CRANIAL NERVES
advertisement

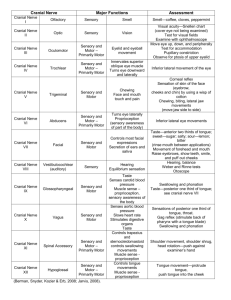
CRANIAL NERVES I, II, IV, VI, VIII, XI, XII Modalities SSS: Special Sensory: Special senses derived from ectoderm: Sight, sound, balance. SVS: Special Visceral Sensory: Special senses derived from endoderm: Taste SVM: Special Visceral Motor: Muscles derived from pharyngeal arches. Modalities GVS: General Visceral Sensory: General sensation from viscera. GVM: General Visceral Motor: To smooth muscles of gut tract. Autonomic motor GSS: General Somatic Sensory: General senses from ectoderm (skin). GSM: General Somatic Motor: Skeletal muscles. Generalizations Cranial nerves have same basic structure as spinal nerves. Dorsal root and ventral root. Dorsal root ganglion. Motor components of cranial nerves begin within brain within motor nuclei. Comparable to spinal cord anterior horns. Cell bodies of sensory fibers are located in dorsal root (cranial) ganglia. Generalizations Special sensory cranial nerves: Are actually tracts. No motor nuclei and no sensory ganglia. Motor cranial nerves: Begin in cranial motor nuclei. Have no sensory roots and no sensory root ganglia. Mixed cranial nerves: Have both cranial motor nuclei and sensory ganglia. Sensory ganglia are usually given specific names. Generalizations For each cranial nerve know: Modality (modalities). Function (functions). Sensory areas and/or muscles innervated. Foramen through which it passes. Specific ganglion (if applicable). Specific information included in this slide presentation. Olfactory Nerve (CN I) Olfactory nerve fibers pass from: Olfactory receptor cells. Through: Cribriform plate. To: Olfactory bulbs. Modality: SVS Optic Nerve (CN II) Begins in ganglionic layer of retina (not rods and cones). Exits orbit through optic canal. 50% decussation in optic chiasma: Near pituitary gland. Near internal carotid. Modality: SSS Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) Supplies four of the six extrinsic muscles of the eye. Has a parasympathetic component. Will be discussed in a group with other parasympathetic nerves. Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) Enters orbit through superior orbital fissure. Innervates superior oblique muscle of the eye. Modality: GSM. Only crossed cranial nerve. Only cranial nerve that emerges dorsally. Abducens Nerve (CN VI) Enters orbit through superior orbital fissure. Lies on medial aspect of lateral rectus muscle. Innervates lateral rectus muscle of the eye. Modality: GSM. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) Leaves cranial cavity via internal acoustic meatus: Accompanied by facial nerve. Modality: SSS Auditory (cochlear) component: Cell bodies in spiral ganglion of cochlea. Function: Hearing. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII) Vestibular component: Cell bodies in vestibular ganglion. From receptors for balance and equilibrium. Function: Balance. Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) Arises from C1-3 (4). Single trunk enters cranial cavity through foramen magnum. Temporarily joins cranial root. Cranial roots leave with vagus nerve. Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI) Spinal accessory trunk exits cranial cavity via jugular foramen. Supplies: Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius. Modality: SVM. Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII) Exits cranial cavity via hypoglossal foramen. Descends anteriorly in neck between internal carotid and internal jugular. In neck gives rise to superior root of ansa cervicalis and a nerve to thyrohyoid muscle. Supplies extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of tongue. Modality: GSM.