College of Administrative Sciences Dr Mohammed El
advertisement

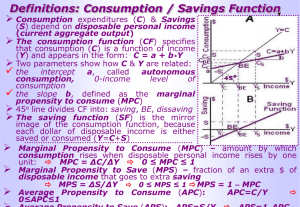
College of Administrative Sciences Principles of Macroeconomics Dr Mohammed El-Sakka Quiz # 1 Name\ ------------------------------------------------------- Univ. No.\--------------------Serial No.\ -----------------1.The most important determinant of consumer spending is: A) the level of household debt. B) consumer expectations. C) the stock of wealth. D) the level of income. Answer: D 2.The MPC can be defined as that fraction of a: A) change in income that is not spent. B) change in income that is spent. C) given total income that is not consumed. D) given total income that is consumed. Answer: B 3.The 45-degree line on a graph relating consumption and income shows: A) all points where the MPC is constant. B) all points at which saving and income are equal. C) all the points at which consumption and income are equal. D) the amounts households will plan to save at each possible level of income. Answer: C 4.As disposable income goes up the: A) APC falls. B) APS falls. C) volume of consumption declines absolutely. D) volume of investment diminishes. Answer: A 5.As disposable income increases, consumption: A) and saving both increase. B) and saving both decrease. C) decreases and saving increases. D) increases and saving decreases. Answer: A 6.If Trent's MPC is .80, this means that he will: A) spend eight-tenths of any increase in his disposable income. B) spend eight-tenths of any level of disposable income. C) break even when his disposable income is $8,000. D) save two-tenths of any level of disposable income. Answer: A 7.The wealth effect is shown graphically as a: A) shift of the consumption schedule. B) movement along an existing consumption schedule. C) shift of the investment schedule. D) movement along an existing investment schedule. Answer: A 8.The investment demand slopes downward and to the right because lower real interest rates: A) expand consumer borrowing, making investments more profitable. B) boost expected rates of returns on investment. C) enable more investment projects to be undertaken profitably. D) create tax incentives to invest. Answer: C 9.Given the expected rate of return on all possible investment opportunities in the economy: 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. A) an increase in the real rate of interest will reduce the level of investment. B) a decrease in the real rate of interest will reduce the level of investment. C) a change in the real interest rate will have no impact on the level of investment. D) an increase in the real interest rate will increase the level of investment. Answer: A If business taxes are reduced and the real interest rate increases: A) consumption and saving will necessarily increase. B) the level of investment spending might either increase or decrease. C) the level of investment spending will necessarily increase. D) the level of investment spending will necessarily decrease. Answer: B The multiplier effect means that: A) consumption is typically several times as large as saving. B) a change in consumption can cause a larger increase in investment. C) an increase in investment can cause GDP to change by a larger amount. D) a decline in the MPC can cause GDP to rise by several times that amount. Answer: C The multiplier is: A) 1/MPC. B) 1/(1 + MPC). C) 1/MPS. D) 1/(1 - MPS). Answer: C The multiplier: A) occurs only in response to a change in the level of investment spending. B) can be found by taking the reciprocal of the MPS. C) occurs only when intended investment increases as GDP increases. D) is measured by the slope of the saving schedule. Answer: B The multiplier effect indicates that: A) a decline in the interest rate will cause a proportionately larger increase in investment. B) a change in spending will change aggregate income by a larger amount. C) a change in spending will increase aggregate income by the same amount. D) an increase in total income will generate a larger change in aggregate expenditures. Answer: B