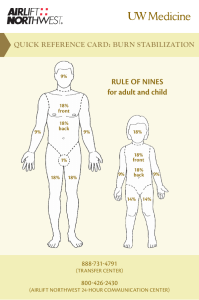
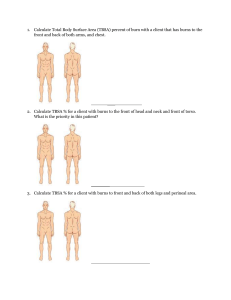
Definition of Burn An injury caused by exposure to heat or flame Classifications of Burn According to Extent of Burn • Various methods are used to estimate Total Body Surface Area (TBSA) affected by burns such as Rule of Nine, Lund and Browder Method and Palmer Method. Note Total body surface area (TBSA) - is an assessment measure of burns of the skin Body Surface Area Estimation RULE OF NINES • An estimation of the TBSA involved in a burn is simplified by using the rule of nine • The rule of nines is a quick way to calculate the extent of burns. The system assigns percentages in multiples of nine to major body surfaces. LUND AND BROWDER METHOD A more precise method of estimating the extent of a burn is the Lund and Browder method, which recognizes that the percentage of TBSA of various anatomic parts, especially the head and legs, and changes with growth. By dividing the body into very small areas and providing an estimate of the proportion of TBSA accounted for by such body parts, one can obtain a reliable estimate of the TBSA burned. PALMAR METHOD In patients with scattered burns, a method to estimate the percentage of burn is the palmer method. Management of Burn Injury Three Phases of Care: 1.Emergent/resuscitative phase 2.Acute/intermediate phase 3.Rehabilitation phase. 1.Emergent/resuscitative phase First Aid a) Stop, drop, cover wound and roll if on fire b) Establish an airway c) Supply O2 d) IV line Fluid Resuscitation Formula • The following example illustrates use of ParkLand/Baxter Formula 4 ml x Kg body weight x % TSBA Day 1: Half to be given in first 8 hours Half to be given over next 16 hours Day 2: Varies, Colloid(volume expander) is added Example: in 70 kg patient with 50% TBSA burn: 4 ml /kg/%TBSA 4ml x 70 kg x 50% =14,000 ml/ 24 hours Plan to administer: first 8 hours= 7000 ml, and next 16 hours= 7000 ml NURSING ALERT • Formulas are only a guide. The patient’s response, evidenced by heart rate, blood pressure, and urine output, is the primary determinant of actual fluid therapy and must be assessed at least hourly. Patient outcomes are improved by optimal fluid resuscitation. Nursing Management • Aseptic management of the burn wounds • Invasive lines continues • Monitors vital signs frequently. • Respiratory status is monitored closely, and apical, carotid, and femoral pulses • Cardiac monitoring(cardiac disease, electrical injury,or respiratory conditions. Burn Wound Care • Wound Cleaning • Topical antibacterial therapy • Wound dressing • Wound debridement