Unsaturated hydrocarbon reactions worksheet (addition reactions
advertisement

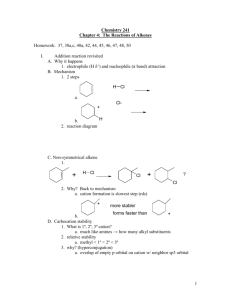
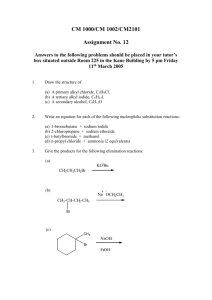
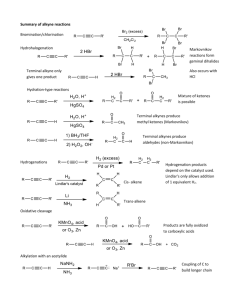
Unsaturated hydrocarbon reactions worksheet (addition reactions) For the following reagents, determine the: type of reaction, (hydrohalide addition, nonpolar (halogen) addition, hydrogenation, hydration (acid catalyzed addition of water), free radical addition), whether a carbocation is formed or not, if its syn/anti addition, or Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov. H-Cl HBr/ROOR (peroxide) X2/CCl4 H2/Pt, Pd, or Ni H3O+ Cl2/AlCl3 Dilute H2SO4 Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Name/Description: Markovnikov/anti-Markovnikov: Syn/anti- addition: Carbocation formed? Predict Products for each of the following. If there is more than one possible product, show all possible products, but identify the major product. The acid-catalyzed hydration of 1-methylcyclohexene gives 1-methylcyclohexanol. Draw the complete step-by-step mechanism for this reaction. Show the complete step-by-step mechanism for the addition of HBr to 2-methyl-2-hexene. If there is more than one product, include them, identifying the major product. When 2-methylpropene reacts with water and an acid catalyst, only one product alcohol is observed: (2-methyl-2-propanol). a. Draw the structures of the two intermediate carbocations that could form from the protonation of 2-methyl-propene. Which is more stable (has lower energy)? b. Draw the mechanism for this reaction show the formation of the more stable product.