Sharrieff_Taiga(Boreal forest)
advertisement

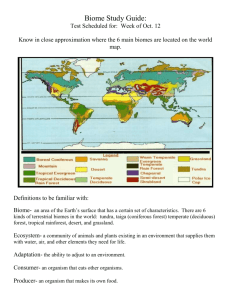
By: Sharrieff Walker aka ReefSqd. • A biome is the type of habitat in certain places, like mountain tops, deserts, and tropical forests, and is determined by the climate of the place. The taiga is the biome of the needleleaf forest. Living in the taiga is cold and lonely. • The Siberian Taiga is a vast forest in the northern regions of Russia covering hundreds of thousands of square miles. Most of the year, it is a very cold place, with low temperatures dropping to -80 F. There is a short, but very hot summer with temperatures going up to 105 F, but the average temperature during the year is below freezing. Due to the prevailing cold, the ground of the Taiga is covered with permafrost. Permafrost is a layer of soil that it always at or below freezing. It is not necessarily covered with sheets of ice, but water particles within the soil are not liquid, but small ice crystals. This makes the soil as hard as rock, and prevents small plants like grasses and shrubs from forming roots in the topsoil. There is a fair amount of precipitation, but it is usually in the form of snow, not rain. These cold conditions create a unique vegetative habitat that is not found in warmer regions on the planet. • The Coniferous Forest aka Taiga is in Dark Green The taiga is located between 50 degrees latitude north and the Arctic circle. • The Eastern Siberian stretching over 20degrees of Latitude and 50degrees of Longitude ( 56 degrees north to 58 degrees north, and 30 degrees east to 80 degrees east.) (Wikipedia) • Siberian/Russian Taiga climate varies on the different things, such as the seasons of the Year. In the winter, the lowest temperature is -65 degrees F. the highest is 30. In the Summer the lowest temp. is 30 degrees F. the highest is 70 Most of the forest consists of different species of Larch, which is a genus of coniferous (cone-bearing) trees. Larch trees are not evergreens, but are deciduous, which means they loose their needle-shaped leaves during parts of the year. These trees are very tall and thick, blocking a lot of sunlight from reaching the forest floor. Aside from larches and other coniferous trees, there is little vegetation due to the permanently frozen soil. Arboreal Lichens, Berries( blueberries, raspberries', cranberries, crowberries) Mosses(reindeer moss, club moss) Dwarf Willow, Wild Lilly of the Valley, Shinleaf, Twinleaf, Aspen • Humans, Owls, Artic Fox, red fox, weasels, Marten, Sables, Fishers, Coyotes, Grizzly Bears, Black Bears, Lynx, Wolves, Grouse, Woodland Caribou, Beaver, Voles, Snowshoe Hares • ADAPTATIONS • One adaptation that animals have is Hibernation. They get ready for the winter by storing extra fat layers on their bodies to keep warm. • Another adaptation is changing their food diet in the summer • Parasitic: The Tent caterpillar and trees. These caterpillars eat about 20% of small trees and spread into tents. • Mutualistic: Lichens and the black Spouse tree. The spouse tree produces dead matter and the lichen feed on it. the tree will be clean and lichens have food • Communalistic : Tree and squirrel. Tree's provide bark for the squirrel to hide from predators in. • A critical threat to the taiga is poaching of animals for skins and bones to sell in international markets. This most directly affects the Siberian Tiget, for these tigers only live in the Primorski Krai and Khabarovsk Krai regions of eastern Siberia. Sadly, there are only 200-300 still in existence today, which proves the deastating effect of poaching on their tiger population • Siberian Tiger This species of tiger is endangered because of the numerous illegal poachers using them for their fur. They are being taken and put into captivity to try and breed. Also known as Captive Breeding. • http://www.bu.edu/gk12/olga/EastSiberianTaiga.htm