ميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب RHYTHMICITY AND CONDUCTIVITY OF THE CARDIAC MUSCLE
advertisement

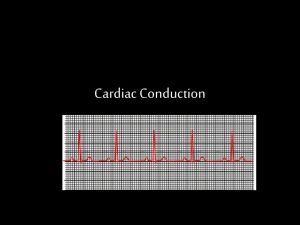
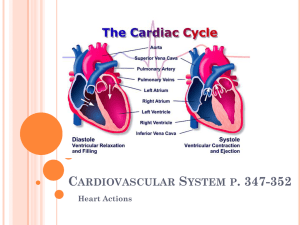
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم RHYTHMICITY AND CONDUCTIVITY OF THE CARDIAC MUSCLE Dr QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the characters auto-rhythmicity of the cardiac muscle. 2. Describe the mechanism of sinus nodal rhythmicity and illustrate the pace-maker potential. 3.Describe the pathway of conduction of cardiac excitation wave through the conducting system of the heart. 4. Compare and explain the slow versus the rapid conduction of cardiac waves. 5. Discuss factors affecting rhythmicity and conductivity of cardiac muscle. Special conducting tissue Autorhythmicity Definition: the ability of the heart to initiate its beat continuously and regularly without external stimulation -----1% of the cardiac muscle fibers Functions 1. Act as a pacemaker (set the rhythm of electrical excitation) 2. Form the conductive system (network of specialized cardiac muscle fibers that provide a path for each cycle of cardiac excitation to progress through the heart) 3 Special conducting tissue SA Node Right Atrial Tracts* Anterior Internodal Pathway* AV Node Middle Internodal Pathway* Posterior Internodal Pathway* Anterior interatrial myocardial band (Bachmann’s Bundle) Left Atrium AN Region N Region NH Region Bundle of His Right Bundle Branch Left Bundle Branch Septal Division Anterior Division Posterior Division Sinoatrial node (SA node) Specialized region in R atrial wall near opening of superior vena cava 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Small, flattened , shape of a crescent ,P+T CELLS 15 X 5 X 1 mm Cells are self-excitatory, (pacemaker cells). Intrinsic rate of 90 -100 beats/ min No fast Na+ current Ca2+ current underlies upstroke Ca2+ current underlies conducted AP Internodal pathwayConnect SA Node and AV Node Faster conduction than Atrial muscles• NORMAL Anterior- Bachman’s bundle Middle-Wenkebach’s bundle Posterior-Thorell’s bundle ABNORMAL -Tract of kent -James tract AV-NODE posterior septal wall of RA immediately behind tricuspid valve 1. Delay of impulses to ventricles by 0.12sec -( 0.09 at AVN & 0.03 at AV bundle) 2. Causes of delayi) smaller size of fibers ii) smaller number of gap junctions iii) more negative RMP Significancea) atria contracts 0.1sec earlier than ventricle b) limits the no impulses transmitted to ventricles- <230/min Bundle of His(after German physician Wilhelm His Jr., 1863-1934 begins from AV Node, passes downwards in the intraventricular septum for 5-15mm along each side of the septum,(divides into R+L bundle branches) Left branch divides 3 fasciculus - anterior -posterior - septal Both divide repeatedly and Lie sub-endocardially Conduction System of the Heart Septal branch Purkinje fibersJan Evangelista Purkinje (Czech; 1787-1869) origin from terminal divisions of bundle branches that diverge to the inner sides of the ventricular walls 2. Largest and Fastest conducting 3.1-2mm thick 4. Passes impulses to ventricular myocytes Generation Of impulses in different tissue intrinsic rhythm -influenced by ANS nervesA- vagal influences being dominant over sympathetic influences at rest. This "vagal tone" reduces the resting heart rate down to 60-80 beats/min. latent pacemakers NOTE;-Non-SA nodal tissues are latent pacemakers that can take over (at a slower rate), should the normal pacemaker (SA node )fail 12 Conduction velocity in different tissue Tissue Conduction rate (m/s) SA node 0.05 Atrial muscle 0.3 Atrial pathways 1 AV node 0.05 Bundle of