NewEnglandColonial - New Smyrna Beach High School
advertisement

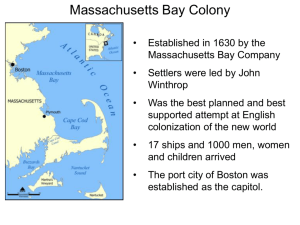
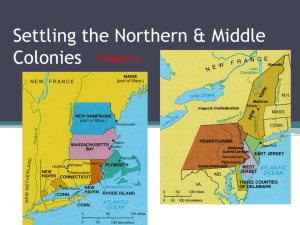
Separatists vs. Puritans Puritanism Calvinism Institutes of the Christian Religion Predestination. • Good works could not save those predestined for hell. • No one could be certain of their spiritual status. • Gnawing doubts led to constantly seeking signs of “conversion.” Puritans: Want to totally reform [purify] the Church of England. Grew impatient with the slow process of Protestant Reformation back in England. Separatists Separatist Beliefs: Puritans who believed only “visible saints” [those who could demonstrate in front of their fellow Puritans their elect status] should be admitted to church membership. Because the Church of England enrolled all the king’s subjects, Separatists felt they had to share churches with the “damned.” Therefore, they believed in a total break from the Church of England. Roman Catholic Church Episcopalians Baptists Protestants Lutherans Presbyterians Church of England Puritans Separatists (Pilgrims) Puritans – a group of English Protestants that tried to simplify the Church of England in the 1600’s. Sort: Catholics, Puritans, Pilgrims (separatist), & Anglicans (Church of England) on the spectrum below 1 I 3 I Radicals Liberals 5 I 7 I 9 I ____________________________________________________ Moderates Conservatives Reactionaries Sources of Puritan Migration The Mayflower 1620 a group of 102 people [half Separatists] Negotiated with the Virginia Company to settle in its jurisdiction. Plymouth Bay way outside the domain of the Virginia Company. Became squatters without legal right to land & specific authority to establish a govt. The Mayflower Compact November 11, 1620 Text • "In the name of God, Amen. We, whose names are underwritten, the Loyal Subjects of our dread Sovereign Lord, King James, by the Grace of God, of England, France and Ireland, King, Defender of the Faith, e&. Having undertaken for the Glory of God, and Advancement of the Christian Faith, and the Honour of our King and Country, a voyage to plant the first colony in the northern parts of Virginia; do by these presents, solemnly and mutually in the Presence of God and one of another, covenant and combine ourselves together into a civil Body Politick, for our better Ordering and Preservation, and Furtherance of the Ends aforesaid; And by Virtue hereof to enact, constitute, and frame, such just and equal Laws, Ordinances, Acts, Constitutions and Offices, from time to time, as shall be thought most meet and convenient for the General good of the Colony; unto which we promise all due submission and obedience. In Witness whereof we have hereunto subscribed our names at Cape Cod the eleventh of November, in the Reign of our Sovereign Lord, King James of England, France and Ireland, the eighteenth, and of Scotland the fifty-fourth. Anno Domini, 1620." Written and signed before the Pilgrims disembarked from the ship. Not a constitution, but an agreement to form a crude govt. and submit to majority rule. Signed by 41 adult males. Led to adult male settlers meeting in assemblies to make laws in town meetings. The First Year…. Winter of 1620-1621 Only 44 out of the original 102 survived. None chose to leave in 1621 when the Mayflower sailed back. Native American Encounter- The Wampanoags Chief Massasoit and English speaking Squanto Peace for 41 years Fall of 1621 First “Thanksgiving.” Plymouth stayed small and economically unimportant. 1691 only 7,000 people Merged with Massachusetts Bay Colony. William Bradford Chosen governor of Plymouth 30 times in yearly elections. Wrote History of Plymouth Plantation Worried about settlements of non-Puritans springing up nearby and corrupting Puritan society. The Mass. Bay Colony (MBC) 1629 non-Separatists got a royal charter to form the MA Bay Co. Wanted to escape attacks by conservatives in the Church of England. They didn’t want to leave the Church, just its “impurities.” 1630 1,000 people set off in 11 well-stocked ships Established a colony with Boston as its hub. First Seal of MA Bay “Great Migration” of the 1630s Turmoil in England [leading to the English Civil War] sent about 70,000 Puritans to America. Not all Puritans 20,000 came to MA. John Winthrop Became 1st governor of Massachusetts, elected 19 times. Believed that he had a “calling” from God to lead there. Model for the rest of the world to follow We shall be as a city on a hill.. Covenant Theology “Covenant of Grace”: between Puritan communities and God. “Social Covenant”: Between members of Puritan communities with each other. Required mutual watchfulness. No toleration of deviance or disorder. No privacy. Puritan (Protestant) Work Ethic • -Value emphasizing the necessity of constant labor in a person's life as a sign of personal salvation. • -Driving force in settlement of New England Common New England Town Structure • Compact population density • Farmers lived in towns rather than on land they farmed • Sense of community develops (to enforce Social Covenant theology) • common fields • Long row system Characteristics of New England Settlements Education Mandatory to build public schools in the founding of towns, Massachusetts