Ancient Middle Eastern Civilizations Presentation
advertisement

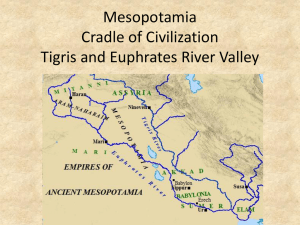
Ancient Middle Eastern Civilizations “THE CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION” Middle East Map 11 Sea 12 18 Sea 13 16 15 10 9 8 7 14 5 17 6 1 4 3 2 3 The Sumerians 4,000 B.C. to 2,300 B.C. Known as the first civilization of Mesopotamia Highly regarded for it’s many ‘firsts’ and ancient buildings Area is eventually conquered and divided Sumerian Culture is the foundation Babylonia in the south and Assyria in the north Land And Geography Approximately 5500 years ago in what is today the southern part of Iraq a civilization was founded The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers are the main features of the fertile crescent or Mesopotamia Mesopotamia” in Greek means “the land between the 2 rivers” Waters flood down off the mountains in Turkey to flood the land Challenges of the land Unpredictable flooding Build dams and canals for irrigation Arid environment Valley is open to invaders History is riddled with conquering groups settling the area Bell work Name one nickname for Mesopotamia. What does the word Mesopotamia mean? What was the name of the first civilization in the region? What two rivers are vital to the region? Use your notes from Tuesday. Section Reading In your rows, you will read one topic from chapter 2, section 3 pg. 30-34. Summarize the key information in a short bullet point list. Make your own list and than meet with your row. Put on the board when finished. Sumerian writing Architecture and science Government and Society Farming and Trade Education and religion Sumerian Cities and Society Society is made up of Upper: High Priests, Rulers individual City-States •Everybody lived in the city •Populations: 10,00050,000+ •Walled enclosures •Surrounded by suburban villages •Market center for region •Ceremonial center Middle: Lower priests, merchants, traders, scribes Lower: Farmers, peasants, Slaves Ur- largest Ancient city Farming and trade are the basis of the economy. Religion and Government Religion Government “Polytheistic” meaning that they believed in many gods They also believed their gods punished people who angered them They made sure to take care of their gods by feeding them daily and cleaning them Main god was Anu-God of Heaven, father of the Gods •Simple and fatalistic •Gods controlled all •No free will •Humans to please gods Gods guard each city, lower gods watch out for people Government is control by the priests and powerful warlords The Famous Ziggurats Achievements Writing System Other achievements Develop the first system of writing known as Cuneiform Used Pictographs on clay tablets Record history, transactions, religion, for education Used personal cylinder seals to sign documents Invent the first wheel, carts Bronze weapons Medicines Domesticate many animals Control flood waters, irrigation Develop the arch- covered structure over an opening Lunar Calendar Advanced math-360 degree circle, number system based on 60,(60 minutes, 60 seconds) Established trade to Asia First Legal System Wrote epic stories and poems Pottery wheel Musical instruments(lyre, drums, reed pipes) Assignment Page 34 Use the pyramid in question 2 to structure an essay similar to the one in question 4. Write an essay that persuaders readers the Sumerians created an important and successful civilization. Use your notes and the book Chapter 2, Section 3 pages 30-34 as a resource for writing your essay. The Babylonians Around 2000 B.C. the Babylonians conquered what was ancient Sumer Culture very similar to Sumerians, except women have far more rights in Babylonian society 1792 B.C. a Babylonian ruler named Hammurabi came to power Conquered by the Hittites around 1600 B.C. The Code Of Hammurabi Created by Hammurabi himself to bring order and justice to his empire 282 laws recorded on stones tablets for all to read Established the “rule of law”, all people equal before the law(punishments differ for social class) Presumption of Innocence Both parties can provide evidence Jury trail Punishments are “eye for an eye” 196. If a man put out the eye of another man, his eye shall be put out 3. If any one bring an accusation of any crime before the elders, and does not prove what he has charged, he shall, if it be a capital offense charged, be put to death. If any one steal the property of a temple or of the court, he shall be put to death, and also the one who receives the stolen thing from him shall be put to death. Code of Hammurabi Assignment In a group of 3 or 4, you have been tasked to create a set of laws and punishments for you civilizations legal system. Create 10 laws and punishments in your society Have a list of behaviors or actions which are not illegal Explain briefly, how does your justice system work? Judges? Juries? Presumption of innocence? Lawyers? Police? Mesopotamian Civilizations Civilization(people) 1. Sumerians 4000 BC-2300 BC 2. Babylonians 2000 BC-1600 BC 3. Hittites 1600BC-1200 BC 4. Assyrians 900 BC-650 BC 5. Chaldeans 625 BC-539 BC 6. Persian Empire 539 BC-331 BC 3 facts 1. Culture similar to Sumerian 2. Women had more rights(more jobs, property rights) 3. Code of Hammurabi-Harsh punishments 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Iron weapons-Warlike people From Asia Minor (Modern Turkey) Fines for small crimes Ruled by Chief-Priests Conquered Mesopotamia, Egypt, Palestine(Israel), Syria Warlike, Effective Warriors- Standing army, Chariots, Calvary, Brutal tactics-Kill and enslave populations, loot and destroy 3. Effective large government-Monarchy Nineveh captial- 70 foot walls, 7.5 miles, massive library The Epic of Gilgamesh 1. 2. 3. 4. Ruled by King Nebuchadnezzar-exiled the Jews Rebuilt Babylon Hanging Gardens- One of the 7 wonders Skilled astronomers, mathematicians, tower of Babel Bell work 1. What traits make a great leader? 2. How can one successful govern over a large area and a diverse group of people? Persian Empire Reading Questions Use both handouts the book (pg.39) to answer the following questions: 1. At it’s height, what area did the Persian empire cover? 2. List 3 reasons Cyrus was a great leader. 3. What were ‘The king’s eyes and ears’? 4. What two tools helped to keep the empire together? 5. Identify and explain the Persian religion. 6. What religion does the Persian’s influence? 7. How does the Persian empire fall? 8. What do the quotes about Cyrus tell you about how others viewed him? Persian Empire 550 BC- 331 BC Largest the world had seen at its time Led by Cyrus the Great Connected empire through roads(royal road) and trade Allow conquered peoples to keep religion and culture, freed the Jews Zoroastrianism Video Summary/ Review Assignment List 5 things you learned about the Persian Empire. Review Chapter 2, section 4 with the worksheet. (Due Friday) Egyptian Poster Project Form a group of 4 Before we make the poster we must first gather information Use your book to complete the worksheet on the Egyptians, take your notes on your assigned topic(Chapter 2, section 1 and 2) Review the Ancient Egypt power point on my website for additional information Once you have all of your information you can start on your poster 50 point project- you will be graded on the content of your material, quality of the final poster, use of time, and group cooperation Egyptian Poster Project Architecture Pyramids Government - Leaders History-3 KingdomsDecline Egypt map Geography ReligionMummificatiton Economy- Daily Life – Social Class Science-Math-Writing