Literature Review outline
advertisement
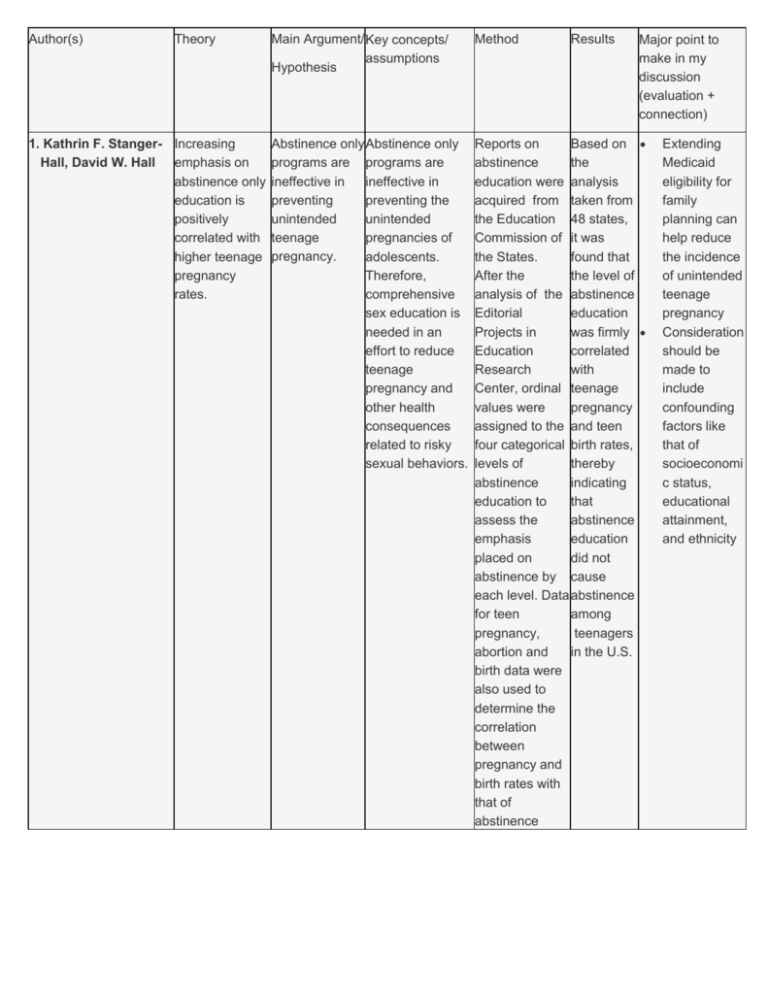
Author(s) Theory 1. Kathrin F. Stanger- Increasing Hall, David W. Hall emphasis on abstinence only education is positively correlated with higher teenage pregnancy rates. Main Argument/ Key concepts/ assumptions Hypothesis Method Results Abstinence only Abstinence only programs are programs are ineffective in ineffective in preventing preventing the unintended unintended teenage pregnancies of pregnancy. adolescents. Therefore, comprehensive sex education is needed in an effort to reduce teenage pregnancy and other health consequences related to risky sexual behaviors. Reports on Based on abstinence the education were analysis acquired from taken from the Education 48 states, Commission of it was the States. found that After the the level of analysis of the abstinence Editorial education Projects in was firmly Education correlated Research with Center, ordinal teenage values were pregnancy assigned to the and teen four categorical birth rates, levels of thereby abstinence indicating education to that assess the abstinence emphasis education placed on did not abstinence by cause each level. Data abstinence for teen among pregnancy, teenagers in the U.S. abortion and birth data were also used to determine the correlation between pregnancy and birth rates with that of abstinence Major point to make in my discussion (evaluation + connection) Extending Medicaid eligibility for family planning can help reduce the incidence of unintended teenage pregnancy Consideration should be made to include confounding factors like that of socioeconomi c status, educational attainment, and ethnicity education. Analysis of four possible confounding factors was also done to determine the role these factors played in the teenage pregnancy rates. 2. Lisa Lieberman, Haiyan Su Abstinence education curriculum has an impact on abstinence attitudes, intentions, and behaviors. The sex By implementing education the CTB program curriculum of improvement to Choosing the existing school Best (CTB)'s efforts can be program is an made. effective Additionally, approach sexual risk taking toward behaviors can be maintenance of reduced. abstinence or a return to sexual inactivity as it is inclusive of accurate medical information emphasizing abstinence, disease, and emotional consequences of sexual intercourse. Study participants included 1,143 ninth graders in two Georgia school districts randomly assigned to six high schools. Four schools comprised the intervention group and two were used for the control group. The control schools included 1,000 ninth graders who received their regular textbooksbased health lectures whereas the 2,000 ninth graders in the intervention schools received eight Results of the study found strong short-term interventio n effects on pro abstinence attitudes, beliefs and commitme nt to abstinence in both the total and virgin student bodies. Data from the study indicated however that virgins in the CTB group were more likely to delay sex than virgins in Adolescent participation in school based sex education is largely dependent on parent compliance Baseline commitment to abstinence is an important factor to consider when evaluating results of the effectiveness of a sex education program sessions of the CTB program during health class. the control group. Future studies will require repetition and increased complexity to determine the long term impact of this particular abstinence program. References Lieberman, L., & Haiyan, S. (2012). Impact of the choosing the best program in communities committed to abstinence education. SAGE open, doi: 10.1177/2158244012442938 Stanger-Hall, K., & Hall, D. (2011). Abstinence-only education and teen pregnancy rates: Why we need comprehensive sex education in the u.s.PLOS one, 6(10), Retrieved from http://www.plosone.org/article/fetchObject.action?uri=info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0024658&repres entation=PDF






