speedy and public trial, by an impartial jury
7th amendment—Right of trial by jury
The concept of refusing to follow laws within a community or ignoring the policies and government of a state or a nation when a person considers the laws unjust.
*Refusing to follow laws considered to be unlawful and/or unconstitutional.
*Examples include boycotts, protests, refusal to pay taxes
*Boston Tea Party is an example of civil disobedience.
Loyalists – these were colonists who remained loyal to the British monarchy and did not feel taxation was a reason to declare independence or break away from the mother country.
Founder of the United States Navy
Led raids on British vessels during the
American Revolution
During a fight with a British vessel he was told to surrender. Instead, Jones said, “I have not yet begun to fight” and was able to defeat the attacking British ship.
Engraving of the Boston Massacre by Paul
Revere
March 5, 1770
Event in which British soldiers fired into a crowd of unarmed citizens of Boston
Killed five
This engraving was used as propaganda to encourage patriotic sympathies and support for American Independence
Paul Rever, a silversmith and engraver, was also a member of the Boston Sons of Liberty
Song sung by British military to mock the unorganized colonial “Yankees” who served in the French and Indian War with
British soldiers.
*The meaning of the song implies that the Americans are so “simple” they think simply sticking a feather in a cap would make them fashion leaders.
*Fighting between the British and the French for control of North America.
*Allies of the French were the Native Americans, or
Indians.
*Broke out in the Ohio River Valley in 1756. Throughout the world it was known as the Seven Years’ War
*Ben Franklin suggested that the colonies join together to fight against the French in the Albany
Plan of Union.
*This was the first attempt to unify the colonies
*French and Indians were defeated.
* British became in debt because of the war and taxed
Year in which representatives of the
Virginia Company of London established the first permanent English settlement in
North America at
Jamestown, Virginia.
First written constitution in the colonies; document that people had the right to elect governors, judges, and a legislature. Was written by the people; the fact that it was written down gave the document credibility.
Written in 1620 by male Pilgrims on the
Mayflower. Created government where none had existed based on majority rule.
A social contract where all agreed to abide by these rules in the colonies.
Economic theory in which a nation’s wealth is based on the amount of revenue is generated from its colonies.
The more gold and silver a nation has determine its wealth.
The buying and selling of millions of Africans to North America.
Trade route from:
Europe→Africa
Africa→West Indies
West Indies→Europe
System of agricultural production based on large scale landownership; depended upon slave labor; Assisted in the development of an agrarian society in the South
First elected body of representatives in the American colonies; met in
Williamsburg, Virginia.
Based on Parliament.
Along the Atlantic Coast
Subsistence farming
Poor soil
Cold climate
Forests
Economic factors: raw materials, logging, fishing shipbuilding
Political factors: town meetings, representative government
Social factors: small coastal towns (Boston only large city)
Religious factors: Puritans, Pilgrims
Rich soil
Broad, deep rivers
More natural ports
River valleys
Mild winters
Raw materials
Economic factors: large farms, logging, fishing, shipbuilding
Political factors: more tolerance; diversity
Social factors small coastal towns (Philadelphia,
Baltimore, New York were large cities)
Religious factors: Quakers, Catholics
Appalachian Mountains
Navigable rivers
Richer soil
Warm climate
Raw materials
Economic factors: plantations, cash crops, tobacco, rice, cotton
Political factors: more slaves, more class-based society
Social factors and small coastal towns (Savannah,
Charleston were large cities)
Religious factors: Church of England, Catholics
(Maryland), more diverse
Physical geographic factors – proximity to Atlantic coastline determined where settlements/colonies were created
The NewEngland Middle colonies had access to waterways that resulted in high population and larger urban areas.
Southern colonies had an abundant amount of fertile soil that resulted in an agricultural society
Human geographic factors – removal of the Native Americans, disease and conflict (ex. Georgia as a buffer between the other
British colonies and Spanish Florida)
Religious movement in the 1730s and 1740s.
Preached personal salvation as opposed to the Puritan beliefs of pre-destination.
JONATHAN EDWARDS – one of the best known preachers of the time – his sermon,
“Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God” urged believers to develop a personal relationship with God.
This movement revitalized American religion by adding emotion. The Abolitionist
Movement began in response to the Great
Awakening.
First written constitution in the colonies; document that people had the right to elect governors, judges, and a legislature. Was written by the people; the fact that it was written down gave the document credibility.