Lect 7 Neo-Assyrian and Persian Empires
advertisement

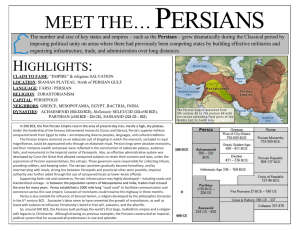
First Empires I. From States to Empires II. Neo-Assyrian Empire, 911-612 BCE III. Persian Empire, 559-331 BCE IDs: Forced Assyrianization, Ashur, Royal Road, eyes and ears Empires: Argument Faced with the same problem of controlling a large multi-ethnic empire, the Neo-Assyrians tried to assimilate subject peoples by force, while the Persians used lenient multi-ethnic policies to attract the support of subject peoples. I. From State to Empire A. CulturesStates (ca. 1500 BCE) States: Union of kingship & religion Nomads Charioteer elites in new states Problems for Kings: *Control of Conquered People Control of Regional Elites Biggest problems of early kings: How to control regional elites (nobility), governors & army leaders Differences between states and empires State Empire Medium to large Very large (whole region) Many ethnic groups, societies, former states One ethnic group (or at most a few) II. World’s First Empire: Neo-Assyria, 911-612 BCE A. Expansion Military Power B. Terror C. Deportation & resettlement of subject populations • Destroy identity Forced “Assyrianization” • Slave labor • Remove trouble D. Annual Appointment of Provincial Governors • Tiglath Pileser III • Abolished hereditary system • Control from center • King gives rewards to new elite E. Ideology & Propaganda • Divine destiny • Ashur • Holy war F. Fall of Neo-Assyrian Empire III. Persian Empire, 559-331 BCE A. Conquest Cyrus the Great Darius I B. Leniancy C. Multicultural Empire D. Propaganda Representatives of Ethnic Groups Bringing Gifts to Persian King Reliefs on Staircase to Audience Hall in Persepolis Ca. 500 BCE E. Administration • Satraps • Satrapy • Eyes and Ears Royal Road: unifying infrastructure (Susa to Sardis) Persepolis F. Ideology Divine kingship “King of kings” Ahura Mazda Religion: Zoroastrianism Zoroaster, 6th century BCE Ahura Mazda dualism Ahiram Argument • The Neo-Assyrians and the Persians had the same problems of controlling a large empire, but they used very different projects to solve those problems. The Neo-Assyrians relied on terror and compulsion, while the Persians used leniency and attraction.