School Laws of 1642 & 1647 “It being the chief project of the old deluder, Satan, to keep men from the knowledge of the Scriptures, as in former times keeping them in a foreign tongue (Latin), it is therefore ordered that every township in this jurisdiction, after the Lord has increased them in number to fifty householders, shall then forthwith appoint one within their town to teach all such children to read and write, and his wages shall be paid by either by the parents, or the inhabitants in general.” -Massachusetts General Court, 1647 Harvard-1st university in America, founded to train ministers Population Comparisons: New England v. the Chesapeake Low mortality average life expectancy was 70 years of age. Many extended families. Average 6 children per family. Average age at marriage: Women – 22 years old Men – 27 years old. Patriarchy Ministers and magistrates controlled church congregations and household patriarchs. • New England Women – Defined gender roles in Puritan society— woman restricted to domestic work – Significant legal barriers for women, could still own property when their husband's died, went back to a man when remarried – Only in churches did Puritan woman command semi-equal standing with men – Made up the majority of many congregations – Salem Witch Trials (1692) – Anne Hutchinson Puritan “Rebels” Young, popular minister in Salem. Argued for a full break with the Anglican Church. Condemned MA Bay Charter. • Did not give fair compensation to Indians. “Liberty of Conscience”- Denied authority of civil Roger Williams govt. to regulate religious behavior. No man should be forced to go to church 1635 found guilty of preaching new & dangerous opinions and was exiled. Rhode Island 1636 Roger Williams fled there. MA Bay Puritans had wanted to exile him to England to prevent him from founding a competing colony. Remarkable political freedom in Providence, RI • Universal manhood suffrage later restricted by a property qualification. • Opposed to special privilege of any kind freedom of opportunity for all. RI becomes known as the “Sewer” because it is seen by the Puritans as a dumping ground for unbelievers and religious dissenters More liberal than any other colony! Puritan “Rebels” Intelligent, strong-willed, well-spoken woman. Threatened patriarchal control. Antinomianism— The theological belief that the Gospel frees Christians from obedience to any law, whether scriptural, moral, or civil and that salvation is attained solely from Gods divine grace, not good works. Carried to logical extremes Puritan doctrine of predestination. Anne Hutchinson Truly saved didn’t need to obey the law of either God or man, including Puritan leaders. Anne Hutchinson’s Trial 1638 she confounded the Puritan leaders for days. Eventually bragged that she had received her beliefs DIRECTLY from God. Direct revelation was even more serious than the heresy of antinomianism. WHY?? Puritan leaders banished her she & her family traveled to RI and later to NY. She and all but one member of her family were killed in an Indian attack in Westchester County. John Winthrop saw God’s hand in this! New England Spreads Out New England Colonies, 1650 Decline of Puritanism • Dispersed settlement patterns • Wave of dissenters: Williams and Hutchinson caused less conversions • 2nd generation Puritans had trouble getting their conversions authenticated • Halfway Covenant- 1662, sought to increase membership by allowing partial membership to the unconverted and their children baptism • Salem Witch Trials- 1692, embarrass Puritan clergy • Overall, Puritans traded purity for wider religious participation, morphed into the Congregationalists Salem Witch Trials- 1692 • Example of Puritan intolerance, Fundamentalism Puritans vs. Native Americans Indians especially weak in New England epidemics wiped out ¾ of the native popul. Wampanoags [near Plymouth] befriended the settlers. Cooperation between the two helped by Squanto. 1621 Chief Massasoit signed treaty with the settlers. Autumn, 1621 both groups celebrated the First Thanksgiving. The First Thanksgiving? In 1863, President Lincoln proclaimed Thanksgiving an official US holiday. The Pequot Wars: Pequots very powerful tribe in CT river valley. 1636-1637 1637 Pequot War Whites, with Narragansett Indian allies, attacked Pequot village on Mystic River. Whites set fire to homes & shot fleeing survivors! Set precedent of total war compared to how Indians fought limited war. Pequot tribe virtually annihilated an uneasy peace lasted for 40 years. A Pequot Village Destroyed, 1637 New England Confederation created to deal with the War King Philip’s War (1675-1676} Only hope for Native Americans to resist white settlers was to UNITE. Metacom [King Philip to white settlers] Massasoit’s son united Indians and staged coordinated attacks on white settlements throughout New England. Frontier settlements forced to retreat to Boston. King Philip’s War (1675-1676} The war ended in failure for the Indians Metacom beheaded and drawn and quartered. His son and wife sold into slavery. Final Expulsion of Indians from N.E. Happened the same time as Bacon’s Rebellion in the South, unrest in Colonial America Population of the New England Colonies The End Colonizing New England