Ch. 5 Biomolecules Vocabulary
advertisement

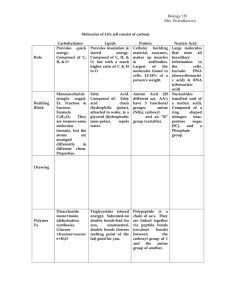
Chapter 5 The Molecules of Life Vocabulary Organic molecules: carbon based molecules that help make up living organisms. Inorganic molecules: non-carbon based molecules such as water, oxygen, and ammonia. Makes up nonliving matter. Monomer: small molecular unit that is the building block of a larger molecule. Polymer: a long chain of small molecular units (monomers). Hydrophilic: water loving – attracted to water molecules. Hydrophopbic: water fearing – repels water. Dehydration reaction: reaction where a water molecule is released every time a monomer is added to a polymer chain. Hydrolysis reaction: reaction where water is added to break apart a polymer chain. Carbohydrate: an organic compound made up of sugar molecules. Contains the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. Molecular structure has a ring shape. Monosaccharide: simple sugars that contain only one sugar unit. Ex: glucose, galactose, & fructose Disaccharide: a double sugar formed by 2 monosaccharides. Ex: sucrose. Polysaccarharide: long polymer chains of simple sugar monomers. Ex: starch, glycogen, cellulose. Fats/Lipids: store energy in the body. Consists of a 3-carbon backbone called a glycerol attached to 3 fatty acids. Ex: steroids & fats. Saturated fat: a fat in which all 3 fatty acid chains contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms. Ex: animal fats, lard and butter. Unsaturated fat: a fat in which one or more of the fatty acid chains contain less than the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms. Ex: corn oil, olive oil, fruits and vegetables, and fish. Protein: a polymer constructed from a set of 20 different kinds of amino acids. Responsible for the everyday functioning of organisms. Fnc: making, hair, muscle and long term nutrient storage. Amino acid: monomer of a protein. 20 different ones (8 essential & 12 nonessential) – essential you must get from the food you eat. Activation energy: the minimum amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction to proceed. Enzyme:special proteins that control the rate of a reaction. They act as catalysts which speed up the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy needed. Substrate: a specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme. The enzyme “fits” into the substrate which attached at the active site to speed up the rate of a reaction. Active site:place where the enzyme attached to the substrate forming the enzyme-substrate complex.. Catalyst:an enzyme that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy. Exothermic reaction:a chemical reaction that releases energy called free energy that can be used for other work. Endothermic reaction:a chemical reaction that requires the input of energy for the reaction to occur.