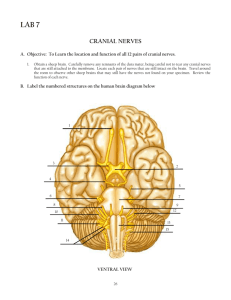
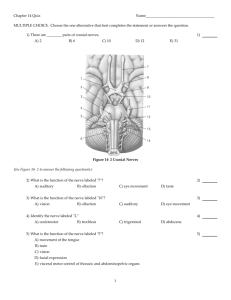
Two VIPs cranial nerves?
advertisement

Chapter 12 Blumenfeild Abdullah Al-Salti R3 29 September 2010 Surface features of the brainstem • What structures form the Tectum of midbrain? • To which parts of the brainstem the cerebellum attach? • In cross section how will differentiate between rostral and caudal medulla? • Name three structures within the floor of the 4th ventricle? • Which nerves commonly affected in cerebellopontine lesions? Skull foramina and cranial nerve exit points. 1. Two VIPs cranial nerves? 2. Mention 2 vital skull foramina anatomically and pathologically important? Sensory and motor organization of the cranial nerves . • Similarity between spinal cord and cranial nerves? • Outline the classification of cranial nerve nuclei into sensory and motor includes: Columns, nuclei, cranial nerves and functions? • What is occipital somites and branchial arches? • Name 4th parasympathetic cranial nerves nuclei and out line their functions? • What are the differences between nucleus ambiguous and solitaries nucleus? • Mention 3 cranial nerve nuclei with multiple C.Nv inputs?SAT Functions and course of the cranial nerves • Classify cranial nerves into pure motor, sensory and mixed? • Outline the function of the mixed (sensory and motor) cranial nerves in functional categories and functions? • Regarding the tongue, which are the cranial nerves contribute for sensation and taste? Peripheral sensory and parasympathetic ganglia. • Which cranial nerves have peripheral ganglia? • Name the parasympathetic ganglia with each cranial nerves? CN: V Trigeminal • What is gasserian ganglion and where is it located? • Remember (SRO) single room occupancy! • Mention others sensory area innervated by CN V? • All primary sensory neurons nuclei located peripherally except one neuron what is it? • What are the muscles innervated by V nerve? • Compare between trigeminal and spinal sensory system? either by diagram or table? • Draw the monosynaptic jaw jerk reflex (including UMN control)? Trigeminal Neuralgia Clinical features. Examination. Differential diagnosis. Managements. Other causes of trigeminal nerve lesion? Case 1.1 PATIENT PRESENTATION 50 years old male ,admitted with GBS Received 5 doses of I.V IgG.He developed acute chest pain with severe facial pain. His neurological exam : no new findings. Labs: Troponin: 0.1 then 0.9 Chest x-ray: normal ECG: Case 1.1 Differential diagnosis? How can you explain his severe bilateral facial pain ? Case 1.2 PATIENT PRESENTATION A 51-year-old woman saw an ophthalmologist because she noticed her left eye seemed to be bulging out increasingly for the past 3 to 4 years, and she had recently developed left-sided headaches. KEY SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS Left-sided headaches Left proptosis Decreased sensation to touch and pinprick over the left cheek Case 1.2 • RELEVANT ANATOMICAL & CLINICAL CONCEPTS – Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) – Skull Foramina Serving as Cranial Nerve Exit Points – Differential Diagnosis? Case 1.2 FINAL DIAGNOSIS Meningioma in region of left foramen rotundum extending into left orbit OUTCOME Meningioma was resected neurosurgically leading to complete recovery.