Chapter 2
advertisement

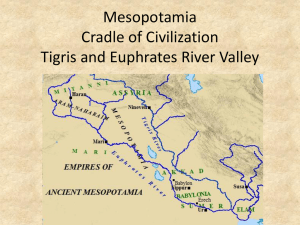
Chapter 2 Early Societies Mesopotamian Society • Land between the rivers • Tigris and Euphrates Rivers • Modern day Iraq • Irrigation system • Defensive walls • Kings ruled in cooperation with nobles Sumer: First Major Mesopotamian Civilization Sumerian City States • Center of political and military authority • Economic center • Cultural center • Educational center • By 3000 BCE, Ur, Erech, and Kish were the major city-states of the first civilization of Sumer Sumer • Developed form of writing known as cuneiform. • Introduction of the wheel • 12 month calendar and math system based on units of sixty – helped develop arches and columns. • Polytheistic; each city state had its own god that was worshipped by its people. Plus common gods. Ziggurats: stepped pyramids associated with Sumerian cities Babylon • 1700 BCE – Sumerian king Akkad was overrun by the Babylonians. • King Hammurabi developed an extensive code of laws that dealt with every part of daily life: • Code of Hammurabi: begins the “rule of law” Code of Hammurabi Mesopotamia changes hands • 1500 BCE – Hittites dominated the region. They became a military superpower. • Assyrians used iron to defeat the Hittites. Then they established their capital at Nineveh and built an empire that swept across the entire Fertile Crescent. • Assyrians were defeated by the Medes and Chaldeans. Chaldean King Nebuchadnezzar rebuilt Babylon, but were taken over by the Persian Empire. Persian Empire Height of Persian Empire was around 500 BCE To improve transportation and communication across the vast empire, Persia built a series of long roads. The longest was the Great Royal Road. 1,600 miles from the Persian Gulf to the Aegean Sea. Lydians, Phoenicians, and Hebrews • Societies existed within the Persian Empire. • Lydians came up with the concept of using coined money. • Phoenicians developed an alphabet system with 22 letters, much less complex than cuneiform. • Hebrews were the first Jews, known for their monotheistic beliefs and establishment of Israel.