Experiment 22':
advertisement

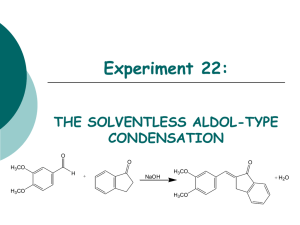
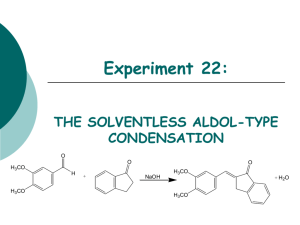
Experiment 22: THE SOLVENTLESS ALDOL-TYPE CONDENSATION O O O H3CO H H3CO + NaOH H3CO + H2O H3CO Objectives: To synthesize an a,b unsaturated ketone from an aldehyde and a ketone using solvent-free conditions. To purify the product through a recrystallization. To identify and analyze purity through TLC and melting point analysis. To analyze the product using IR and NMR spectra. Before coming to lab… Review these techniques: Recrystallization TLC Analysis Melting Point Analysis ALDOL CONDENSATIONS Aldol condensations are nucleophilic additions of an enolate ion, which are strong nucleophiles, to another C=O group under basic conditions. Protonation gives the aldol product. Once formed, the aldol product undergoes dehydration in base. Abstraction of an a proton gives an enolate that can expel an –OH ion to give a conjugated product. Dehydration is usually exothermic because it leads to a very stable conjugated product. H H C O b C CH3 Ca H CHEMICAL EQUATION O O O H3CO H + NaOH H3CO 3,4-dimethoxy benzaldehyde H3CO + H2O H3CO 1-indanone Aldol Product MECHANISM Base removes a proton to form enolate ion. O O resonance -H2O H O H + NaOH H H O Resonance stabilized enolate forms carbanion, which attacks C=O of aldehyde OH O H + H O O + H2O H C H O O When new C-C bond forms, C=O p bond breaks, electrons stay with oxygen. H O O -OH O O H OH -OH O + NaOH + H2O -H2O C H O O O H Oxygen anion removes proton from water, releasing –OH. Acidic a proton is removed by –OH. Electrons form new p bond. TYPICAL ALDOL CONDENSATION A typical aldol condensation reaction is carried out in an organic solvent, such as ethanol, requiring eventual waste disposal. Isolation of the product requires a much more involved work up, not to mention the hazards to the experimenter and the environment due to waste disposal. Another challenge is that solution phase reaction is reversible, so low product yields may result. GREEN CHEMISTRY CONCERNS One of the main themes of greener chemistry is to cut down on the use of solvent, and hence cut down on solvent waste. The best way to do this is simply not to use any solvent at all. Workup is generally easier since as the reaction proceeds, the product separates from the melt as a solid, making work up much less complicated. Another benefit is that unlike a solution phase reaction, the solid-state reaction is irreversible, resulting in higher chemical yields. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis) Place aldehyde and ketone in large test tube. Crush solids with glass rod until liquefied. Add NaOH. Mix and scrape sides of test tube until pale green solid forms. Continue to react for 15 minutes at room temperature. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Purification and Product Isolation) Place test tube in a 90oC water bath. Add 90:10 PROPANOL/WATER and heat until solid dissolves. Suction filter. Transfer solid to PREWEIGHED WATCH GLASS AND PLACE IN OVEN 15 MINUTES to dry. Obtain final product mass and calculate % yield. Proceed to PRODUCT ANALYSIS (TLC, mp, IR). Table 22.1 Determine limiting reagent first, before calculating theoretical yield. Theoretical yield (g) Actual yield (g) % yield Melting range (oC) Product Appearance Record Ti-Tf range. Compare to literature value to determine purity of product. Record the physical state and color of product. Table 22.4 Atom Economy Experimental Atom Economy E product Cost per Gram Calculate based on reactants ONLY! Review Experiment 13 for calculation. Calculate based on reactants ONLY! Review Experiment 13 for calculation. Review Experiment 13 for calculation. Calculate COST PER SYNTHESIS 1st based on reactants and catalyst. Table 22.2 TLC Rf values Compound 1-indanone 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde Aldol Product Standard Sample Rf values are UNITLESS! Rf values are 2 decimal places ONLY! Product Analysis (IR) Table 22.3 Functional Group Base Values (cm-1) sp3 CH stretch 2800-3000 sp2 CH stretch 3000-3100 C=O stretch 1680-1740 C-O stretch 1000-1200 aromatic C=C 1500-1600 stretch (2) aldehyde CH 2700-2800 stretch (2) 1-Indanone 3,4-dimethoxy -benzaldehyde Aldol Product Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) SAFETY CONCERNS Solid NaOH is very corrosive! Immediately flush skin with water if any gets on your skin! Propanol is very flammable! Use extreme caution during purification! WASTE MANAGEMENT After final mass is determined, and small amount of product has been set aside for further TLC and mp analyses, place product in container labeled “Aldol Product”. Pour all liquid waste into bottle labeled “ Organic Waste (Aldol)”. Leave TLC chambers with lids off in your lab drawer. Place all used TLC capillaries and melting point capillaries in broken glass container, NOT TRASHCAN! CLEANING Clean all glassware with soap, water, and brush, followed by a rinse with wash acetone before returning to lab drawer. DO NOT return any glassware to lab drawer dirty or wet!