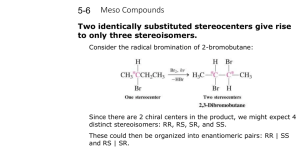
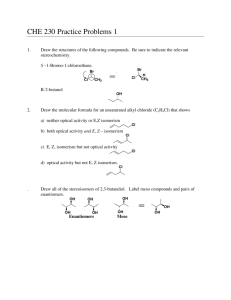
Stereoisomers of 2,3
advertisement

Resolution of Enantiomers Part II • Diastereomeric Salt Formation – Separation of enantiomers from a racemic mixture – Enantiomers are temporarily converted into a mixture of diastereomers • Diastereomers have different physical properties • Do this by combining enantiomers with a resolving agent – Resolving agent » Chiral compound » Enantiomerically pure 1 • By this method a racemic mixture of an amine may be resolved with a chiral carboxylic acid Racemic Mixture Resolving Agent 2 • Two diastereomeric salts are formed • These salts have different physical properties • The (S,R,R)-diastereomer is less soluble in methanol and can be selectively crystallized 6.8 Enantiomeric Resolution 3 • Each pure enantiomer may then be recovered by decomposition of the salt with base 6.8 Enantiomeric Resolution 4 Meso Compounds • Meso compounds: molecules that have two or more chiral carbons yet are achiral – not optically active – Possess an internal mirror plane Stereoisomers of 2,3-Butanediol Stereoisomers of 2,3-Butanediol • An internal plane of symmetry is present 6.7 Meso Compounds 6 Stereoisomers of 2,3-Butanediol • Two of the stereoisomers are the same • Hence, there are only three stereoisomers of 2,3-butanediol 6.7 Meso Compounds 7 Stereoisomers of 2,3-Butanediol • Relationship among the 2,3-butanediol stereoisomers 6.7 Meso Compounds 8 Meso Compounds • A molecule with n stereocenters, can exist as 2n stereoisomers • This number is reduced if a meso compound is present among the possibilities • 2,3-Butanediol possesses two stereocenters = 2n = 22 = 4 possible stereoisomers 6.7 Meso Compounds 9 Problems • Which of the following structures represent meso compounds? 10