Writing and Naming Compounds
advertisement
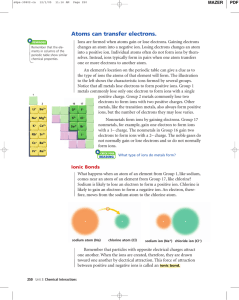
Writing Chemical Formulas Metals vs Nonmetals Metals Nonmetals Lose electrons (e-) Form Cations (+ ions) Gain electrons (e-) Form Anions ( - ions) Attracted to Cathode Attracted to Anode Positive Ions: Protons # > Electron # = Cation Negative Ions: Protons# < Electron # = Anion OXIDATION NUMBER is the overall charge on an ion after it has lost electrons (metals) or gained electrons (nonmetals). When ions are combined together to form compounds, THE OVERALL CHARGE OF THE COMPOUND WHICH RESULTS MUST BE “ZERO” OR NEUTRAL. Subscripts Subscript: Small numbers placed to the lower right of the symbols. In chemistry this indicates the number of atoms of an element. When there is only 1 atom of an element the subscript is not written. Example SiO3 one silicon atom three oxygen atoms Parenthesis When there is a parenthesis in a chemical formula the chemicals inside are multiplied by the number outside. Example Ca(OH2)2 1-- Calcium atom. 2 -- Oxygen atoms. 4 -- Hydrogen atoms. Coefficients Coefficient: A large number placed in front of a chemical formula. This number indicates how many of each molecules there are. Everything in the formula is multiplied by the number in front. 3MgCO3 3 atoms of Mg 3 of C 9 of O Writing Chemical Formulas To write chemical formulas you need to know: Which elements are involved The number of electrons (e-) that elements lose, gain, or share to become stable NOTICE: METAL ION IS ALWAYS WRITTEN FIRST NONMETAL ION IS WRITTEN LAST SWAP & DROP Method *When ions are combined to form compounds, THE OVERALL CHARGE OF THE COMPOUND WHICH RESULTS MUST BE “ZERO” OR NEUTRAL. 1. If a the oxidation #s cancel do not swap & drop Lithium and Fluorine Li+ Fl= LiFl 2. If the oxidations #s do not cancel, swap & drop Aluminum and Oxygen Al3+ O2= Al2O3 Write a correct formula for the compound, which would form between. calcium and sulfur cesium and oxygen aluminum and oxygen sodium and sulfur potassium an oxygen