Electrical Activity of Heart
advertisement

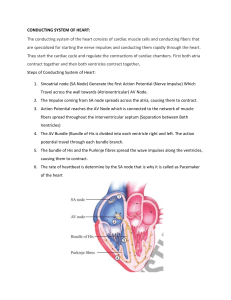
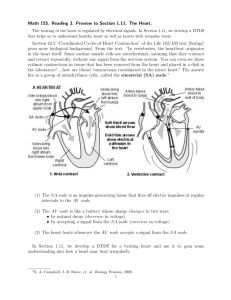
Electrical Activity of Heart Presentation by: Tarique Ahmad John Frost Grant Post Ian Osborne Introduction Video Cardiac Conduction System: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdoSreUAt hA Conducting System • • • also known as cardiac conducting system or the nodal system its a network of specialized cardiac muscle cells that initiates and distributes electrical impulses includes: Sinoatrial (SA) Node o Atrioventricular (AV) Node o Conducting Cells Bundle of his (hiss )/ Atrioventricular (AV) Bundle Purkinje Fibers o Continued... • conducting system allows heart to be automaticity, or autorhythmicity o • it contracts on its own, in absence of neural and hormonal stimulation actual contraction lags behind the electrical pulse o due to time is takes calcium ions to enter the sarcoplasm http://www.ceufast.com/courses/239/04_Cardiac_Conduction_System.jpg Sinoatrial (SA) Node • • • In the upper part of the right atrium specialized bundle of neurons known as the sinoatrial node (SA node) Acting as the heart's natural pacemaker, o "fires" at regular intervals to cause the heart to beat at a rhythm of 60 to 70 beats per minute AV / Atrioventricular Node • • • Specialized Cardiocytes relay the contractile stimulus to the AV bundle, the bundle branches, the Purkinje fibers, and the ventricular myocardium Located between the atria and the ventricles There's a 100 millisecond delay once signal is received at AV node = 100 millisecond long delay Lasts a total of 225 Milliseconds http://washingtonhra.com/16.html Conducting Cells: Bundle of His • • • Also known as the AV bundle Carry the contracting stimulus from the AV node to the Purkinje Fibers Separates into left and right bundle branches, which are spread across the inner surfaces of the left and right http://www.ambulancetechnicianstudy.co.uk/card.html#.UXHG16KsiSo Conducting Cells: Purkinje Fibers • • • • Located in the inner ventricle walls of the heart just below the epicardium Assist the conduction system in the synchronization of contractions Carry the electrical impulses from the Sinoatrial Node to the Myocardium Conduct action potentials Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) • • graphic record of heart, monitored by electrical activity of heart at certain locations Electrical events of heart are powerful enough to be detected by electrodes on body surface http://smartmedicalindo.com/product_images/w/452/Schiller_Cardiovit_AT- Continued... • • • comparing information from different locations to monitor and check performance of heart o specific components can be checked as well tracing varies on placement of electrodes, also called leads used to detect cardiac arrhythmias o abnormal cardiac activity Understanding an ECG/EKG • • • P Wave- small wave that accompanies depolarization of atria QRS Complex- wave that appears after contraction of ventricles o ventricles begin contraction at peak of R wave T Wave- small wave that indicates ventricular repolarization http://www.usfca.edu/fac-staff/ritter/Image20.gif Analyzing an EKG • • • involves measuring size of voltage changes determining temporal relations between components focus on amount depolarization during P wave and QRS complex POP QUIZ!!! 1. What is the pacemaker of the heart? a. Where is it located? 2. What does AV stand for? a. Where is the node located? 3. What does the bundle of hiss do? 4. Where are the Purkinje Fibers located? 5. What does ECG/EKG stand for? Works Cited Martini, Frederic H., and Edwin F. Bartholomew. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology. 4th ed. San Francisco: Pearson, 2007. Print. Martini, Frederic H., and Judi L. Nath. Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology. 8th ed. San Francisco: Prentice Hall, 2009. Print.