Ionic Compound Smart Notes as PowerPoint
advertisement

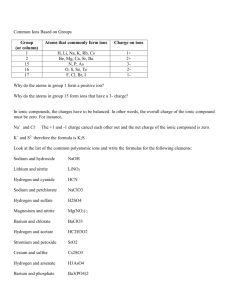
Ionic Bonds and Compounds Ionic Bonds and Compounds (in a future unit we'll learn about covalent or molecular bonds and compounds) Ionic Bonds and Compounds Dogs can teach chemistry! Ionic Bonds and Compounds So can stick figures ... Except for the noble gasses, atoms of all elements are unstable! All chemical reactions occur so atoms can achieve stability. Atoms achieve stability when they have full electron energy levels. That is, when they have a "noble gas configuration" of electrons. Metals Metals, having 1, 2, or 3 valence electrons, can become stable (full energy levels) by losing electrons. When metals lose electrons, they become positive ions, known as cations. Non-Metals Non-metals, having 5, 6, or 7 valence electrons, can become stable (full energy levels) by gaining electrons. When non-metals gain electrons, they become negative ions, known as anions. So... metals form positive ions non-metals form negative ions So... metals form positive ions non-metals form negative ions Mini-Quiz #1 What charge do the following atoms have when they lose or gain electrons to become ions? Li Cl Mg Na O Al S N Se P F Ca Br K Be Al Ba Fr BUT... atoms can't just gain or lose electrons in isolation. They must have another atom to give to or take electrons from. Metals (that want to lose electrons), transfer electrons to nonmetals (that want to gain electrons). The metal atoms become positive ions, and the nonmetal atoms become negative ions. These oppositely charged ions attract each other forming IONIC BONDS. Using Lewis Dot structure to understand Ionic Compound formation (remember: Lewis Dot structures consist of an atom's symbol surrounded by dots representing valence electrons) Na + Cl Mg + O Mg + Cl Na + O Al + Cl Al + O Ions always combine in ratios that neutralize the charges. So the ionic compound has an overall zero charge. Ionic compound formulas are always written with the positive ion first! 2+2 4 landscape Mini Quiz #2 Balance the following formulas A Ca Cl Ca O Na N K Cl KO Ba N B Na F Na S Na O Mg N Ba O Na Br Polyatomic Ions As the name implies, polyatomic ions are made of several atoms. These atoms are joined by strong covalent bonds (which we'll study in another unit). For now, just think of them as a group of atoms glued together that, as a group, have a charge. Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic ions are everywhere and are important. The sooner you learn to recognize them, the easier your understanding of chemistry will be. You will need to memorize 10 of the most common (there are MANY more). The ten you need to know are: Ammonium NH4 Sulfate +1 SO4 Carbonate Nitrate -2 CO3 -2 NO3 -1 ClO3 Chlorate -1 Permanganate -1 Acetate -1 Hydroxide MnO4 Chromate CrO4 -2 Phosphate PO4 -3 C2H3O2 OH -1 C2H3O2 NH4 Acetate -1 Ammonium +1 CO3 Carbonate -2 ClO3 Chlorate -1 CrO4 Chromate -2 OH Hydroxide -1 NO3 Nitrate -1 MnO4 PO4 Permanganate Phosphate -3 SO4 Sulfate -2 -1 Acetate C2H3O2 -1 Ammonium NH4 +1 Carbonate CO3 -2 Chlorate ClO3 -1 Chromate CrO4 -2 Hydroxide OH -1 Nitrate Permanganate Phosphate -3 Sulfate NO3 -1 MnO4 -1 PO4 SO4 -2 Polyatomic ions act just like single-atom ions. They bond with ions of the opposite charge in the same way. Binary Compound (made of 2 elements) Ca+2 Cl-1 with Ternary Compound (made of more than 2 elements -- includes a polyatomic ion) Ca+2 with NO3-1 Illustration: NO3-1 Cl-1 Ca+2 Ca+2 Cl-1 NO3-1 Formula: Ca Cl2 Ca (NO3)2 Instructions for constructing ionic compound activity. If needed, cut out ions. Match one type of cation (+ ion) with one type of anion (- ion) in ratios that result in a rectangle (zero overall charge). Always list the positive ion first Fill in the missing information Name Formula Charge Sulfate PO4 Ammonium C2H3O2 MnO4 Nitrate CO3 Hydroxide Mini Quiz #4 Balance the following formulas K SO4 Ba PO4 NH4 OH NH4 C2H3O2 Ba C2H3O2 K MnO4 NH4 SO4 NH4 Cl Al NO3 K OH Mg CO3 K SO4 Attachments Dogs Teaching Chemistry - Chemical Bonds.mp4