Ecosystems (Powerpoint)
advertisement

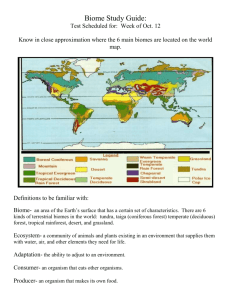
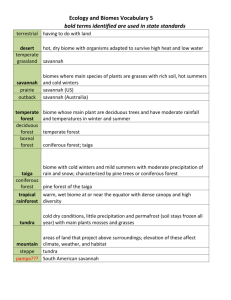
A system is a set of connected things or parts which link together to make it work. There are inputs, processes, stores and outputs. Flour, water, yeast, butter, salt Mixing Baking Dough Mixture Bread An ecosystem is a community of living things, plus the non-living things they need. Living things e.g. plants and animals are known as BIOTIC. Non-living things e.g. climate, relief and soil are known as ABIOTIC. Parts of the ecosystem are linked together. Climate Vegetation Living Creatures Soil Figure 1. A simple ecosystem Processes Reproduction Photosynthesis Decay Inputs Solar Radiation Water Nutrients Oxygen Recycling of nutrients Outputs Evaporation Oxygen There are a number of different scales that ecosystems can exist at. MICRO – Small e.g. a plant, or a pond MESO – Medium e.g. a forest. There are also large ecosystems normally called BIOMES e.g. Tropical Rainforest. Within an ecosystem there is a complex system of energy flows. This can be shown within a food chain or food web. PRODUCER – Tree PRIMARY CONSUMER – Herbivore SECONDARY CONSUMER – Carnivore TERTIARY CONSUMER - Carnivore What would happen if your top predators died? How does BIODIVERSITY influence the stability of an ecosystem? How are humans influencing this? SUSTAINABILITY IS THE KEY! Tropical rainforests are located in a band around the equator, mostly in the area between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N latitude) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S latitude). This 4800 km wide band is called the “tropics”. Tropical rainforests are found in South America, West Africa, Australia, southern India, and Southeast Asia. Savannas are located in Africa, Madagascar (an island off the east coast of Africa), Australia, South America, India, and the Myanmar-Thailand region of Southeast Asia. A savanna is a hot, seasonally dry grassland with scattered trees. This environment is intermediate between a grassland and a forest. Savannas are located in the dry tropics and the subtropics, often bordering a rainforest. Savannas have an extended dry season and a rainy season. The animals that live in savannas have adapted to a great deal of variability in the food supply throughout the year; there are times of plenty (during and after the wet season) and times of almost no food or water (during the dry season). Many savanna animals migrate to deal with this problem. Many animals live in savannas, from invertebrates (like grasshoppers, termites, and beetles) to large mammals (like lions and leopards). The different savannas of the world support different populations of animals. The coniferous forests are located in the northern hemisphere and stretch across the North American, Europe, and Asia continents. These coniferous forests are also known as the "taiga" or "boreal" forest. The trees that make up the forest are cone-bearing trees like the pine, fir, spruce and hemlock. These evergreen trees have needlelike leaves that keep their green color all year long. These trees have a shallow root system. The coniferous forests have short warm summers and long, cold winters lasting up to seven months. The coniferous forest or taiga (the word the Russians use for coniferous forest) is located in the northern latitudes. It is mainly located in Canada and the upper parts of Asia and Europe. The coniferous forest gets the name coniferous because the main type of vegetation located in it is conifers such as pines. There are also a variety of animals such as caribou, black bears, and lynx. The taiga is located in the northern parts of Alaska, Canada, Asia, and Europe. The taiga is wrapped in a band around the world and has the tundra above it and the deciduous forest in the parts below it. This means that the tundra is at a latitude that is farther away from the equator then the taiga is and the deciduous forest is closer to the equator then the taiga is. The animals of the coniferous forest have special adaptations to help them survive the long cold winters. Animals such as the ermine, snowshoe hair and the ptarmigan use camouflage to blend in with the environment and hide from predators. Many birds migrate to warmer places and return to the forest to feed on insects and nest during the summer months. Several of the larger mammals (mule deer, elk, bighorn sheep) also migrate to find warmer temperatures and food. While other animals (bears, marmots, ground squirrels, and other small mammals) eat large amounts of food before they hibernate. The main trees that inhabit the coniferous forest are the pines and other trees like it. The reason that these trees are there is they have needles that stay on them all year round. Almost all of the trees in the taiga also produce cones, thus they have the species name conifer. The climate of the taiga is very cold and dry but not as much as the tundra is. The taiga gets between 25-75 cm of rain per year. The taiga has cold snowy winters and warm summers. Also most of the precipitation comes in the summer months. Some other things about the climate of the taiga is that the average temperature is below freezing for six months of the year. maquis garigue Maquis The Amazon (uses, consequences of deforestation) Sustainable forestry in Malaysia (good practice) The Sahel (soil erosion)