Presentation

1.History.
2.Purposes
1. Characteristics of teaching & learning process
2.Areas of language emphasized.
3.Principles.
The grammar translation method
Reading the passage & answer the question
Practice
Grammar
Word study
Translation
The modern method
Reading.
Speaking
Listening.
Writing.
Practice pronunciation
Grammar.
The grammar-translation method
Dating back to the early nineteenth, it was first known as Prussian Method in U.S.A
Being originally used to teach classical languages (and literatures) such as Latin and
Greek. Classical Method.
Purposes
Translate better
Purposes
Develop reading & writing skills.
Avoid misunderstanding.
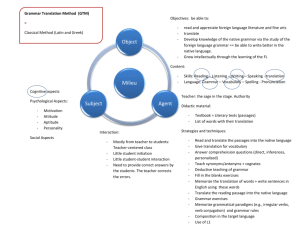
Characteristics of teaching & learning process
Grammar deductively
Translation from L1-L2, L2-L1.
Memorize vocabulary L1=l2
Areas of language emphasized
Vocabulary and grammar (teaching form)=form based.
Reading & writing
Principles
View of Culture: literary language is superior to spoken language.
Principles
Goal of learner:
To improve reading and writing skills.
To translate each language into each other.
Principles
Role of teacher: The authority in the classroom ( teacher centered)
Principles
Role of students:
Principles
Students-teacher interaction (mostly)
Student- student interaction (little)
Principles
Teacher’s response to students’ error
Techniques
6.
7.
8.
9.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Translation of a literary passage
Reading comprehension questions
Antonyms/ Synonyms
Cognates
Deductive application of the rule
Fill-in-the-blanks
Memorization
Use Words in Sentences
Composition
Techniques
Translation of a literary passage:
A men and a woman applied for a job. They both had the same experience, so the manager gave them both a test. After the test, both of them missed only one question. The manager told the first man: “Sorry. I will hire her.” “Why?” screamed the man. “We both missed the same question!” “That’s right,” said the manger, “but she answered the question with ‘I don’t know’ and you wrote, ‘Neither do I”.
Techniques
Reading comprehension questions:
1. Questions about the information contained in the passage.
(What did the man answer? What did the woman answer?)
2. Questions for making inferences.
(what do you infer from the answer with “neither do I “ of the man?)
3. Questions to relate the passage
(Have you ever applied for a job?)
Techniques
Antonyms/ Synonyms:
Find antonyms and synonyms in the reading passage
Define a set of words based on their understanding of them
Techniques
Cognates: to recognize sound patterns between the languages.
Deductive application of the rule:
Ex: I wouldn’t like to go there.
Neither would I
Use Neither + auxiliary + I with negative sentences to say that you have something in common with somebody.
Techniques
Fill- in- the- blanks: to complete sentences with words missing.
Ex:…………. is a person who works all her life to become famous and then wears sunglasses so people don’t recognize her.
Techniques
Memorization: words and grammatical rules.
Use words in sentences: they make up sentences in which they use the new vocabulary they learn
Techniques
Composition: to write about a topic in the target language based on some aspect of the reading passage.
Advantages
The phrasing of the target language is quickly explained.
Eg:
: is a person who puts metal in your mouth and takes coins out of your pocket.
Advantages
Advantages
Teacher’s labor is saved:
Few demands in teachers
Classes are taught in the mother tongue.
Disadvantages
It is an unnatural method.
The Grammar Translation Method does not provide any such practice to the learner of a language
Disadvantages
the wrong idea of what language is
Disadvantages
Worst effect of this method is on pupil’s motivation.
Thank you for listening!
Have you got any question for us?