heart outcomes
advertisement

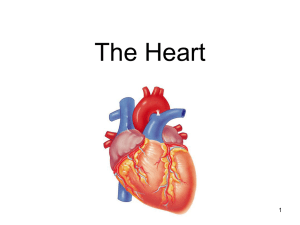
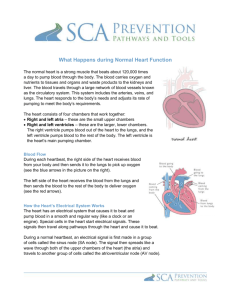
BIOLOGY 12: Heart Study Guide Mr. Kruger Name:__________________________________________ Blk:_____ For any diagram of a heart given, you must be able to identify all of the parts. The following is a sample of possible questions. Unit # 5 Heart Structure and Function L.O. K – 1 Heart Identification and Functions ___ 1. Explain why the side of the heart on your left in diagrams is called the right side. ___ 2. What is meant by myocardium? ___ 3. What is the function of the Septum? ___ 4. What is found between the atria and the ventricles? ___ 5. What is different between the valves on the right and left side of the heart? ___ 6. What structures support the valves of the heart? ___ 7. What are found at the junction of the ventricles and the aorta or Pulmonary Trunk? ___ 8. What is the difference between the Pulmonary Trunk and a Pulmonary Artery. ___ 9. Why are the walls of the Left Ventricle thicker than those of the Right Ventricle? ___ 10. What is the function of the atria? ___ 11. ***What might happen to a person’s circulation if the Chordae Tendinae attached to one of the atrioventricular valves pulled loose?*** L.O. K – 2 SA Node, AV Node, and Pukinje Fibres BIOLOGY 12: Heart Study Guide Mr. Kruger ___ 1. What is meant by the phrase “the heartbeat is intrinsic”? ___ 2. Another word for the contraction of the heart muscle is? ___ 3. Another word for the relaxation of the heart muscle is? ___ 4. List the phases of the cardiac cycle and the length of time required by each phase. ___ 5. What causes the Lubb-Dubb sound of a heart beat? ___ 6. What are the two names for the tissue found in the upper wall of the right atrium? ___ 7. At the bottom of the right atrium is another type of tissue. Name it. ___ 8. What is the function of the sinoatrial node? ___ 9. What happens to the heartbeat if the sinoatrial node is damaged? ___ 10. What is the function of the Atrioventricular node? ___ 11. What carries the message from the AV Node to the ventricle muscle tissue? ___ 12. Draw and identify the different stages of a normal EKG. L.O. K – 3 Autonomic Regulation of the Heart ___ 2. The medulla oblongata can alter the rate of the heart beat by way a nerver in the nervous system called the ___ 3. The nerve that sends electrical information from the medulla oblongata to the SA Node is the? ___ 4. The autonomic nervous system has two parts to it. Name them. ___ 5. The part the speeds up the heart is called the? ___ 6. The part the slows down the heart is called the? L.O. K – 4 Blood Pressure: Hypertension and Hypotension BIOLOGY 12: Heart Study Guide Mr. Kruger ___ 1. What is the name for the device that takes blood pressure readings? ___ 2. What is a normal blood pressure for a young adult? ___ 3. The first number in a blood pressure reading stands for what? ___ 4. The second number in a blood pressure reading stands for what? ___ 5. A pulse is initiated by what part of the heart? ___ 6. What features of the arteries make a pulse possible? ___ 7. How does the expansion and contraction of an artery help maintain blood pressure? ___ 8. Define hypertension. ___ 9. Define hypotension ___ 10. Be able to list at least 5 very important factors that are responsible for high blood pressure. ___ 11. Explain how the arterioles and capillaries can regulate blood pressure. L.O. K – 5 Systolic Pressure vs Diastolic Preesure ___ 1. The highest arterial pressure is called? ___ 2. The lowest arterial pressure is called? ___ 3. Diastolic pressure occurs while the heart ventricles are? ___ 4. Systolic pressure occurs while the heart is? ___ 5. What blood vessel has the highest blood pressure? ___ 6. What blood vessel has the lowest blood pressure? ___ 7. Can you have a blood pressure of 120/140? Explain.