His 1 Purkinje system 4 Ventricular muscle 1 Msec. Action potential in sinoatrial cardiac cells Very similar to the ventricular cardiac cells with a few major exceptions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Do not have a stable rest. AP is driven by the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel in most SA cells Rising phase is due the opening of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel As the Ca2+ channel inactivates the membrane is repolarized by the delayed rectifier K+channel Spontaneously depolarize once the delayed K+ channel has closed Due to presence of an ion channel that is activated by hyperpolarization – the funny channel. FUNNY CHANNEL ( If) Also called the HCN channel or hyperpolarization, cyclic nucleotide gated ion channel 1. Activated by hyperpolarization 2. As membrane repolarizes after AP the threshold for opening of the If is reached at about -50 Mv 3. If opens and allows Na+ to preferentially flow into the cell 4. cAMP can influences ( If) and shift threshold of activation from 50 to -40 mV. . PACEMAKER ACTIVITY IN SA NODE T-type L type pacemaker depolarization Diastolic depolarizaton (Nodal) Action Potential Inward Na+ and Ca+ + ions (depolarization ) Outward K+ current (repolarization ) 0 3 Increased HR) threshold 4 Slow spontaneous Inward Na+ ions Automaticity - a pacemaker cell’s ability to spontaneously depolarize, reach threshold, and propagate an AP (d HR) Cardiac Action Potential Types Are Either Fast Or Slow Response 1. Fast-response action potentials 1. Atrial myocardial fibers 2. Ventricular myocardial fibers 3. Purkinje fibers 2. Slow-response action potentials 1. Sinoatrial node 2. Atrioventricular node 3. Bundle of his 4. Atrial internodal tracts 5. Bundle branches Differences between fast and slow cardiac action potentials: 1.Phases Fast response – all present Slow response – 1 & 2 absent Slow > Fast 2. RMP Fast response – voltage constant Slow response – voltage slowly decreases 3. Slope of upstroke 4.Amplitude of action potential 5. Overshoot of action potential Fast > Slow Fast > Slow Fast > Slow STEPS OF CARDIAC EXCITATION 1. Cardiac impulse originates at SA node 2. AP spreads throughout R and L atria 3. Impulse passes from atria into ventricles through AV node (only 4. 5. 6. 7. point of electrical contact between chambers) AP briefly delayed at AV node (ensures atrial contraction precedes ventricular contraction to allow complete ventricular filling) Impulse travels rapidly down interventricular septum by means of bundle of His Impulse rapidly disperses throughout myocardium by means of Purkinje fibers Rest of ventricular cells activated by cell-to-cell spread of impulse through gap junctions 23 Electrical Activity of Myocardium FACTORS AFFECTING AUTORHYTHMICITY 1.Hormonal and chemical factors ( adren. ,NE, , alkali , While Ach, acids, ether, bacterial toxins, chloroform decrease. 2.T emperature ( warming increase, cooling decrease). 3.Oxygen supply ( hypoxia decrease.) 4..Autonomic nerve stimulation;- G protein a) vagal stimulation ↓ the slope of pre-potential and ↓ the rate of impulse generation b) sympathetic stimulation increases the slope and increases the impulse rate 5. Ions- a) K+ b) ca++ 6.Drugs Digitalis,. -80 mV SUMMARY Comparison of APs AP from VENTRICULAR MUSCLE AP from SA node or AV node 0 spontaneous depolarization conducted AP to cell triggers depolarization pacemaker depolarization -80 mV AP from ATRIAL MUSCLE No pacemaker depolarization maximum diastolic potential 27

![Cardio Review 4 Quince [CAPT],Joan,Juliet](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005719604_1-e21fbd83f7c61c5668353826e4debbb3-300x300.png)