14.3 Art and Culture in the High Middle Ages
advertisement

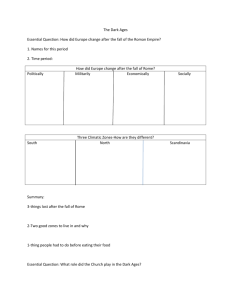
The High Middle Ages Section 3 Art and Culture of the Middle Ages Preview • Main Idea / Reading Focus • Visual Arts • Literature • Thinking and Learning • Faces of History: Thomas Aquinas The High Middle Ages Section 3 Art and Culture of the Middle Ages Main Idea During the Middle Ages, great achievements were made in the visual arts, literature, and thinking and learning. Reading Focus • What were the major achievements of the visual arts during the Middle Ages? • What were the great literary works of the Middle Ages? • What new developments were made in medieval thinking and learning? Section 3 The High Middle Ages Visual Arts Many art historians consider the Cathedral of Notre Dame in Paris to be one of the finest artistic achievements of the Middle Ages. Like most art in the Middle Ages, it was created as a symbol of God. Gothic Architecture Engineering Airy Feeling • Some of greatest examples of religious feelings found in churches • Gothic designs possible through advances in engineering • Flying buttresses allowed higher ceilings, eliminated columns • Built in new Gothic style • New type of support, flying buttress • Larger windows possible • Taller, brighter than previous churches • Supported walls from outside • Stained glass showed Biblical scenes, saints The High Middle Ages Section 3 Decorations • Cathedrals lavishly decorated • Statues of saints, kings, figures from Old Testament • Exterior had gargoyles, spouts to drain rainwater from roof • Many gargoyles carved into likenesses of hideous beasts Adornments • Walls painted with elaborate murals of religious scenes • Candleholders, crosses, statues intricate works of art • Many decorated with gold, precious stones • Clothes of priests heavily embroidered, woven with gold threads Section 3 The High Middle Ages Visual Arts Illumination • Religious texts richly decorated by illumination, decorating manuscript with pictures, designs • Illuminators brought pages to life with scenes from manuscript; painted plants, animals, people • Decorated the first letter on a page, making it large, colorful, and flowing Tapestry • Most medieval art religious; some showed daily life, history • Tapestries, large woven wall hangings, hung in castles to prevent drafts • Many tapestries show scenes from daily life, fantastic creatures, unicorns, dragons • Bayeux Tapestry, story of William the Conqueror The High Middle Ages Section 3 Find the Main Idea What were three forms of medieval art? Answer(s): architecture, illumination, and tapestries Section 3 The High Middle Ages Literature Writers from the Middle Ages produced works that covered a wide spectrum, including religion, romance and epic adventures. Religious Texts Songs and Poems • Many writings dealt with religion • Medieval writers created religious songs, poems • Few people other than monks, priests could read or write • Hildegard of Bingen, famous poet, nun • Range of works • Wrote dozens of poems, music to accompany them – Sermons on how to live – Interpretations of Bible passages – Lives of saints • Widely read by nobility, clergy • Hildegard, other writers, used Latin, language of Roman Catholic Church Section 3 The High Middle Ages Literature Literature included epics, romances • Long poems, stories of heroes, villains, written in language people spoke every day • Epic Poems – Tell tales related to war, heroes – The Song of Roland, Charlemagne’s fight against Muslims in Spain • Romances – Tell tales of true love, chivalry – Many tell stories of King Arthur and knights of Round Table • Epics, romances often performed by troubadours Section 3 The High Middle Ages Major Works Canterbury Tales • Geoffrey Chaucer’s collection of stories • Group of pilgrims traveling to Canterbury; each tells story to entertain others • Characters give insight into what life was like in the Middle Ages The Divine Comedy • Dante Alighieri’s story of his imaginary trip through the afterlife • Composed in three parts, or cantos • On journey, met people from own life, as well as figures from history Contributions • Chaucer helped increase use of written English language in England, where many had been speaking French • Dante’s writing shaped development of Italian language for centuries Section 3 The High Middle Ages Summarize What subjects did medieval authors write about? Answer(s): religious subjects; heroes, villains, love; chivalry Section 3 The High Middle Ages Thinking and Learning New Ideas • Religious writers of Middle Ages spread new ideas throughout Europe • New ideas gave rise to new ways of thinking and learning Constrictions Alchemy • People in Middle Ages curious about how world worked • Began to conduct scientific experiments in alchemy, early form of chemistry Great Secrets • Experiments constricted by reliance on authority of Greek writers • Alchemists convinced they could find way to turn base metals into gold, but could not • Also by teaching of the Catholic Church • Work in alchemy influenced later growth of science Section 3 The High Middle Ages Universities • Growth of European universities influenced by Islamic scholarship • Blending of European, Islamic cultures led to translation of Aristotle, other Greek scholars, from Arabic into Latin • European scholars exposed to new ideas • Universities taught mainly religious courses first, but later broadened scope to include medicine, law Thomas Aquinas • One of most influential medieval scholars, Thomas Aquinas • Keenly interested in works of ancient philosophers, especially Aristotle • He tried to use Aristotle’s methods of logic to prove existence of God Teachings • Aquinas’ use of intellect and logic to bring together opposing ideas became known as Scholasticism • Teachings helped expand former ways of thinking, understanding • New methods helped Europeans place themselves in wider world The High Middle Ages Section 3 Section 3 The High Middle Ages Analyze How did thinking and learning change in the Middle Ages? Answer(s): experiments in alchemy; universities appeared; Aquinas's development of Scholasticism