Burns
advertisement

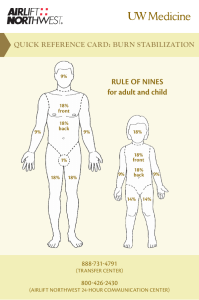
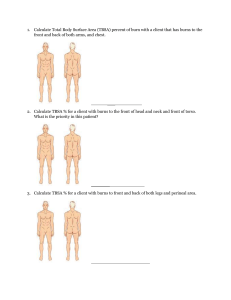
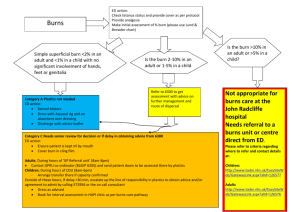
Chapter 11: Burns Lisa Spiguel Which of the below is not a criteria for transfer to a burn center by the American Burn Association? 1. All burns > 10% of TBSA 2. Burns that involve the hands, feet, genitalia 3. Burns in patients with co-existing complex medical comorbidities 4. Burns in patients with concomitant trauma State of Florida mandates that hot water heaters in multi-dwelling facilities to be set at which temperature (ο F)? 1. 82 2. 95 3. 110 4. 120 Which of the following below is not a zone of injury following a burn injury? 1- Zone of Coagulation 2- Zone of Liquefaction 3- Zone of Stasis 4- Zone of Hyperemia Which Zone represents 3rd degree or full thickness burns? 1- Zone of Coagulation 2- Zone of Liquefaction 3- Zone of Stasis 4- Zone of Hyperemia What factors Transition one zone to a deeper zone? 1- Edema 2- Infection 3- Poor perfusion 4- All of the above Zones of Injury The following picture represents which type of burn? 1- Superficial 2- Superficial Partial thickness 3- Deep Partial thickness 4- Full thickness Burns Superficial Thickness Partial Thickness Full Thickness Diffusion of nutrients to the healing tissues is called? 1- Imbibition 2- Inosculation 3- Granulation 4- Neovascularization Burn Healing • Full Thickness – Heals from epithelialization from wound edges • Partial Thickness – Heals from re-epithelialization from epidermal appendages • Hair Follicles • Sweat Glands • Sebaceous Glands Burn Healing • Imbibition – Osmotic nutrient and oxygen deliver – Day 0-3 • Neovascularization – Days 3+ • Epithelialization – From epidermal appendages • Contraction Evaluation of a Burn Patient • • • • • • ABCs – Primary Survey Secondary Survey Resuscitation Estimate size and depth of burn Concomitant Injuries Diagnostic Studies/ Lab work – Labs:paO2, pCO2, CO, CBC, BMP, Coags, +/- UA – Diagnostic Studies based on concomitant trauma • Wound Care • Nutrition UW Protocol Table 11.3 True or False: An easy method of calculating a patient’s TBSA burn is to use the palm of your hand, which constitutes 1% TBSA. A child has disproportionately a large TBSA designated to which part of the body as compared to an adult? 1- Head 2- Feet 3- Legs 4- Torso A 54 yo 70kg man is transferred to your burn center, as shown in the picture. Estimate the TBSA involved? 1- 10% 2- 20% 3- 40% 4- 50% How much volume will you give this patient in the first 8 hours of resuscitation? 1- 1800 mL 2- 2800 mL 3- 3800 mL 4- 4800 mL Estimating Extent • Rule of Nines – Differs for adults and Children – Children have larger head and smaller leg % • Size of Patients palm Calculating Fluid Requirement • Parkland Formula: 4 cc/kg x % TBSA • Fluid: – Adults: LR (1st 24 hours) D5 ½ NS – Pediatrics: D5 0.45%NS • Administer: – First ½ in the first 8 hours – Second ½ in the Second 16 hours • Monitor MAP and UO – MAP > 60 mmHg – U/O: • Adults: > 30 ml/hr, (concerned about Rhabdo – 100mL/hr) • Pediatric: > 1.5 -2 mL/kg/hr • Avoid large volume crystalloid boluses, increase hourly rate 10% A 72 yo male was rescued from a house fire. On initial evaluation he has stupor and confusion. What is his likely carboxyhemoglobin level? 1- 5% 2- 10% 3- 20% 4- 30% Carboxyhemoglobin T1/2 is? 1- 30 minutes 2- 1 hour 3- 2 hours 4- 4 hours Airway swelling following an inhalational injury is worst at which time following injury? 