Chapter 11 - Bringoldville
advertisement

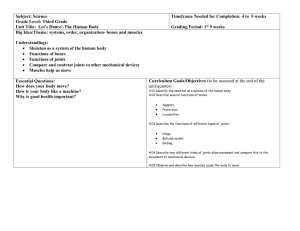
Chapter 5 What Are Some Ways You Can Stay Fit? Lesson 1: Physical Fitness & You • What does it mean to be fit? • Being fit means having the energy to meet all of the regular demands and any unexpected demands. • How does developing healthy habits benefit you in the future? Benefits to Fitness • Physical-better sleep, coordination, improved strength, and posture • Social-ability to work more efficiently, chances to meet more people that share your interests. • Mental/EmotionalReduced stress, relaxed attitude, sharpen mental alertness. Strength and Endurance • Most work is measured in amount of work your muscles do. • Strength-crunches strengthen abs, push-ups strengthen upper arms and chest, and step-ups or jumping strengthens leg muscles. • Endurance is being able to perform an activity without getting tired. Walking/Jogging, jumping rope, and swimming are all great ways to improve endurance. • Flexibility is ability to move joints easily and is important to increase so you don’t get injured. Vocabulary • Fitness- the ability to handle the physical work and play of everyday life without becoming overly tired • Exercise- physical activity that develops fitness • Body composition- proportions of fat, bones, muscle, and fluid that make up body weight • Strength- the ability of your muscles to exert a force • Endurance-your ability to perform vigorous physical activity without getting overly tired • Aerobic exercise-nonstop, rhythmic, vigorous activity that increases breathing and heartbeats • Anaerobic exercise- intense physical activity that requires short burst of energy • Flexibility-ability to move joints fully and easily Lesson 2: The Circulatory System • The heart pumps the blood through your circulatory system, through veins, and arteries. Having good health helps circulatory system. • Pulmonary circulation carries the blood from the heart to the lungs, and back to the heart. How Circulation Works • Blood goes from left atrium of heart to left ventricle with oxygen rich blood. • The left ventricle pumps blood to aorta, body’s largest artery. • The aorta send blood to rest of body(not lungs), and the blood stream brings back wastes, like carbon dioxide. • Veins carry blood back to right atrium. • Sends blood to right ventricle to get rid of carbon dioxide, and the lungs lets CO2 out of body and brings good blood back to heart through pulmonary vein. The Blood • Blood delivers oxygen to all body parts. Blood transports CO2 to lungs for removal. Blood transports other wastes to kidneys for removal. Blood delivers nutrients to body cells. Blood carries special cells that fight germs in body. Blood promotes healing and carries hormones and chemicals throughout body. Parts of Blood • Blood is made of plasma (watery part of blood), platelets (clot wounds), red blood cells (carry oxygen), and white blood cells (fight infections off). • Blood pressure is taken to see how your circulatory system is doing and your health affects this. • There are 4 different blood types A, B, AB, and O all which are positive and negative. Vocabulary • Circulatory system-group of organs and tissues that transport essential materials to body cells & remove waste products • Cardiovascular system- another name for the circulatory system • Artery-blood vessels that carry blood away from heart • Capillary-smallest blood vessels, which provides body cells blood and connect arteries with veins • Vein-carry blood from all parts of body to the heart • Pulmonary circulation- carries blood from the heart, through the lungs, and back to the heart • Systemic circulation- sends oxygen- rich blood to body • Plasma- yellowish fluid, watery portion of blood • Blood pressure- force of blood pushing against walls of blood vessels. Lesson 3 The Skeletal and Muscular Systems • The skeletal system supports all of your major organs help you move. • Muscles help move your body too and protect it from harm. There are 206 bones, and more than 600 muscles in the body. • Both the muscles and bones are supplied by blood vessels. Joints • Joints are where two or more bones meet. There are pivots, where they move up and down, side to side. There are gliding where the bones allow for some movement sideways. There are Ball and Socket where the bone fits in a place and can move all around. There are lastly, hinge joints, where the bone can move in one direction. Connecting Tissue & Muscle • Cartilage is flexible and cushions bones. Ligaments connect bone to bone, and tendons connect bones to muscles. • Skeletal muscle is muscle that is attached to bone like biceps. Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles like your stomach, and cardiac muscles are only in your heart which pumps 70 times per minute. Working Out • When you flex one muscle the opposite muscle lengthens or extends. • Exercise regularly, eat a nutritious diet, watch your posture, and treat injuries promptly to make sure you keep the skeletal and muscular systems are in good health! Vocabulary • Fitness- the ability to handle the physical work and play of everyday life without becoming overly tired • Exercise- physical activity that develops fitness • Body composition- proportions of fat, bones, muscle, and fluid that make up body weight • Strength- the ability of your muscles to exert a force • Endurance-your ability to perform vigorous physical activity without getting overly tired • Aerobic exercise-nonstop, rhythmic, vigorous activity that increases breathing and heartbeats • Anaerobic exercise- intense physical activity that requires short burst of energy • Flexibility-ability to move joints fully and easily Lesson 4:Planning a Fitness Program • Now that you know a little about the body it is time to plan a fitness program. While doing this you should select the right type of exercises for YOU. Everyone needs a slightly different workout. • Do you want to gain endurance, strength, or flexibility? • Also make sure you take the right safety precautions. Schedule • After you choose the exercise you must make a schedule of what and when to perform the workout plan. • You should have a routine before you actually start working out, a warm-up, and when you are done you should have a routine to slow your body down, a cool-down. • You should make sure to workout on a regular basis, exercise frequency and use the right amount of energy, exercise intensity. FIT & Target Heart Rate • F-Frequency; increase workouts from twice a week to daily. • I-Intensity; Start at ½ a mile and get up to 3 miles. • T-Time; Start at 10-15 minutes and get to 45-60 min. • You should try to keep your heart within a certain range so you don’t over work your heart or over work your body. Vocabulary • Fitness- the ability to handle the physical work and play of everyday life without becoming overly tired • Exercise- physical activity that develops fitness • Body composition- proportions of fat, bones, muscle, and fluid that make up body weight • Strength- the ability of your muscles to exert a force • Endurance-your ability to perform vigorous physical activity without getting overly tired • Aerobic exercise-nonstop, rhythmic, vigorous activity that increases breathing and heartbeats • Anaerobic exercise- intense physical activity that requires short burst of energy • Flexibility-ability to move joints fully and easily Lesson 5:Weight Management • A good way to figure out whether you may need to lose or gain weight is to find out your BMI. Ideal weight is different for everyone. • Obesity is a growing problem in America so you have to be aware of your health. Nutrition and Diet • To maintain weight you need to intake as many calories as you burn in a day. • To gain you have to intake more than you burn, and to lose weight you have to burn more calories than you take in. • To do this you need to be aware of the activities that you are doing and what you are eating. Tips to Lose and Gain Weight • To lose, do not try to lose more than 1-2 pounds a week. Eat smaller servings, increase exercise and don’t skip meals. • To gain weight, eat larger nutritious meals, don’t eat high fat meals, exercise so you gain muscle, not fat, and eat healthful snacks between meals, not too close to mealtimes though. Vocabulary • Fitness- the ability to handle the physical work and play of everyday life without becoming overly tired • Exercise- physical activity that develops fitness • Body composition- proportions of fat, bones, muscle, and fluid that make up body weight • Strength- the ability of your muscles to exert a force • Endurance-your ability to perform vigorous physical activity without getting overly tired • Aerobic exercise-nonstop, rhythmic, vigorous activity that increases breathing and heartbeats • Anaerobic exercise- intense physical activity that requires short burst of energy • Flexibility-ability to move joints fully and easily