1- First 12 hours 2- 12-24 hours 3- 24-48 hours 4- 48-72 hours Inhalation Injury • Clinical Exam • CarboxyHb levels – Coughing, wheezing, stridor – Carbonaceous material on face – Singed facial hair • Laryngoscopy – Erythema – Edema – Carbonaceous sputum below level of vocal cords • Smokers < 20% A 70 kg man is HD#2 following admission for a 35% TBSA burn as demonstrated in the picture below. Over the past 3 hours he his BPs are 90/50s, his u/o has decreased to 5 mL/hr, and his Peak Airway pressures are 40 mmHg. What is the next step in management? 1. Decrease his PEEP 2. Bolus 1 L of 0.9 NS 3. Start vasopressin 4. Check bladder pressures Fluid Resuscitation Complications • Poor tissue Healing • Pulmonary Complications – Edema/ARDS – Effusions • Extremity Compartment Syndrome – Escharotomies – Fasciotomies • Abdominal Compartment HTN/Syndrome – Bladder pressures > 25 mmHg – Decompressive laparotomy Escharotomity Which of the following below is a side effect of silver sulfadiazine (Silvadene)? 1. Neutropenia 2. Leukocytosis 3. Metabolic Acidosis 4. Metabolic Alkalosis Which topical antimicrobial is best used to for ear burns? 1. 2. 3. 4. Silvadene Sulfamylon Silver Nitrate Bacitracin Which topical antimicrobial is contraindicated in patients with sulfa allergy? 1. 2. 3. 4. Silvadene Sulfamylon Silver Nitrate Bacitracin Which topical antimicrobial is associated with methemoglobinemia? 1. 2. 3. 4. Silvadene Sulfamylon Silver Nitrate Bacitracin Topical Antimicrobials Side Effects Neutropenia, Thrombocytopenia Metabolic Acidosis Painful Methemoglobinemia Electrolyte imbalances What is the thickness of a split thickness skin graft? 1. 2. 3. 4. 0.001 cm 0.012 cm 0.12 cm 1.2 cm Burn Excision • Optimal timing is 3-4 days post injury • Surgical Excision: – Fascial excision: Excising involved tissue down to muscle fascia – Tangential excision: Sequential excision of eschar until the wound bed displays punctate bleeding Autograft • Use of patients skin as donor sites • Full thickness – Less wound contracture – Limited donor sites (behind ear, groin, clavicle) – Have to be closed by primary closure • Split thickness – 0.012-0.015 cm thickness – Includes epidermis and part of dermis Additional Options • Allografts • Xenografts – Temporary biologic – Porcine dressing – Similar to allograft process – Meshed 1:1 • Epidermal Skin Substitutes – Provides physiologic – Cultured autologous wound coverage for 2-4 keratinocytes weeks • Dermal Skin Substitutes – Rejection occurs at 2-4 – Integra (inner matrix of type 1 weeks removal and collagen and chondroitin autograft or re-allograft sulfate) – No allografts in pregnancy: – Becomes vascularized in 2-3 fetal deaths from HLA weeks then can by autografted mismatch Treatment of an alkali chemical burn is? 1. 2. 3. 4. Copious irrigation with tap water for 30 minutes Neutralization of the alkali agent Intra-arterial calcium gluconate infusion Both 1 and 2 Treatment of an acidic chemical burn is? 1. 2. 3. 4. Copious irrigation with tap water for 30 minutes Neutralization of the acidic agent Intra-arterial calcium gluconate infusion Both 1 and 3 Treatment of a hydrofluoric acid chemical burn is? 1. 2. 3. 4. Copious irrigation with tap water for 30 minutes Neutralization of the acidic agent Intra-arterial calcium gluconate infusion Both 1 and 3 What is the daily protein requirement for a 70 kg man with a 35% TBSA partial thickness burn? 1. 75 gm/day 2. 175 gm/day 3. 250 gm/day 4. 425 gm/day Nutritional Support • Protein catabolism results in 1500 to 200 gm of nitrogen loss/day • Protein Requirement: – 1gm/kg/day + (3 g/day x % TBSA) • Caloric Requirement: – 25 kcal/kg/day + (30 kcal/day x % TBSA)